SkyView Surveys
Frequency vs Data Pixel Resolution plot of all SkyView Surveys
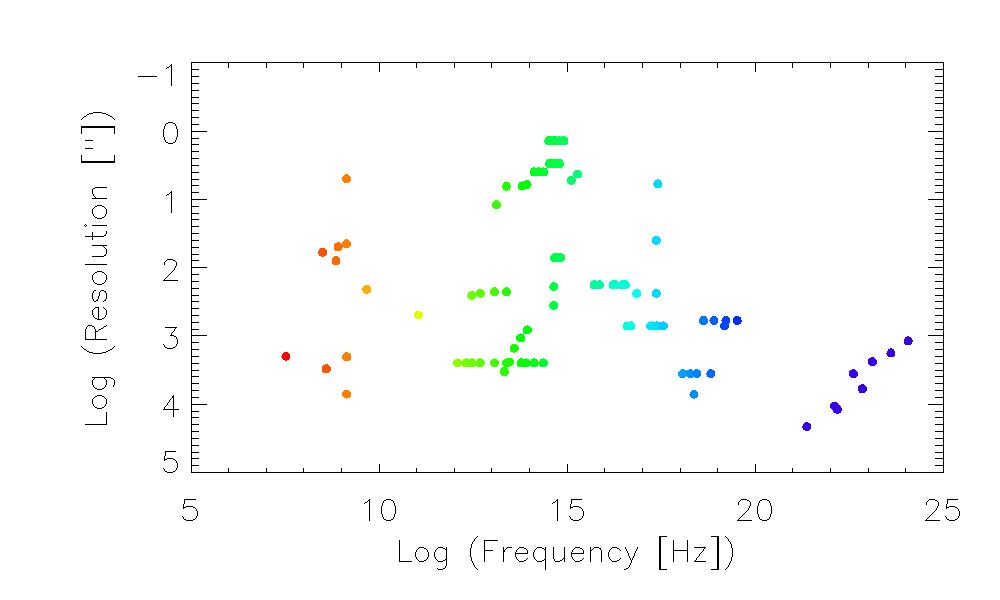
Click image to add survey names.
The diversity of
SkyView surveys is shown here. Data ranges over about 18 orders of magnitude in energy and about 5 orders of magnitude in resolution. See our
SkyView Blog post for more information.
This document gives a short overview of each of the surveys included
in SkyView. The descriptions include textual description which describe
special properties of these surveys and a short
table giving basic information for the survey.
The table includes:
- The provenance of the data.
- The copyright status of the data.
- The spectral regime of the data.
- Number of surveys, i.e., typically the number of separate
frequency bands in SkyView.
- The approximate frequency of the data. In addition
to the frequency other indicators of the spectral range
may be included (e.g., photon energy, wavelength, band).
- The coverage of the survey on the sky. All-sky indicates that
the survey covers substantially the entire sky although
there may be small patches not covered.
- Pixel scale. The angular size of the pixels. If only
a single value is given then the pixels are assumed
square.
- Pixel units. The units in which the intensity at the
pixel is given.
- Resolution. A measure of the intrinsic resolution of the
image. It may be greater or less than the pixel scale.
- Coordinate system. The native coordinate system of the
survey as used in SkyView.
- Equinox. For data in Equatorial or Ecliptic coordinates,
the equinox year of the coordinates.
- Projection. The native projection of the data.
- Reference. Reference to material giving further
information on the survey.
Radio surveys
GTEE 0035 MHz Radio Survey
GMRT 150 MHz All-sky Radio Survey
Bonn 1420 MHz Survey
Effelsberg-Bonn HI Survey
HI All-Sky Continuum Survey
4850 MHz Survey/GB6
CO Galactic Plane Survey
FIRST
Dickey and Lockman HI map
NVSS
Sydney University Molonglo Sky Survey
VLA Low-frequency Sky Survey
Westerbork Northern Sky Survey
GOODS North Observations with the VLA
Millimeter surveys
Planck 030 GHz Survey
Planck 044 GHz Survey
Planck 070 GHz Survey
Planck 100 GHz Survey
Planck 143 GHz Survey
Planck 217 GHz Survey
Planck 353 GHz Survey
Planck 545 GHz Survey
Planck 857 GHz Survey
LABOCA Extended Chandra Deep Field South Submillimetre Survey
Infrared surveys
Two Micron All Sky Survey (H-Band)
Two Micron All Sky Survey (J-Band)
Two Micron All Sky Survey (K-Band)
WISE 3.4 All-Sky Release Survey
WISE 4.6 All-Sky Release Survey
WISE 12 Micron All-Sky Survey
WISE 22 Micron All-Sky Survey
AKARI WIDE-S
AKARI N160
Cosmic Background Explorer DIRBE Annual Average Map
Cosmic Background Explorer DIRBE Zodi-Subtracted Mission Average
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 100 micron
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 12 micron
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 25 micron
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 60 micron
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 100
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 12
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 25
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 60
Schlegel, Finkbeiner and Davis 100 micron survey
Schlegel, Finkbeiner and Davis Dust Survey
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey H-band
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey J-band
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey K-band
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey Y-band
WMAP Five Year Galaxy Removed
WMAP Five Year Ka-Band
WMAP Five Year K-Band
WMAP Five Year Q-Band
WMAP Five Year V-Band
WMAP Five Year W-band
Optical surveys
Original Digitized Sky Survey
First Digitized Sky Survey: Blue Plates
First Digitized Sky Survey: Red Plates
2nd Digitized Sky Survey (Blue)
2nd Digitized Sky Survey (Infrared)
2nd Digitized Sky Survey (Red)
Mellinger All Sky Mosaic: Blue
Mellinger All Sky Mosaic: Green
Mellinger All Sky Mosaic: Red
H-alpha Full Sky Map
Near-Earth Asteriod Tracking System Archive
Sloan Digitized Sky Survey G-band
Sloan Digitzed Sky Survey I-band
Sloan Digitzed Sky Survey R-band
Sloan Digitzed Sky Survey U-band
Sloan Digitzed Sky Survey Z-band
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: Continuum
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: Continuum-Corrected
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: H-alpha
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: Smoothed
GOODS HST ACS V Filter
GOODS HST ACS I Filter
GOODS HST ACS B Filter
GOODS HST ACS Z Filter
Ultraviolet surveys
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 83 A
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 171 A
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 405 A
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 555 A
Galaxy Explorer All Sky Survey: Far UV
Galaxy Explorer All Sky Survey: Near UV
ROSAT Wide Field Camera: F1
ROSAT Wide Field Camera: F2
X-ray surveys
Swift XRT Combined Counts
Swift XRT Exposure
Swift XRT Intensity
Swift BAT All-Sky Survey: Flux and Significance
GRANAT/SIGMA Flux
GRANAT/SIGMA
HEAO 1A
ROSAT High Resolution Image Pointed Observations Mosaic: Intensity
INTEGRAL/Spectral Imager Galactic Center Survey
PSPC summed pointed observations, 1 degree cutoff, intensity
PSPC summed pointed observations, 2 degree cutoff, counts
PSPC summed pointed observations, 2 degree cutoff, exposure
PSPC summed pointed observations, 2 degree cutoff, intensity
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Broad Band
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Hard Band
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Soft Band
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Bands 1
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Bands 2
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Bands 3
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Bands 4
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Bands 5
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Bands 6
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Bands 7
ROSAT All-Sky Broad Band Intensity
ROSAT All-Sky Hard Band Intensity
ROSAT All-Sky Broad Band Intensity
RXTE Allsky 3-20keV Significance
RXTE Allsky 3-8keV Significance
RXTE Allsky 8-20keV Significance
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-35 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Flux
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-60 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Flux
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 35-80 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Flux
GOODS ACIS: Hard band (2-8 keV)
GOODS ACIS: Soft band (0.5-2 keV)
GOODS ACIS: Full band (0.5-8 keV)
Gamma ray surveys
CGRO Compton Telescope: 3 channel data
Energetic Gamma-Ray Event Telescope: 10 channel data
Energetic Gamma-Ray Event Telescope: Hard
Energetic Gamma-Ray Event Telescope: Soft
Fermi Map: Band 1
Fermi Map: Band 2
Fermi Map: Band 3
Fermi Map: Band 4
Fermi Map: Band 5
Radio surveys
4850 MHz Survey - GB6/PMN
Bonn 1420 MHz Survey
CO Galactic Plane Survey
Dickey and Lockman HI map
Effelsberg-Bonn HI Survey
FIRST
GLEAM 103-134: GaLactic and Extragalactic Allsky MWA Survey
GLEAM 139-170: GaLactic and Extragalactic Allsky MWA Survey
GLEAM 170-231: GaLactic and Extragalactic Allsky MWA Survey
GLEAM 72-103: GaLactic and Extragalactic Allsky MWA Survey
GMRT 150 MHz All-sky Radio Survey: First Alternative Data Release
GOODS North Observations with the VLA
GTEE 0035 MHz Radio survey
HI All-Sky Continuum Survey
LABOCA Extended Chandra Deep Field South Submillimetre Survey
NRA) VLA Sky Survey
Sydney University Molonglo Sky Survey
The HI 4-PI Survey
VLA Low-frequency Sky Survey
VLA Survey of SDSS Stripe 82
Westerbork Northern Sky Survey
Millimeter surveys
Planck 030 GHz Survey
Planck 044 GHz Survey
Planck 070 GHz Survey
Planck 100 GHz Survey
Planck 143 GHz Survey
Planck 217 GHz Survey
Planck 353 GHz Survey
Planck 545 GHz Survey
Planck 857 GHz Survey
Infrared surveys
2nd Digitized Sky Survey-Near Infrared
AKARI N160
AKARI N60
AKARI WIDE-L
AKARI WIDE-S
Cosmic Background Explorer DIRBE Annual Average Map
Cosmic Background Explorer DIRBE Zodi-Subtracted Mission Average
GOODS Herschel 100 micron, DR1 data release
GOODS Herschel 160 micron, DR1 data release
GOODS Herschel 250 micron, DR1 data release
GOODS Herschel 350 micron, DR1 data release
GOODS Herschel 500 micron, DR1 data release
GOODS NICMOS Survey
HIPS Survey:Ultradeep survey using the ESO Vista surveys telescope: Band H
HIPS Survey:Ultradeep survey using the ESO Vista surveys telescope: Band J
HIPS Survey:Ultradeep survey using the ESO Vista surveys telescope: Band Ks
HIPS Survey:Ultradeep survey using the ESO Vista surveys telescope: Band NB118
HIPS Survey:Ultradeep survey using the ESO Vista surveys telescope: Band Y
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 100 micron
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 12 micron
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 25 micron
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 60 micron
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 100
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 12
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 25
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 60
Schlegel, Finkbeiner and Davis 100 Micron survey
Schlegel, Finkbeiner and Davis dust map survey
Southern GOODS Field: VLT ISAAC Observations, H band
Southern GOODS Field: VLT ISAAC Observations, J band
Southern GOODS Field: VLT ISAAC Observations, KS band
Spitzer IRAC GOODS 3.6 micron data, channel 1
Spitzer IRAC GOODS 4.5 micron data, channel 2
Spitzer IRAC GOODS 5.8 micron data, channel 3
Spitzer IRAC GOODS 8.0 micron data, channel 4
Spitzer MIPS GOODS 24 Micron Data
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band I
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band Z
Two Micron All Sky Survey (H-Band)
Two Micron All Sky Survey (J-Band)
Two Micron All Sky Survey (K-Band)
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey H-band
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey J-band
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey K-band
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey Y-band
VLT ISAAC Ks Observations of the Southern Hubble Ultradeep Field
WISE 12 Micron All-Sky Survey>: All-WISE data release
WISE 22 Micron All-Sky Survey>: All-WISE data release
WISE 3.4 Micron All-Sky Survey>: All-WISE data release
WISE 4.6 Micron All-Sky Survey>: All-WISE data release
WMAP Nine Year Galaxy Removed
WMAP Nine Year K-Band
WMAP Nine Year Ka-Band
WMAP Nine Year Q-Band
WMAP Nine Year V-Band
WMAP Nine Year W-Band
Optical surveys
2nd Digitized Sky Survey (Blue)
2nd Digitized Sky Survey (Red)
First Digitized Sky Survey: Blue Plates
First Digitized Sky Survey: Red Plates
GOODS HST ACS B Filter
GOODS HST ACS I Filter
GOODS HST ACS V Filter
GOODS HST ACS Z Filter
H-alpha Full Sky Map
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS D g
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS D i
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS D r
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS D u
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS D z
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS W g
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS W i
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS W r
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS W u
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS W z
Mellinger All Sky Mosaic: Blue
Mellinger All Sky Mosaic: Green
Mellinger All Sky Mosaic: Red
Near-Earth Asteriod Tracking System Archive
Original Digitized Sky Survey
Sloan Digital Sky Survey g-band
Sloan Digital Sky Survey g-band DR7
Sloan Digital Sky Survey i-band
Sloan Digital Sky Survey i-band DR7
Sloan Digital Sky Survey r-band
Sloan Digital Sky Survey r-band DR7
Sloan Digital Sky Survey u-band
Sloan Digital Sky Survey u-band DR7
Sloan Digital Sky Survey z-band
Sloan Digital Sky Survey z-band DR7
Southern GOODS Field: VLT VIMOS Observations, R band
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band B
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band R
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band V0201
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band V0401
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: Continuum
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: Continuum-Corrected
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: H-Alpha
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: Smoothed
Ultraviolet surveys
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 171 A
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 405 A
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 555 A
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 83 A
Galaxy Explorer All Sky Survey: Far UV
Galaxy Explorer All Sky Survey: Near UV
ROSAT Wide Field Camera: F1
ROSAT Wide Field Camera: F2
Southern GOODS Field: VLT VIMOS Observations, U band
Swift UVOT Combined B Counts Images
Swift UVOT Combined B Exposure Images
Swift UVOT Combined B Intensity Images
Swift UVOT Combined U Counts Images
Swift UVOT Combined U Exposure Images
Swift UVOT Combined U Intensity Images
Swift UVOT Combined UVM2 Counts Images
Swift UVOT Combined UVM2 Exposure Images
Swift UVOT Combined UVM2 Intensity Images
Swift UVOT Combined UVW1 Counts Images
Swift UVOT Combined UVW1 Exposure Images
Swift UVOT Combined UVW1 Intensity Images
Swift UVOT Combined UVW2 Counts Images
Swift UVOT Combined UVW2 Exposure Images
Swift UVOT Combined UVW2 Intensity Images
Swift UVOT Combined V Counts Images
Swift UVOT Combined V Exposure Images
Swift UVOT Combined V Intensity Images
Swift UVOT Combined WHITE Counts Images
Swift UVOT Combined WHITE Exposure Images
Swift UVOT Combined WHITE Intensity Images
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band U
X-ray surveys
GOODS Chandra ACIS: Full band (0.5-8 keV)
GOODS Chandra ACIS: Hard band (2-8 keV)
GOODS Chandra ACIS: Soft band (0.5-2 keV)
GRANAT/SIGMA Flux
GRANAT/SIGMA Significance
HEAO 1A
INTEGRAL/Spectral Imager Galactic Center Survey
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-35 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Exposure
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-35 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Flux
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-35 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Significance
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-60 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Exposure
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-60 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Flux
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-60 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Significance
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 35-80 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Exposure
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 35-80 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Flux
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 35-80 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Significance
PSPC summed pointed observations, 0.6 degree cutoff, Counts
PSPC summed pointed observations, 0.6 degree cutoff, Exposure
PSPC summed pointed observations, 0.6 degree cutoff, Intensity
PSPC summed pointed observations, 1 degree cutoff, Counts
PSPC summed pointed observations, 1 degree cutoff, Exposure
PSPC summed pointed observations, 1 degree cutoff, Intensity
PSPC summed pointed observations, 2 degree cutoff, Counts
PSPC summed pointed observations, 2 degree cutoff, Exposure
PSPC summed pointed observations, 2 degree cutoff, Intensity
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 1
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 2
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 3
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 4
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 5
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 6
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 7
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Broad Band: Counts
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Broad Band: Intensity
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Hard Band: Counts
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Hard Band: Intensity
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Soft Band: Counts
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Soft Band: Intensity
ROSAT High Resolution Image Pointed Observations Mosaic: Intensity
RXTE Allsky 3-20 keV Flux
RXTE Allsky 3-20 keV Significance
RXTE Allsky 3-8 keV Flux
RXTE Allsky 3-8 keV Significance
RXTE Allsky 8-20 keV Flux
RXTE Allsky 8-20 keV Significance
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 100-150 keV: flux
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 100-150 keV: snr
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 14-195 keV: snr
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 14-20 keV: flux
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 14-20 keV: snr
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 150-195 keV: flux
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 150-195 keV: snr
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 20-24 keV: flux
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 20-24 keV: snr
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 24-35 keV: flux
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 24-35 keV: snr
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 35-50 keV: flux
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 35-50 keV: snr
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 50-75 keV: flux
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 50-75 keV: snr
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 75-100 keV: flux
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 75-100 keV: snr
Swift XRT Combined Counts Images
Swift XRT Combined Exposure Images
Swift XRT Combined Intensity Images
Gamma ray surveys
CGRO Compton Telescope: 3 channel data
Energetic Gamma-Ray Event Telescope: 10 channel data
Energetic Gamma-Ray Event Telescope: Hard
Energetic Gamma-Ray Event Telescope: Soft
Fermi Map: Band 1
Fermi Map: Band 2
Fermi Map: Band 3
Fermi Map: Band 4
Fermi Map: Band 5
Radio surveys
Bonn 1420 MHz Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: 1420MHz, 1420MHz (Bonn)
Description
This survey was taken with the Bonn Stockert 25m telescope. It was
distributed on the NRAO Images from the Radio Sky CD-ROM. This image
was delivered as a four map mosaic but was combined into a single
map before being included in SkyView.
| Provenance | Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy, generated by P. Reich and W. Reich |
| Copyright | Max-Planck-Institut fur Radioastronomie (permission for educational and private non-commercial use granted without further
request) |
| Regime | Radio |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 1420 MHz |
| Bandpass | 1418.8-1421.2 MHz |
| Coverage | Declination > -16 |
| PixelScale | 0.25 deg/pixel |
| PixelUnits | millikelvins |
| Resolution | 34' |
| CoordinateSystem | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 1950 |
| Projection | Rectangular (CAR) |
| Epoch | 1972-09 to 1973-05, 1973-08 to 1974-04 |
| Reference |
Reich, 1982, A&AS48, 219. Reich and Reich, 1986, A&AS63, 205
(ADS)
|
HI All-Sky Continuum Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: 408MHz,0408MHz
Description
This survey is a mosaic of data taken at Jodrell Bank, Effelsberg and Parkes
telescopes. The data was distributed in the NRAO Images from the
Radio Sky CD ROM.
| Provenance | Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy, generated by Glyn Haslam |
| Copyright | Max-Planck-Institut fur Radioastronomie (permission for educational and private non-commercial use granted without further
request) |
| Regime | Radio |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 408 MHz |
| Bandpass | 406.25-409.75 MHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.3515 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | Kelvins |
| Resolution | 0.85 degrees |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Rectangular (CAR) |
| Epoch |
Jodrell Bank: 1965-11 to 1966-02 and 1978-08 to 1979-09
MPI: 1971-07 to 1972-02
PKS: 1973-12 to 1975-05
|
| Reference |
Haslam et al., 1982,A&AS47, 1 (ADS).
|
4850 MHz Survey - GB6/PMN
Short name[s] used to specify survey: 4850MHz,GB6/PMN,PMN,GB6,GB6 (4850MHz)
Description
The 4850MHz data is a
combination of data from three different surveys: Parkes-MIT-NRAO (PMN)
Southern (-88° to -37° declination) and tropical surveys (-29°
to -9° declination, and (86+87) Green Bank survey (0° to +75°
declination). The data contains gaps between -27° to -39°,
-9° to 0°, and
+77° to +90° declination.
The 4850MHz survey data were obtained by tape from J.J. Condon and are comprised
of 576 images and are used by permission. Full information pertaining to
these surveys are found in the references.
| Provenance |
NRAO, generated by J.J. Condon, J.J. Broderick and G.A. Seielstad, Douglas, K., and Gregory, P.C.
|
| Copyright | Used by permission of J.J. Condon |
| Regime | Radio |
| NSurvey | 2 |
| Frequency | 4850 MHz continuum |
| Bandpass | 4550 - 5150 MHz |
| Coverage | RA: 0d - 360d, DEC: -88d to +75d |
| PixelScale | 1'/pixel (PMN), and 0.66' /pixel ((86+87) GB) |
| PixelUnits | janskies/beam (ca. 200,000 beams/steradian) |
| Resolution | 3.5' FWHM |
| CoordinateSystem | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 1950 |
| Epoch |
Greenbank: 1986-11,1987-10
PMN: 1990
|
| Projection | Orthographic (SIN) |
| Reference |
Condon, et al., 1991;
1993,
1994
|
LABOCA Extended Chandra Deep Field South Submillimetre Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:CDFS LESS, CDFS: LESS
Description
The LABOCA Extended Chandra Deep Field South (ECDFS) Submillimetre Survey (LESS)
is a public legacy survey of the ECDFS at 870 ??m using the LABOCA camera
(Siringo et al. 2009) on the APEX telescope.
The LABOCA data presented here were obtained between 2007 May and 2008 November
in excellent conditions using time from both ESO and Max Planck allocations.
The mapping pattern was designed to uniformly cover the 30'x30' extent of the ECDFS,
centered on 03:32:29.0, -27:48:47.0 (J2000).
The project used a total of 310 hrs of observations to achieve a beam-smoothed noise of
1.2 mJy/beam over 900 sq. arcmin (and <1.6mJy/beam over 1260 sq. arcmin).
The flux calibration of the map came from observations of Mars, Uranus and Neptune
(as well as secondary calibrators) and is accurate to within 8.5%.
| Regime | Radio |
| Frequency | 345 GHz |
| Bandwidth | 315-375 GHz |
| Provenance | Data downloaded from ESO archive |
| Copyright |
Data freely available from ESO archive.
When using data products provided in this release,
it is requested that authors refer to the publication Weiss et al. 2009, ApJ, 707, 1201
In addition, please also use the following statement in articles using these data:
"Based on observations collected at the European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, Chile, under programmes 078.F-9028(A), 079.F-9500(A), 080.A-3023(A), and 081.F-9500(A)."
|
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Coverage | 30'x30' in Chandra deep field south. |
| Resolution | 19.2" |
| PixelSize | 6" |
| CoordinateSystem | J2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| PixelUnits | Jy/beam |
| Epoch | 2007-07-12/2008-10-04 |
| Reference |
Paper and
web site.>
|
CO Galactic Plane Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: CO2D,CO
Description
New large-scale CO surveys of the first and second Galactic quadrants and the
nearby molecular cloud complexes in Orion and Taurus, obtained with the
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 1.2 m telescope, have been
combined with 31 other surveys obtained over the past two decades with that
instrument and a similar telescope on Cerro Tololo in Chile, to produce a
new composite CO survey of the entire Milky Way. The survey consists of
488,000 spectra that Nyquist or beamwidth (1/8 deg) sample the entire Galactic
plane over a strip 4 deg-10 deg wide in latitude, and beamwidth or 1/4 deg sample
nearly all large local clouds at higher latitudes. Compared with the previous
composite CO survey of Dame et al. (1987), the new survey has 16 times more
spectra, up to 3.4 times higher angular resolution, and up to 10 times higher
sensitivity per unit solid angle.
Users should be aware that both the angular resolution and the
sensitivity varies from region to region in the velocity-integrated map.
The component surveys were integrated individually using clipping or
moment masking in order to display nearly all statistically significant
emission but little noise above a level of ~1.5 K km/s. See the reference
below and the
Millimeter-Wave Group site for more details
| Provenance | Data taken by two nearly-identical 1.2 m
telescopes in Cambridge, MA and on Cerro Tololo, Chile combined into a
complete survey of the Milky Way with CO integrated over all velocities.
|
| Copyright | Permission is granted for publication and
reproduction of this material for research or educational purposes so
long as the reference (see below) is included.
|
| Regime | Radio |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 115 GHz |
| Bandpass | 114.89 - 115.12 GHz |
| Coverage | 9,853 sq. deg; All galactic longitudes, irregular bands between -35 and +35 latitudes
|
| PixelScale | 0.125d/pixel |
| Resolution | 9-18' |
| PixelUnits | Pixel values are velocity-integrated main beam brightness temperature, in units of K km/s |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Rectangular |
| Epoch | 1980 to 2000 |
| Reference |
Dame, T. M., Hartmann, Dap, Thaddeus, P., ApJ, 2001 (ADS)
|
Effelsberg-Bonn HI Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:EBHIS, EBHIS(NHI)
Description
The Effelsberg-Bonn HI Survey (EBHIS) is a 21-cm survey performed with the
100-m telescope at Effelsberg. It covers the whole northern sky out to a
redshift of z ~ 0.07 and comprises HI line emission from the Milky Way and the
Local Volume. This dataset is the atomic neutral hydrogen (HI) column density
map derived from the Milky-Way part of EBHIS (|Vlsr| < 600 km/s).
| Provenance |
Argelander-Institut für Astronomie (AIfA) and Max-Planck-Institut
für Radioastronomie (MPIfR); data provided by B. Winkel
|
| Regime | Radio |
| Copyright |
Permission is granted for publication and reproduction of this
material for scientific, scholarly, educational, and private non-commercial use by the Argelander-Institut für Astronomie (AIfA)
and the Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie (MPIfR), Germany.
In addition, please also use the following statement in articles
using the data: "The EBHIS data are based on observations performed
with the 100-m telescope of the MPIfR at Effelsberg. EBHIS was
funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) under the
grants KE757/7-1 to 7-3."
|
| Frequency | 1420 MHz |
| Coverage | All sky where δ > -5 |
| Bandpass | 1417.5 - 1423.5 MHz |
| PixelScale | 1.5' |
| PixelUnit | atoms/cm2 |
| Sensitivity | 4.7 x 1018 cm-2 |
| Resolution | 10.8' |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2009-2013 |
| Reference |
Winkel et al., AA 585, A41, 2016;
Kerp et al., 2011, AN 332, 637.
|
FIRST
Short name[s] used to specify survey:FIRST, VLA FIRST (1.4 GHz)
Description
The VLA FIRST (Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-centimeters)
is a project designed to produce the radio equivalent
of the Palomar Observatory Sky Survey over 10,000 square
degrees of the North Galactic Cap. The
FIRST home page
has details of the instrumentation, status of the project,
and data available. Currently about 5000 images
of approximately .775x.58 degrees are available.
These FIRST data have been retrieved from the
FIRST FTP archive
at the
Space Telescope Science Institute.
The FIRST survey is included on the SkyView High Resolution Radio
Coverage map. This map shows
coverage on an Aitoff projection of the sky in equatorial coordinates.
| Provenance | The FIRST project team: R.J. Becker, D.H. Helfand, R.L. White
M.D. Gregg. S.A. Laurent-Muehleisen. |
| Copyright |
1994, University of California.
Permission is granted for publication and reproduction of this
material for scholarly, educational, and private non-commercial
use. Inquiries for potential commercial uses should be
addressed to:
Robert Becker,
Physics Dept,
University of California,
Davis, CA 95616
|
| Regime | Radio |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 1.4 GHz Continuum |
| Bandpass | 1.3635 - 1.4365 GHz |
| Coverage |
Eventually will cover entire North Galactic Polar region (about 10,000 square degrees). See Status of FIRST Survey Observations
|
| PixelScale | 1.8"/pixel |
| PixelUnits | Janskies/beam |
| Resolution | 5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Orthographic |
| Epoch | 1993-2004, 2009-2011 |
| Reference |
FIRST home page
Becker et al., 1995 (ADS)
|
GLEAM 103-134: GaLactic and Extragalactic Allsky MWA Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: GLEAM103-134, GLEAM 103-134,GLEAM 103-134 MHz, GLEAM2, GLEAM 2
Description
GLEAM, the GaLactic and Extragalactic All-sky MWA survey, is a survey of
the entire radio sky south of declination 30 degrees at frequencies
between 72 and 231 MHz. It was made with the Murchison Widefield Array
(MWA) using a drift scan method that makes efficient use of the MWA's very
large field-of-view. The survey is described in Wayth et al. (2015) and
the website at http://mwatelescope.org/science/gleam-survey.
The data presented here are from the first year of GLEAM observing,
published in Hurley-Walker et al. (2017). The 25,000 square degrees of
available sky excludes the Galactic Plane, the Magellanic Clouds,
Centaurus A, and a few other small regions described in the catalogue
paper.
The most sensitive and highest-resolution image is the 170-231MHz image
which was used for all source-finding in generating the catalogue. It has
a resolution of approximately 2.2 x 2.2/cos (dec + 26.7) arcmin at this
frequency. However, due to ionospheric distortions, the final resolution
of the survey varies by ~10% over the sky, with a direction-dependent PSF.
The SkyView data for the GLEAM surveys was extracted using the team's
cutout server, into small (3 degree) raw cutouts over the region covered
by the GLEAM survey. These cutouts have somewhat variable size and resolution. The
default scale (i.e., pixel size) used for SkyView images is given in the table
below.
SkyView resamples the cutouts retreived from the GLEAM web site into the image
geometry requested by the user. Only four wide-band datasets are included here.
The table below gives the frequency range, central frequency and a typical pixel
scale for each of these bands.
| GLEAM Bands In SkyView |
|---|
| Band |
fmin (MHz) |
fmax (MHz) |
fC (MHz)
| Pixel scale (") |
|---|
| 1 | 72 | 103 | 88 | 56 |
| 2 | 103 | 134 | 118 | 44 |
| 3 | 138 | 170 | 155 | 34 |
| 4 | 170 | 231 | 200 | 28 |
These data and 20 narrower bands are available through the team web site.
To minimize resampling artifacts, this survey defaults to the Lanczos third order resampler.
GLEAM 139-170: GaLactic and Extragalactic Allsky MWA Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: GLEAM139-170, GLEAM 139-170,GLEAM 139-170 MHz, GLEAM3, GLEAM 3
Description
GLEAM, the GaLactic and Extragalactic All-sky MWA survey, is a survey of
the entire radio sky south of declination 30 degrees at frequencies
between 72 and 231 MHz. It was made with the Murchison Widefield Array
(MWA) using a drift scan method that makes efficient use of the MWA's very
large field-of-view. The survey is described in Wayth et al. (2015) and
the website at http://mwatelescope.org/science/gleam-survey.
The data presented here are from the first year of GLEAM observing,
published in Hurley-Walker et al. (2017). The 25,000 square degrees of
available sky excludes the Galactic Plane, the Magellanic Clouds,
Centaurus A, and a few other small regions described in the catalogue
paper.
The most sensitive and highest-resolution image is the 170-231MHz image
which was used for all source-finding in generating the catalogue. It has
a resolution of approximately 2.2 x 2.2/cos (dec + 26.7) arcmin at this
frequency. However, due to ionospheric distortions, the final resolution
of the survey varies by ~10% over the sky, with a direction-dependent PSF.
The SkyView data for the GLEAM surveys was extracted using the team's
cutout server, into small (3 degree) raw cutouts over the region covered
by the GLEAM survey. These cutouts have somewhat variable size and resolution. The
default scale (i.e., pixel size) used for SkyView images is given in the table
below.
SkyView resamples the cutouts retreived from the GLEAM web site into the image
geometry requested by the user. Only four wide-band datasets are included here.
The table below gives the frequency range, central frequency and a typical pixel
scale for each of these bands.
| GLEAM Bands In SkyView |
|---|
| Band |
fmin (MHz) |
fmax (MHz) |
fC (MHz)
| Pixel scale (") |
|---|
| 1 | 72 | 103 | 88 | 56 |
| 2 | 103 | 134 | 118 | 44 |
| 3 | 138 | 170 | 155 | 34 |
| 4 | 170 | 231 | 200 | 28 |
These data and 20 narrower bands are available through the team web site.
To minimize resampling artifacts, this survey defaults to the Lanczos third order resampler.
GLEAM 170-231: GaLactic and Extragalactic Allsky MWA Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: GLEAM170-231, GLEAM 170-231,GLEAM 170-231 MHz, GLEAM4, GLEAM 4
Description
GLEAM, the GaLactic and Extragalactic All-sky MWA survey, is a survey of
the entire radio sky south of declination 30 degrees at frequencies
between 72 and 231 MHz. It was made with the Murchison Widefield Array
(MWA) using a drift scan method that makes efficient use of the MWA's very
large field-of-view. The survey is described in Wayth et al. (2015) and
the website at http://mwatelescope.org/science/gleam-survey.
The data presented here are from the first year of GLEAM observing,
published in Hurley-Walker et al. (2017). The 25,000 square degrees of
available sky excludes the Galactic Plane, the Magellanic Clouds,
Centaurus A, and a few other small regions described in the catalogue
paper.
The most sensitive and highest-resolution image is the 170-231MHz image
which was used for all source-finding in generating the catalogue. It has
a resolution of approximately 2.2 x 2.2/cos (dec + 26.7) arcmin at this
frequency. However, due to ionospheric distortions, the final resolution
of the survey varies by ~10% over the sky, with a direction-dependent PSF.
The SkyView data for the GLEAM surveys was extracted using the team's
cutout server, into small (3 degree) raw cutouts over the region covered
by the GLEAM survey. These cutouts have somewhat variable size and resolution. The
default scale (i.e., pixel size) used for SkyView images is given in the table
below.
SkyView resamples the cutouts retreived from the GLEAM web site into the image
geometry requested by the user. Only four wide-band datasets are included here.
The table below gives the frequency range, central frequency and a typical pixel
scale for each of these bands.
| GLEAM Bands In SkyView |
|---|
| Band |
fmin (MHz) |
fmax (MHz) |
fC (MHz)
| Pixel scale (") |
|---|
| 1 | 72 | 103 | 88 | 56 |
| 2 | 103 | 134 | 118 | 44 |
| 3 | 138 | 170 | 155 | 34 |
| 4 | 170 | 231 | 200 | 28 |
These data and 20 narrower bands are available through the team web site.
To minimize resampling artifacts, this survey defaults to the Lanczos third order resampler.
GLEAM 72-103: GaLactic and Extragalactic Allsky MWA Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: GLEAM72-103, GLEAM 72-103,GLEAM 72-103 MHz, GLEAM1, GLEAM 1
Description
GLEAM, the GaLactic and Extragalactic All-sky MWA survey, is a survey of
the entire radio sky south of declination 30 degrees at frequencies
between 72 and 231 MHz. It was made with the Murchison Widefield Array
(MWA) using a drift scan method that makes efficient use of the MWA's very
large field-of-view. The survey is described in Wayth et al. (2015) and
the website at http://mwatelescope.org/science/gleam-survey.
The data presented here are from the first year of GLEAM observing,
published in Hurley-Walker et al. (2017). The 25,000 square degrees of
available sky excludes the Galactic Plane, the Magellanic Clouds,
Centaurus A, and a few other small regions described in the catalogue
paper.
The most sensitive and highest-resolution image is the 170-231MHz image
which was used for all source-finding in generating the catalogue. It has
a resolution of approximately 2.2 x 2.2/cos (dec + 26.7) arcmin at this
frequency. However, due to ionospheric distortions, the final resolution
of the survey varies by ~10% over the sky, with a direction-dependent PSF.
The SkyView data for the GLEAM surveys was extracted using the team's
cutout server, into small (3 degree) raw cutouts over the region covered
by the GLEAM survey. These cutouts have somewhat variable size and resolution. The
default scale (i.e., pixel size) used for SkyView images is given in the table
below.
SkyView resamples the cutouts retreived from the GLEAM web site into the image
geometry requested by the user. Only four wide-band datasets are included here.
The table below gives the frequency range, central frequency and a typical pixel
scale for each of these bands.
| GLEAM Bands In SkyView |
|---|
| Band |
fmin (MHz) |
fmax (MHz) |
fC (MHz)
| Pixel scale (") |
|---|
| 1 | 72 | 103 | 88 | 56 |
| 2 | 103 | 134 | 118 | 44 |
| 3 | 138 | 170 | 155 | 34 |
| 4 | 170 | 231 | 200 | 28 |
These data and 20 narrower bands are available through the team web site.
To minimize resampling artifacts, this survey defaults to the Lanczos third order resampler.
GOODS North Observations with the VLA
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSNVLA,GOODS: VLA North,GOODS N VLA
Description
A combination of VLA measurements in all four configurations
combined to generate a very deep image of the GOODS North region. A total of about 150
hours of VLA time was used. Data are sensitive to about 5 microJanskies in
the central region. A total of 1230 discrete sources where found in the 40'x40' region.
| Provenance |
VLA Observations taken by Morrison et al. as provided
through their web site.
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Radio |
| Frequency | 1.4 GHz |
| Bandpass | 1.365-1.435 GHz |
| PixelScale | 0.5" |
| PixelUnits | Jy/beam |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Resolution | 1.7" |
| Coverage | North GOODS field ~0.01% of sky |
| Projection | Sin |
| Coordinates | ICRS |
| Epoch | 1996-11/1996-12, 2005-2,2005-8,2005-12 |
| Reference |
Morrison, et al, 2010
|
GTEE 0035 MHz Radio survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:0035MHz,35MHz,GTEE,GEETEE,GTEE 35MHz
Description
This survey is a mosaic of data taken at the low frequency T-array near Gauribidanur, India.
The data was distributed in the NRAO Images from the Radio Sky CD ROM.
The original 287x101 tiles had only 1 pixel overlap. To allow
higher order resampling, the data were retiled into two hemisphere
files of 1726x600 pixels with an overlap of 10 pixels.
The southernmost tiles were only 287x100 pixels. We assumed
that bottom row of these tiles (as compared with the others)
was truncated.
The HI 4-PI Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:HI4PI,HI4PI(NHI)
Description
The HI 4-PI Survey (HI4PI) is a 21-cm all-sky survey of neutral atomic
hydrogen. It is constructed from the Effelsberg-Bonn HI Survey (EBHIS), made
with the 100-m radio telescope at Effelsberg/Germany, and the Galactic All-Sky
Survey (GASS), observed with the Parkes 64-m dish in Australia. HI4PI
comprises HI line emission from the Milky Way. This dataset is the atomic
neutral hydrogen (HI) column density map derived from HI4PI
(|Vlsr| < 600 km/s).
| Provenance |
Argelander-Institut f??r Astronomie (AIfA), Max-Planck-Institut f??r
Radioastronomie (MPIfR), and CSIRO/Australia; data provided by B. Winkel
|
| Regime | Radio |
| Copyright |
Permission is granted for publication and reproduction of this material for scientific and educational purposes. When using data products provided in this release, it is requested that authors refer to the HI4PI publication. We also ask that publications making use of these data include the following acknowledgement: "The Parkes Radio Telescope is part of the Australia Telescope National Facility which is funded by the Australian Government for operation as a National Facility managed by CSIRO. The EBHIS data are based on observations performed with the 100-m telescope of the MPIfR at Effelsberg. EBHIS was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) under the grants KE757/7-1 to 7-3.
|
| Frequency | 1420 MHz |
| Coverage | All sky |
| Bandpass | 1417.5 - 1423.5 MHz |
| PixelScale | 1.5' |
| PixelUnit | atoms/cm2 |
| Sensitivity | 2.3 x 1018 cm-2 |
| Resolution | 16.2' |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2005-2013 |
| Reference |
HI4PI Collaboration, AA 594, 116, 2016
|
Dickey and Lockman HI map
Short name[s] used to specify survey:nH,HI map
Description
This survey is derived from the 21cm maps presented by Dickey and Lockman
in the ARAA 28, p215. The nH is derived assuming optically thin
emission. The nH given should be considered a lower limit when the nH is
greater than several times 1020.
| Provenance | provided by S. Snowden from data by Dickey and Lockman |
| Regime | Radio |
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Frequency | 1420 MHz line survey |
| Bandpass | 1418.8 - 1421.2 MHz |
| PixelScale | 40' |
| PixelUnit | atoms/cm^2 |
| Resolution | 1 degree |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Aitoff |
| Epoch | 1980 to 1990 |
| Reference |
Dickey and Lockman, ARAA 28, 1990, 215 (ADS)
|
NRA) VLA Sky Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: NVSS,N-VSS
Description
SkyView
has copied the NVSS intensity data from the NRAO FTP site. The full
NVSS survey data includes information on other Stokes parameters.
Observations for the 1.4 GHz NRAO VLA Sky Survey (NVSS) began in 1993
September and should cover the sky north of -40 deg declination (82%
of the celestial sphere) before the end of 1996. The principal data
products are:
- A set of 2326 continuum map "cubes," each covering 4 deg X 4 deg
with three planes containing Stokes I, Q, and U images. These maps
were made with a relatively large restoring beam (45 arcsec FWHM) to
yield the high surface-brightness sensitivity needed for completeness
and photometric accuracy. Their rms brightness fluctuations are
about 0.45 mJy/beam = 0.14 K (Stokes I) and 0.29 mJy/beam = 0.09 K
(Stokes Q and U). The rms uncertainties in right ascension and
declination vary from 0.3 arcsec for strong (S > 30 mJy) point
sources to 5 arcsec for the faintest (S = 2.5 mJy) detectable
sources.
- Lists of discrete sources.
The NVSS is being made as a service to the astronomical community, and
the data products are being released as soon as they are produced and
verified.
The NVSS survey is included on the SkyView High Resolution Radio
Coverage map. This map shows
coverage on an Aitoff projection of the sky in equatorial coordinates.
| Provenance |
National Radio Astronomy Observatory. The NVSS
project includes J. J. Condon, W. D. Cotton, E. W. Greisen, Q. F. Yin,
R. A. Perley (NRAO), and J. J. Broderick (VPI).
|
| Copyright |
Copyright 1994,
Associated Universities, Inc.,
National Radio Astronomy Observatory
Permission is granted for publication and reproduction of this material for
scholarly, educational, and private non-commerical use.
1994 Associated Universities, Inc. Inquiries for potential commercial
uses should be addressed to:
NRAO 520 Edgemont Road Charlottesville, VA 22903-2475
|
| Regime | Radio |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 1.4 GHz Continuum |
| Bandpass | 1.3628 - 1.4472 GHz |
| Coverage | Declinations @gt; -40 |
| PixelScale | 15"/pixel |
| PixelUnits | Janskies/beam |
| Resolution | 45" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Orthographic |
| Epoch | 1993-1997 |
| Reference |
NVSS home page
Condon et al. 1998 (ADS)
|
VLA Survey of SDSS Stripe 82
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Stripe82VLA,Stripe 82 VLA
Description
This survey is a deep, high resolution radio survey of a relatively small region that has particularly deep coverage
in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. As described in the reference abstract:
This is a high-resolution radio survey of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Southern Equatorial
Stripe, a.k.a., Stripe 82. This 1.4 GHz survey was conducted from 2007 to 2009 with the Very Large Array primarily in the A-configuration,
with supplemental B-configuration data to increase sensitivity to extended structure.
The survey has an angular resolution of 1.8" and achieves a median rms noise of 53 microJy/beam over 92 square degrees.
This is the deepest 1.4 GHz survey to achieve this large of an area filling in the
phase space between small&deep and large&shallow surveys.
The astrometric accuracy of the data is excellent with errors in observed sources of 0.10" in both RA and declination.
A comparison with the SDSS DR7 Quasar Catalog confirms that the astrometry is well tied to the optical reference
frame with mean offsets of 0.02+/-0.01" in RA and 0.01+/-0.02 in declination.
| Provenance |
TBD
|
| Regime | Radio |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 1.4 GHz Continuum |
| Bandpass | 1.3635 - 1.4365 GHz |
| Coverage | 92 square degrees (0.23%) |
| PixelScale | 0.6" |
| PixelUnits | Janskies/beam |
| Sensitivity | 0.52 microJy/beam |
| Resolution | 1.8" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Orthographic |
| Epoch | 2007-2009 |
| Reference |
Survey paper:
Hodge et al., AJ 142, 3, 2011
|
Sydney University Molonglo Sky Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: SUMSS, SUMSS 843 MHz
Description
The Sydney University Molonglo Sky Survey (SUMSS) is a deep radio
survey at 843 MHz of the entire sky south of declination -30°, made using
the Molonglo Observatory Synthesis Telescope ( MOST ), located near Canberra, Australia.
The images from the SUMSS are produced as 4 x 4 degree mosaics of up to
seventeen individual observations, to ensure even sensitivity across
the sky. The mosaics slightly overlap each other. Data were last updated on January 28, 2015.
Images can also be obtained from the SUMSS Postage Stamp Server.
The SUMSS is intended to complement the NRAO-VLA Sky Survey (NVSS) which
covered the sky between +90 and -40 deg declination, at a
frequency of 1400MHz.
| Provenance |
The SUMSS project team, University of Sydney
|
| Copyright |
1997-2000 School of Physics, The University of Sydney.
Permission is granted for publication and reproduction of this
material for scholarly, educational, and private non-commerical use.
Inquiries for potential commercial uses should be addressed to:
Dr. R.W. Hunstead or Dr. E.M. Sadler
Astrophysics Department, A29
University of Sydney
Sydney, NSW 2006
Australia
email: sumss@physics.usyd.edu.au
|
| Regime | Radio |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 843 MHz |
| Bandpass | 841.5 - 844.5 MhZ |
| Coverage | Declination < -30°.
|
| PixelScale | 11" x 11" cosec (|Dec|). Default scale for retrieval is 11" x 11" |
| PixelUnits | Janskys/beam |
| Resolution | 45" (RA) x 45" cosec (|Dec|) |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Orthographic (SIN) representation of the NCP projection plane |
| Epoch | 1997 to 2007 |
| Reference |
ADS
SUMSS home page
|
GMRT 150 MHz All-sky Radio Survey: First Alternative Data Release
Short name[s] used to specify survey:TGSS, TGSS ADR1, TGSS_ADR1
Description
The first full release of a survey of the 150 MHz radio sky observed with
the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope between April 2010 and March 2012 as
part of the TGSS project.
Aimed at producing a reliable compact source survey, the automated data reduction
pipeline efficiently processed more than 2000 hours of observations with minimal
human interaction. Through application of innovative techniques such as image-based
flagging, direction-dependent calibration of ionospheric phase errors, correcting
for systematic offsets in antenna pointing, and improving the primary beam model,
good quality images were created for over 95 percent of the 5336 pointings.
This data release covers 36,900 square degrees (or 3.6 pi steradians) of the
sky between -53 deg and +90 deg DEC, which is 90 percent of the total sky.
The majority of pointing images have a background RMS noise below 5 mJy/beam
with an approximate resolution of 25" x 25" (or 25" x 25" / cos (DEC - 19 deg)
for pointings south of 19 deg DEC).
The associated catalog has 640 thousand radio sources derived from an initial,
high reliability source extraction at the 7 sigma level.
The measured overall astrometric accuracy is better than 2" in RA and DEC,
while the flux density accuracy is estimated at ~10 percent.
Data is stored as 5336 mosaic images (5 deg x 5 deg).
SkyView uses Lanczos resampling and Sqrt image scaling by default for this
survey.
| Provenance | TGS ADR Team |
| Copyright |
© Public Domain.
If you are using the TGSS ADR survey products for your research, please add this reference
(Intema et al. 2016) in your publication.
Please also add the standard GMRT acknowledgement:
"We thank the staff of the GMRT that made these observations possible.
GMRT is run by the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics of the Tata Institute
of Fundamental Research."
|
| Regime | Radio |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 150 MHz (2 meters) |
| Bandpass | 140-156 MHz |
| Coverage | All sky north of declination -53. (0.9 of all sky) |
| PixelScale | 6.2" |
| PixelUnits | μJy |
| Resolution | 25" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Sine |
| Epoch | April 2010 to March 2012 |
| Reference |
Intema, et al., 2016, or
TGSS web site.
|
VLA Low-frequency Sky Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:VLSSr,4MASS,VLSS
Description
The VLA Low-Frequency Sky Survey (VLSS) is a 74 MHz continuum survey
covering the entire sky north of -30 degrees declination. Using the
VLA in BnA and B-configurations, it will map the entire survey region
at a resolution of 80" and with an average rms noise of 0.1 Jy/beam.
This version include the data from the VLSS redux which increased the coverage
region slightly and substantially improved the data reduction. Details are in the
Lane et al. (2012) reference.
| Provenance |
VLSS Team: R.A. Perley, J.J. Condon, W.D. Cotton (NRAO);
A.S. Cohen, W.M. Lane (NRC/NRL),
N.E. Kassim, T.J.W. Lazio (NRL),
W.C. Erickson (UMd)
|
| Copyright |
|
| Regime | Radio |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 74 MHz |
| Bandpass | 73.02-74.58 MHz |
| Coverage | Declinations above -30 degrees |
| PixelScale | 25"/pixel |
| PixelUnits | Janskies/beam |
| Resolution | 75" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Orthographic (Sin) |
| Epoch | ca. 2006 |
| Reference |
VLSS download page .
Details of the VLSSr reduction including comparisons with the original VLSS data are given in
Lane et al. (2012)
|
Westerbork Northern Sky Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: WENSS,W-NSS
Description
The Westerbork Northern Sky Survey (WENSS) is a low-frequency
radio survey that covers the whole sky north of delta=30 degree at a
wavelength of 92 cm to a limiting flux density of approximately 18 mJy
(5 sigma). This survey has a resolution of 54" x 54" cosec (delta)
and a positional accuracy for strong sources of 1.5''.
Further information on the survey including links to catalogs
derived from the survey is available at the
WENSS
web site.
The WENSS survey is included on the SkyView High Resolution Radio
Coverage map. This map shows
coverage on an Aitoff projection of the sky in equatorial coordinates.
| Provenance |
WENSS Team. Data downloaded
from
WENSS FTP site 1999-03-18.
The WENSS project is a collaboration between the
Netherlands Foundation for Research in
Astronomy (NFRA/ASTRON) and the
Leiden Observatory.
|
| Copyright |
WENSS team. Anyone using data from the WENSS database in publications is asked to acknowledge this.
|
| Regime | Radio |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 325 MHz Continuum |
| Bandpass | 322.5 - 327.5 MHz |
| Coverage | North of declination +30. |
| PixelScale | 21"/pixel |
| PixelUnits | Janskies/beam |
| Resolution | 54" cosec(declination) |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 1950 |
| Projection | Orthographic |
| Epoch | ca. 1991-1996 |
| Reference |
Rengelink et al., 1997, A&A Supp. 124, p 259.
ADS
|
Millimeter surveys
Planck 353 GHz Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Planck353,Planck 353,Planck-353
Description
Planck is ESA's third generation space based cosmic microwave background
experiment, operating at nine frequencies between 30 and 857 GHz and was
launched May 2009. Planck provides all-sky survey data at all nine
frequencies with higher resolution at the 6 higher frequencies.
It provides substantially higher resolution and sensitivity
than WMAP. Planck orbits in the L2 Lagrange point.
These data come from Release 1 of the Planck mission.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the HEALPix data. Users of the SkyView Jar will be able to access this survey through the web
but performance may be poor since the FITS files are 150 to 600 MB in size and must be completely
read in. SkyView will not automatically
cache these files on the user machine as is done for non-HEALPix surveys.
Data from the frequencies of 100 GHz or higher are stored
in a HEALPix file with a resolution of approximately 1.7' while lower frequencies are stored with
half that resolution, approximately 3.4'.
| Provenance | Planck Team |
| Copyright | |
| Regime | Millimeter |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 353 GHz |
| Bandpass | 310-410 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 1.7' |
| PixelUnits | K |
| Resolution | 5.0' |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2009-2013 |
| Reference |
Planck Release 1 results
|
Planck 217 GHz Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Planck217,Planck 217,Planck-217
Description
Planck is ESA's third generation space based cosmic microwave background
experiment, operating at nine frequencies between 30 and 857 GHz and was
launched May 2009. Planck provides all-sky survey data at all nine
frequencies with higher resolution at the 6 higher frequencies.
It provides substantially higher resolution and sensitivity
than WMAP. Planck orbits in the L2 Lagrange point.
These data come from Release 1 of the Planck mission.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the HEALPix data. Users of the SkyView Jar will be able to access this survey through the web
but performance may be poor since the FITS files are 150 to 600 MB in size and must be completely
read in. SkyView will not automatically
cache these files on the user machine as is done for non-HEALPix surveys.
Data from the frequencies of 100 GHz or higher are stored
in a HEALPix file with a resolution of approximately 1.7' while lower frequencies are stored with
half that resolution, approximately 3.4'.
| Provenance | Planck Team |
| Copyright | |
| Regime | Millimeter |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 217 GHz |
| Bandpass | 190-250 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 1.7' |
| PixelUnits | K |
| Resolution | 5.5' |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2009-2013 |
| Reference |
Planck Release 1 results
|
Planck 143 GHz Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Planck143,Planck 143,Planck-143
Description
Planck is ESA's third generation space based cosmic microwave background
experiment, operating at nine frequencies between 30 and 857 GHz and was
launched May 2009. Planck provides all-sky survey data at all nine
frequencies with higher resolution at the 6 higher frequencies.
It provides substantially higher resolution and sensitivity
than WMAP. Planck orbits in the L2 Lagrange point.
These data come from Release 1 of the Planck mission.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the HEALPix data. Users of the SkyView Jar will be able to access this survey through the web
but performance may be poor since the FITS files are 150 to 600 MB in size and must be completely
read in. SkyView will not automatically
cache these files on the user machine as is done for non-HEALPix surveys.
Data from the frequencies of 100 GHz or higher are stored
in a HEALPix file with a resolution of approximately 1.7' while lower frequencies are stored with
half that resolution, approximately 3.4'.
| Provenance | Planck Team |
| Copyright | |
| Regime | Millimeter |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 143 GHz |
| Bandpass | 130-160 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 1.7' |
| PixelUnits | K |
| Resolution | 7.1' |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2009-2013 |
| Reference |
Planck Release 1 results
|
Planck 545 GHz Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Planck545,Planck 545,Planck-545
Description
Planck is ESA's third generation space based cosmic microwave background
experiment, operating at nine frequencies between 30 and 857 GHz and was
launched May 2009. Planck provides all-sky survey data at all nine
frequencies with higher resolution at the 6 higher frequencies.
It provides substantially higher resolution and sensitivity
than WMAP. Planck orbits in the L2 Lagrange point.
These data come from Release 1 of the Planck mission.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the HEALPix data. Users of the SkyView Jar will be able to access this survey through the web
but performance may be poor since the FITS files are 150 to 600 MB in size and must be completely
read in. SkyView will not automatically
cache these files on the user machine as is done for non-HEALPix surveys.
Data from the frequencies of 100 GHz or higher are stored
in a HEALPix file with a resolution of approximately 1.7' while lower frequencies are stored with
half that resolution, approximately 3.4'.
| Provenance | Planck Team |
| Copyright | |
| Regime | Millimeter |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 545 GHz |
| Bandpass | 450-650 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 1.7' |
| PixelUnits | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | 5.0' |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2009-2013 |
| Reference |
Planck Release 1 results
|
Planck 030 GHz Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Planck030,Planck 030,Planck-030
Description
Planck is ESA's third generation space based cosmic microwave background
experiment, operating at nine frequencies between 30 and 857 GHz and was
launched May 2009. Planck provides all-sky survey data at all nine
frequencies with higher resolution at the 6 higher frequencies.
It provides substantially higher resolution and sensitivity
than WMAP. Planck orbits in the L2 Lagrange point.
These data come from Release 1 of the Planck mission.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the HEALPix data. Users of the SkyView Jar will be able to access this survey through the web
but performance may be poor since the FITS files are 150 to 600 MB in size and must be completely
read in. SkyView will not automatically
cache these files on the user machine as is done for non-HEALPix surveys.
Data from the frequencies of 100 GHz or higher are stored
in a HEALPix file with a resolution of approximately 1.7' while lower frequencies are stored with
half that resolution, approximately 3.4'.
| Provenance | Planck Team |
| Copyright | |
| Regime | Millimeter |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 030 GHz |
| Bandpass | 20-33 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 3.4' |
| PixelUnits | K |
| Resolution | 33' |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2009-2013 |
| Reference |
Planck Release 1 results
|
Planck 100 GHz Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Planck100,Planck 100,Planck-100
Description
Planck is ESA's third generation space based cosmic microwave background
experiment, operating at nine frequencies between 30 and 857 GHz and was
launched May 2009. Planck provides all-sky survey data at all nine
frequencies with higher resolution at the 6 higher frequencies.
It provides substantially higher resolution and sensitivity
than WMAP. Planck orbits in the L2 Lagrange point.
These data come from Release 1 of the Planck mission.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the HEALPix data. Users of the SkyView Jar will be able to access this survey through the web
but performance may be poor since the FITS files are 150 to 600 MB in size and must be completely
read in. SkyView will not automatically
cache these files on the user machine as is done for non-HEALPix surveys.
Data from the frequencies of 100 GHz or higher are stored
in a HEALPix file with a resolution of approximately 1.7' while lower frequencies are stored with
half that resolution, approximately 3.4'.
| Provenance | Planck Team |
| Copyright | |
| Regime | Millimeter |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 100 GHz |
| Bandpass | 85-130 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 1.7' |
| PixelUnits | K |
| Resolution | 10' |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2009-2013 |
| Reference |
Planck Release 1 results
|
Planck 070 GHz Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Planck070,Planck 070,Planck-070
Description
Planck is ESA's third generation space based cosmic microwave background
experiment, operating at nine frequencies between 30 and 857 GHz and was
launched May 2009. Planck provides all-sky survey data at all nine
frequencies with higher resolution at the 6 higher frequencies.
It provides substantially higher resolution and sensitivity
than WMAP. Planck orbits in the L2 Lagrange point.
These data come from Release 1 of the Planck mission.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the HEALPix data. Users of the SkyView Jar will be able to access this survey through the web
but performance may be poor since the FITS files are 150 to 600 MB in size and must be completely
read in. SkyView will not automatically
cache these files on the user machine as is done for non-HEALPix surveys.
Data from the frequencies of 100 GHz or higher are stored
in a HEALPix file with a resolution of approximately 1.7' while lower frequencies are stored with
half that resolution, approximately 3.4'.
| Provenance | Planck Team |
| Copyright | |
| Regime | Millimeter |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 070 GHz |
| Bandpass | 60-80 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 3.4' |
| PixelUnits | K |
| Resolution | 14' |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2009-2013 |
| Reference |
Planck Release 1 results
|
Planck 857 GHz Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Planck857,Planck 857,Planck-857
Description
Planck is ESA's third generation space based cosmic microwave background
experiment, operating at nine frequencies between 30 and 857 GHz and was
launched May 2009. Planck provides all-sky survey data at all nine
frequencies with higher resolution at the 6 higher frequencies.
It provides substantially higher resolution and sensitivity
than WMAP. Planck orbits in the L2 Lagrange point.
These data come from Release 1 of the Planck mission.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the HEALPix data. Users of the SkyView Jar will be able to access this survey through the web
but performance may be poor since the FITS files are 150 to 600 MB in size and must be completely
read in. SkyView will not automatically
cache these files on the user machine as is done for non-HEALPix surveys.
Data from the frequencies of 100 GHz or higher are stored
in a HEALPix file with a resolution of approximately 1.7' while lower frequencies are stored with
half that resolution, approximately 3.4'.
| Provenance | Planck Team |
| Copyright | |
| Regime | Millimeter |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 857 GHz |
| Bandpass | 750-1000 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 1.7' |
| PixelUnits | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | 5.0' |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2009-2013 |
| Reference |
Planck Release 1 results
|
Planck 044 GHz Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Planck044,Planck 044,Planck-044
Description
Planck is ESA's third generation space based cosmic microwave background
experiment, operating at nine frequencies between 30 and 857 GHz and was
launched May 2009. Planck provides all-sky survey data at all nine
frequencies with higher resolution at the 6 higher frequencies.
It provides substantially higher resolution and sensitivity
than WMAP. Planck orbits in the L2 Lagrange point.
These data come from Release 1 of the Planck mission.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the HEALPix data. Users of the SkyView Jar will be able to access this survey through the web
but performance may be poor since the FITS files are 150 to 600 MB in size and must be completely
read in. SkyView will not automatically
cache these files on the user machine as is done for non-HEALPix surveys.
Data from the frequencies of 100 GHz or higher are stored
in a HEALPix file with a resolution of approximately 1.7' while lower frequencies are stored with
half that resolution, approximately 3.4'.
| Provenance | Planck Team |
| Copyright | |
| Regime | Millimeter |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 044 GHz |
| Bandpass | 39-58 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 3.4' |
| PixelUnits | K |
| Resolution | 24' |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2009-2013 |
| Reference |
Planck Release 1 results
|
Infrared surveys
Two Micron All Sky Survey (H-Band)
Short name[s] used to specify survey:2MASSH,2MASS-H
Description
2MASS data were collected by uniformly scanning the entire sky in three
near-infrared bands to detect and characterize point sources brighter than
about 1 mJy in each band, with signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) greater than 10,
using a pixel size of 2.0". This achieves an 80,000-fold improvement in
sensitivity relative to earlier surveys.
2MASS used two new, highly-automated 1.3-m telescopes, one at Mt. Hopkins,
AZ, and one at CTIO, Chile. Each telescope is equipped with a three-channel
camera, each channel consisting of a 256 by 256 array of HgCdTe detectors,
capable of observing the sky simultaneously at J (1.25 microns),
H (1.65 microns), and Ks (2.17 microns).
2MASS images and other data products can be obtained at the NASA/IPAC Infrared Science Archive
| Provenance |
The Two Micron All Sky Survey is a joint project of the University of
Massachusetts and the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center, funded by
the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and the National
Science Foundation.
|
| Copyright |
Researchers are asked to include the following
acknowledgment in any published material that
makes use of data products from the
Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS):
"This publication makes use of data products from the
Two Micron All Sky Survey, which is a joint project of
the University of
Massachusetts and the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center,
funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and
the National Science Foundation."
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 180 THz (1.65 microns) |
| Bandpass | 167-197 THz |
| Coverage | All sky |
| PixelScale | 1"/pixel |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 4" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Orthographic (SIN) |
| Epoch | 1997 - 2002 |
| Reference |
2MASS web site
|
Two Micron All Sky Survey (J-Band)
Short name[s] used to specify survey:2MASSJ,2MASS-J
Description
2MASS data were collected by uniformly scanning the entire sky in three
near-infrared bands to detect and characterize point sources brighter than
about 1 mJy in each band, with signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) greater than 10,
using a pixel size of 2.0". This achieves an 80,000-fold improvement in
sensitivity relative to earlier surveys.
2MASS used two new, highly-automated 1.3-m telescopes, one at Mt. Hopkins,
AZ, and one at CTIO, Chile. Each telescope is equipped with a three-channel
camera, each channel consisting of a 256 by 256 array of HgCdTe detectors,
capable of observing the sky simultaneously at J (1.25 microns),
H (1.65 microns), and Ks (2.17 microns).
2MASS images and other data products can be obtained at the NASA/IPAC Infrared Science Archive
| Provenance |
The Two Micron All Sky Survey is a joint project of the University of
Massachusetts and the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center, funded by
the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and the National
Science Foundation.
|
| Copyright |
Researchers are asked to include the following
acknowledgment in any published material that
makes use of data products from the
Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS):
"This publication makes use of data products from the
Two Micron All Sky Survey, which is a joint project of
the University of
Massachusetts and the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center,
funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and
the National Science Foundation."
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 240 THz (1.25 microns) |
| Bandpass | 222-375 THz |
| Coverage | All sky |
| PixelScale | 1"/pixel |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 4" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Orthographic (SIN) |
| Epoch | 1997 - 2002 |
| Reference |
2MASS web site
|
Two Micron All Sky Survey (K-Band)
Short name[s] used to specify survey:2MASSK,2MASS-K
Description
2MASS data were collected by uniformly scanning the entire sky in three
near-infrared bands to detect and characterize point sources brighter than
about 1 mJy in each band, with signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) greater than 10,
using a pixel size of 2.0". This achieves an 80,000-fold improvement in
sensitivity relative to earlier surveys.
2MASS used two new, highly-automated 1.3-m telescopes, one at Mt. Hopkins,
AZ, and one at CTIO, Chile. Each telescope is equipped with a three-channel
camera, each channel consisting of a 256 by 256 array of HgCdTe detectors,
capable of observing the sky simultaneously at J (1.25 microns),
H (1.65 microns), and Ks (2.17 microns).
2MASS images and other data products can be obtained at the NASA/IPAC Infrared Science Archive
| Provenance |
The Two Micron All Sky Survey is a joint project of the University of
Massachusetts and the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center, funded by
the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and the National
Science Foundation.
|
| Copyright |
Researchers are asked to include the following
acknowledgment in any published material that
makes use of data products from the
Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS):
"This publication makes use of data products from the
Two Micron All Sky Survey, which is a joint project of
the University of
Massachusetts and the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center,
funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and
the National Science Foundation."
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 137 THz (2.17 microns) |
| Bandpass | 129-222 THz |
| Coverage | All sky |
| PixelScale | 1"/pixel |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 4" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Orthographic (SIN) |
| Epoch | 1997 - 2002 |
| Reference |
2MASS web site
|
AKARI N160
Short name[s] used to specify survey:AKARI N160, AKARI-N160, AKARI_N160
Description
The AKARI (formerly Astro-F) mission is a Japanese second generation all-sky infrared
survey mission. SkyView currently includes surveys from the four bands of the FIS instrument:
N60, WIDE-S, WIDE-L and N160.
These surveys cover
99% of the sky in four photometric bands centred at 65??m, 90??m, 140??m, and 160??m,
with spatial resolutions ranging from 1-1.5'.
These data provide crucial information on the investigation and characterisation of the proper-
ties of dusty material in the interstellar medium (ISM), since a significant portion of its
energy is emitted between
???50 and 200 ??m. The large-scale distribution of interstellar
clouds, their thermal dust temperatures, and their column densities can be investigated
with the improved spatial resolution compared to earlier all-sky survey observations.
In addition to the point source distribution, the large-scale distribution of ISM cirrus emis-
sion, and its filamentary structure, are well traced.
Data are obtained using using the JVO AKARI Simple Image Access Service.
| Provenance |
AKARI FIS map making team [Univ of Tokyo, ISAS/JAXA, Tohoku Univ, Tsukuba Univ,
The Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, The Open Univ]
|
| Copyright |
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 1.7 x 1012 |
| Bandpass | 1.3-2.1 x 1012 |
| Coverage | All Sky |
| PixelScale | 44.2" |
| PixelUnits | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | 88" |
| Coordinates | Ecliptic |
| Projection | Tangent plane |
| Epoch | 2006-2007 |
| Reference | Doi, et al., 2016 and
Takita, et al. 2015
|
AKARI N60
Short name[s] used to specify survey:AKARI N60, AKARI-N60, AKARI_N60
Description
The AKARI (formerly Astro-F) mission is a Japanese second generation all-sky infrared
survey mission. SkyView currently includes surveys from the four bands of the FIS instrument:
N60, WIDE-S, WIDE-L and N160.
These surveys cover
99% of the sky in four photometric bands centred at 65??m, 90??m, 140??m, and 160??m,
with spatial resolutions ranging from 1-1.5'.
These data provide crucial information on the investigation and characterisation of the proper-
ties of dusty material in the interstellar medium (ISM), since a significant portion of its
energy is emitted between
???50 and 200 ??m. The large-scale distribution of interstellar
clouds, their thermal dust temperatures, and their column densities can be investigated
with the improved spatial resolution compared to earlier all-sky survey observations.
In addition to the point source distribution, the large-scale distribution of ISM cirrus emis-
sion, and its filamentary structure, are well traced.
Data are obtained using using the JVO AKARI Simple Image Access Service.
| Provenance |
AKARI FIS map making team [Univ of Tokyo, ISAS/JAXA, Tohoku Univ, Tsukuba Univ,
The Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, The Open Univ]
|
| Copyright |
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 5 x 1012 |
| Bandpass | 3.7-6.0 x 1012 |
| Coverage | All Sky |
| PixelScale | 26.8" |
| PixelUnits | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | 63" |
| Coordinates | Ecliptic |
| Projection | Tangent plane |
| Epoch | 2006-2007 |
| Reference | Doi, et al., 2016 and
Takita, et al. 2015
|
AKARI WIDE-L
Short name[s] used to specify survey:AKARI WIDE-L, AKARI-WIDE-L, AKARI_WIDE-L
Description
The AKARI (formerly Astro-F) mission is a Japanese second generation all-sky infrared
survey mission. SkyView currently includes surveys from the four bands of the FIS instrument:
N60, WIDE-S, WIDE-L and N160.
These surveys cover
99% of the sky in four photometric bands centred at 65??m, 90??m, 140??m, and 160??m,
with spatial resolutions ranging from 1-1.5'.
These data provide crucial information on the investigation and characterisation of the proper-
ties of dusty material in the interstellar medium (ISM), since a significant portion of its
energy is emitted between
???50 and 200 ??m. The large-scale distribution of interstellar
clouds, their thermal dust temperatures, and their column densities can be investigated
with the improved spatial resolution compared to earlier all-sky survey observations.
In addition to the point source distribution, the large-scale distribution of ISM cirrus emis-
sion, and its filamentary structure, are well traced.
Data are obtained using using the JVO AKARI Simple Image Access Service.
| Provenance |
AKARI FIS map making team [Univ of Tokyo, ISAS/JAXA, Tohoku Univ, Tsukuba Univ,
The Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, The Open Univ]
|
| Copyright |
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 2.14 x 1012 |
| Bandpass | 1.7-2.7 x 1012 |
| Coverage | All Sky |
| PixelScale | 44.2" |
| PixelUnits | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | 88" |
| Coordinates | Ecliptic |
| Projection | Tangent plane |
| Epoch | 2006-2007 |
| Reference | Doi, et al., 2016 and
Takita, et al. 2015
|
AKARI WIDE-S
Short name[s] used to specify survey:AKARI WIDE-S, AKARI-WIDE-S, AKARI_WIDE-S
Description
The AKARI (formerly Astro-F) mission is a Japanese second generation all-sky infrared
survey mission. SkyView currently includes surveys from the four bands of the FIS instrument:
N60, WIDE-S, WIDE-L and N160.
These surveys cover
99% of the sky in four photometric bands centred at 65??m, 90??m, 140??m, and 160??m,
with spatial resolutions ranging from 1-1.5'.
These data provide crucial information on the investigation and characterisation of the proper-
ties of dusty material in the interstellar medium (ISM), since a significant portion of its
energy is emitted between
???50 and 200 ??m. The large-scale distribution of interstellar
clouds, their thermal dust temperatures, and their column densities can be investigated
with the improved spatial resolution compared to earlier all-sky survey observations.
In addition to the point source distribution, the large-scale distribution of ISM cirrus emis-
sion, and its filamentary structure, are well traced.
Data are obtained using using the JVO AKARI Simple Image Access Service.
| Provenance |
AKARI FIS map making team [Univ of Tokyo, ISAS/JAXA, Tohoku Univ, Tsukuba Univ,
The Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, The Open Univ]
|
| Copyright |
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 3.3 x 1012 |
| Bandpass | 2.7-5.0 x 1012 |
| Coverage | All Sky |
| PixelScale | 26.8" |
| PixelUnits | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | 78" |
| Coordinates | Ecliptic |
| Projection | Tangent plane |
| Epoch | 2006-2007 |
| Reference | Doi, et al., 2016 and
Takita, et al. 2015
|
Cosmic Background Explorer DIRBE Annual Average Map
Short name[s] used to specify survey: COBEAAM, COBE DIRBE/AAM
Description
The DIRBE Project Data Sets cover the whole sky and provide photometric data
in 10 bands ranging in wavelength from 1.25 to 240 microns. SkyView has supported
three maps: an early averaged map including including zodiacal and
Galactic components (COBE DIRBE (OLD)), a more recent cleaner version of
that data (COBE DIRBE/AAM) and a map with the zodaical light subtracted out
(COBE DIRBE/ZSMA). The early data is no longer supported. Please contact us if you
want access to these data.
Detailed descriptions of the DIRBE, the data processing, and the data products
are given in an Explanatory Supplement. A Small Source Spectral Energy Distribution
Browser can be used to assess the visibility of an unresolved or small extended source
in the DIRBE data and see its spectral energy distribution. As noted in section
5.6.6 of the Explanatory Supplement, the DIRBE Time-ordered Data are required to
derive definitive point source fluxes.
These maps provide an estimate of the infrared intensity at each pixel and
wavelength band based on an interpolation of the observations made at
various times at solar elongations close to 90°.
These COBE DIRBE maps are a combination original ten band passes with the following wavelengths:
- Band 1 - 1.25 µm
- Band 2 - 2.2 µm
- Band 3 - 3.5 µm
- Band 4 - 4.9 µm
- Band 5 - 12 µm
- Band 6 - 25 µm
- Band 7 - 60 µm
- Band 8 - 100 µm
- Band 9 - 140 µm
- Band 10 - 240 µm
The default two dimensional array uses Band 8 (100 µm).
The COBE DIRBE/Annual Average Maps (AAM) is the cumulative weighted
average of the photometry. This average is calculated using the
weighted number of observations from each Weekly Averaged Map
( WtNumObs from the Weekly Averaged Map) as the weight, such that
annual_average =sum( weekly_average * weekly_weight )/ sum( weekly_weight )
COBE DIRBE/Zodi-Subtracted Mission Average (ZSMA) Skymap represents
the extra-Solar system sky brightness. It is the average
residual map that results after the modelled interplanetary dust (IPD) signal
is subtracted from each of the DIRBE Weekly Skymaps from the cryogenic mission.
Individual weekly residual maps can be reconstructed from the data supplied in
the DIRBE Sky and Zodi Atlas (DSZA).
| Provenance |
COBE Team
|
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 2 (10 bands) |
| Frequency | 1.25-240 THz
| Frequency Bands |
|---|
| Band | Central | Min | |
|---|
| 10 | | 1.2491 THz | 1.0016 THz | 1.4966 THz |
| 9 | | 2.1414 THz | 1.8394 THz | 2.1717 THz |
| 8 | | 2.9979 THz | 2.5159 THz | 3.4799 THz |
| 7 | | 4.9965 THz | 3.8365 THz | 6.1565 THz |
| 6 | | 11.992 THz | 9.9270 THz | 14.057 THz |
| 5 | | 24.983 THz | 18.333 THz | 31.633 THz |
| 4 | | 61.182 THz | 57.087 THz | 65.277 THz |
| 3 | | 85.655 THz | 74.655 THz | 96.655 THz |
| 2 | | 136.70 THz | 1.2550 THz | 147.90 THz |
| 1 | | 239.83 THz | 210.08 THz | 269.58 THz |
|
| Coverage | All-sky |
| Scale | 0.32 deg/pix |
| Units | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | ca. .75 deg |
| Coordinates | Ecliptic |
| Projection | CobeCube (CSC) |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1989-1990 |
| Reference |
COBE Diffuse Infrared Background Experiment (DIRBE)
Explanatory Supplement ed. M.G. Hauser, T. Kelsall, D. Leisawitz, and
J. Weiland COBE Ref. Pub. No. 97-A (Greenbelt, MD: NASA/GSFC)
available in electronic form (in a slightly more up-to-date version)
from the COBE Web page.
Specific DIRBE information
is available including an instrument description (PostScript).
|
Cosmic Background Explorer DIRBE Zodi-Subtracted Mission Average
Short name[s] used to specify survey: COBEZSMA, COBE DIRBE/ZSMA
Description
The DIRBE Project Data Sets cover the whole sky and provide photometric data
in 10 bands ranging in wavelength from 1.25 to 240 microns. SkyView has supported
three maps: an early averaged map including including zodiacal and
Galactic components (COBE DIRBE (OLD)), a more recent cleaner version of
that data (COBE DIRBE/AAM) and a map with the zodaical light subtracted out
(COBE DIRBE/ZSMA). The early data is no longer supported. Please contact us if you
want access to these data.
Detailed descriptions of the DIRBE, the data processing, and the data products
are given in an Explanatory Supplement. A Small Source Spectral Energy Distribution
Browser can be used to assess the visibility of an unresolved or small extended source
in the DIRBE data and see its spectral energy distribution. As noted in section
5.6.6 of the Explanatory Supplement, the DIRBE Time-ordered Data are required to
derive definitive point source fluxes.
These maps provide an estimate of the infrared intensity at each pixel and
wavelength band based on an interpolation of the observations made at
various times at solar elongations close to 90°.
These COBE DIRBE maps are a combination original ten band passes with the following wavelengths:
- Band 1 - 1.25 µm
- Band 2 - 2.2 µm
- Band 3 - 3.5 µm
- Band 4 - 4.9 µm
- Band 5 - 12 µm
- Band 6 - 25 µm
- Band 7 - 60 µm
- Band 8 - 100 µm
- Band 9 - 140 µm
- Band 10 - 240 µm
The default two dimensional array uses Band 8 (100 µm).
The COBE DIRBE/Annual Average Maps (AAM) is the cumulative weighted
average of the photometry. This average is calculated using the
weighted number of observations from each Weekly Averaged Map
( WtNumObs from the Weekly Averaged Map) as the weight, such that
annual_average =sum( weekly_average * weekly_weight )/ sum( weekly_weight )
COBE DIRBE/Zodi-Subtracted Mission Average (ZSMA) Skymap represents
the extra-Solar system sky brightness. It is the average
residual map that results after the modelled interplanetary dust (IPD) signal
is subtracted from each of the DIRBE Weekly Skymaps from the cryogenic mission.
Individual weekly residual maps can be reconstructed from the data supplied in
the DIRBE Sky and Zodi Atlas (DSZA).
| Provenance |
COBE Team
|
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 2 (10 bands) |
| Frequency | 1.25-240 THz
| Frequency Bands |
|---|
| Band | Central | Min | |
|---|
| 10 | | 1.2491 THz | 1.0016 THz | 1.4966 THz |
| 9 | | 2.1414 THz | 1.8394 THz | 2.1717 THz |
| 8 | | 2.9979 THz | 2.5159 THz | 3.4799 THz |
| 7 | | 4.9965 THz | 3.8365 THz | 6.1565 THz |
| 6 | | 11.992 THz | 9.9270 THz | 14.057 THz |
| 5 | | 24.983 THz | 18.333 THz | 31.633 THz |
| 4 | | 61.182 THz | 57.087 THz | 65.277 THz |
| 3 | | 85.655 THz | 74.655 THz | 96.655 THz |
| 2 | | 136.70 THz | 1.2550 THz | 147.90 THz |
| 1 | | 239.83 THz | 210.08 THz | 269.58 THz |
|
| Coverage | All-sky |
| Scale | 0.32 deg/pix |
| Units | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | ca. .75 deg |
| Coordinates | Ecliptic |
| Projection | CobeCube (CSC) |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1989-1990 |
| Reference |
COBE Diffuse Infrared Background Experiment (DIRBE)
Explanatory Supplement ed. M.G. Hauser, T. Kelsall, D. Leisawitz, and
J. Weiland COBE Ref. Pub. No. 97-A (Greenbelt, MD: NASA/GSFC)
available in electronic form (in a slightly more up-to-date version)
from the COBE Web page.
Specific DIRBE information
is available including an instrument description (PostScript).
|
2nd Digitized Sky Survey-Near Infrared
Short name[s] used to specify survey:DSS2IR, DSS2 IR
Description
This survey was generated by scanning Schmidt near-IR plates
of the sky at 1" resolution. Scanning and compression was performed
at the Space Telescope Science Institute. See
the ST DSS site for
further details.
The native projection of these data is described as a high-order polynomial
distortion of a gnomonic projection using the same terms as the DSS.
SkyView has a copy of the compressed images which cover
the entire sky. In previous versions of SkyView (prior
to July 2007), this survey was served as a remote survey and data
was retrieved in tiles from the ST ScI web site. Image generation
using the local copy should be much faster at the SkyView web site.
However data from this survey is not currently cached when it is
used in the SkyView-in-a-Jar application so that data will be
downloaded from the SkyView web site whenever an image is requested.
Future updates to SkyView-in-a-Jar should address this caching issue.
| Provenance | Data taken by ROE, AAO, and CalTech, Compression
and distribution by Space Telescope Science Institute.
|
| Copyright |
There are multiple copyright holders depending
upon the source plate or plates.
See full copyright
notices The coverage link below describes the
coverage for each element of the surveys when the original plate used is
not included in the SkyView files. |
.
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 353 THz |
| Bandpass | 327-422 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 1" |
| PixelUnits | Pixel values are given as scaled densities |
| Resolution | Depends on plate. Typically 2-3". |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Schmidt |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1987-2002 |
| Reference |
Some information on the DSS2 is given in
McLean, 2000, The Second Generation Guide Star Catalog.
Characteristics of the DSS surveys are summarized in
this document.
|
GOODS Herschel 100 micron, DR1 data release
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSHerschel1, GOODS Herschel 100, GOODS: Herschel 100
Description
GOODS-Herschel is an open time key program of more than 360 hours of observation with the Hershel, SPIRE and PACS, from 100 um and 500.
North and South GOODS data is available for 100 and 160 microns (using PACS) but only the northern field is
available at 250, 350 and 500 microns (using SPIRE).
Note that the scale and resolution of the underlying pixels is different in each band.
| Regime | Infrared |
| Frequency | 3 THz |
| Bandpass | 2.5-3.5 THz |
| Provenance |
Downloaded from the Herschel Database in Marseille. Release DR1.
|
| Copyright |
All papers using GOODS-Herschel data downloaded from HeDaM should include the following acknowledgements:
The GOODS-Herschel data was accessed through the Herschel Database in Marseille (HeDaM) - http://hedam.lam.fr -
operated by CeSAM and hosted by the Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Marseille.
|
| NSurvey | 5 |
| PixelScale | 1.2" |
| Resolution | 6.7" |
| PixelUnits | Jy/pixel |
| Coverage | North and South GOODS Fields. 1.5e-6 |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2009/2011 |
| Reference | Elbaz, et al 2011
|
GOODS Herschel 160 micron, DR1 data release
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSHerschel2, GOODS Herschel 160, GOODS: Herschel 160
Description
GOODS-Herschel is an open time key program of more than 360 hours of observation with the Hershel, SPIRE and PACS, from 100 um and 500.
North and South GOODS data is available for 100 and 160 microns (using PACS) but only the northern field is
available at 250, 350 and 500 microns (using SPIRE).
Note that the scale and resolution of the underlying pixels is different in each band.
| Regime | Infrared |
| Frequency | 1.9 THz |
| Bandpass | 1.6-2.2 THz |
| Provenance |
Downloaded from the Herschel Database in Marseille. Release DR1.
|
| Copyright |
All papers using GOODS-Herschel data downloaded from HeDaM should include the following acknowledgements:
The GOODS-Herschel data was accessed through the Herschel Database in Marseille (HeDaM) - http://hedam.lam.fr -
operated by CeSAM and hosted by the Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Marseille.
|
| NSurvey | 5 |
| PixelScale | 2.4" |
| Resolution | 11.0" |
| PixelUnits | Jy/pixel |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Coverage | North and South GOODS fields: 1.e-5 |
| Epoch | 2009/2011 |
| Reference | Elbaz, et al 2011
|
GOODS Herschel 250 micron, DR1 data release
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSHerschel3, GOODS Herschel 250, GOODS: Herschel 250
Description
GOODS-Herschel is an open time key program of more than 360 hours of observation with the Hershel, SPIRE and PACS, from 100 um and 500.
North and South GOODS data is available for 100 and 160 microns (using PACS) but only the northern field is
available at 250, 350 and 500 microns (using SPIRE).
Note that the scale and resolution of the underlying pixels is different in each band.
| Regime | Infrared |
| Frequency | 1.2 THz |
| Bandpass | 1.0-1.4 THz |
| Provenance |
Downloaded from the Herschel Database in Marseille. Release DR1.
|
| Copyright |
All papers using GOODS-Herschel data downloaded from HeDaM should include the following acknowledgements:
The GOODS-Herschel data was accessed through the Herschel Database in Marseille (HeDaM) - http://hedam.lam.fr -
operated by CeSAM and hosted by the Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Marseille.
|
| NSurvey | 5 |
| PixelScale | 3.6" |
| Resolution | 18.1" |
| PixelUnits | Jy/pixel |
| Coverage | Extended North GOODS Fields. 1.6e-5 |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2009/2011 |
| Reference | Elbaz, et al 2011
|
GOODS Herschel 350 micron, DR1 data release
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSHerschel4, GOODS Herschel 350, GOODS: Herschel 350
Description
GOODS-Herschel is an open time key program of more than 360 hours of observation with the Hershel, SPIRE and PACS, from 100 um and 500.
North and South GOODS data is available for 100 and 160 microns (using PACS) but only the northern field is
available at 250, 350 and 500 microns (using SPIRE).
Note that the scale and resolution of the underlying pixels is different in each band.
| Regime | Infrared |
| Frequency | 860 MHz |
| Bandpass | 740-1000 MHz |
| Provenance |
Downloaded from the Herschel Database in Marseille. Release DR1.
|
| Copyright |
All papers using GOODS-Herschel data downloaded from HeDaM should include the following acknowledgements:
The GOODS-Herschel data was accessed through the Herschel Database in Marseille (HeDaM) - http://hedam.lam.fr -
operated by CeSAM and hosted by the Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Marseille.
|
| NSurvey | 5 |
| PixelScale | 4.8" |
| Resolution | 24.9" |
| PixelUnits | Jy/pixel |
| Coverage | Extended North GOODS Fields. 1.6e-5 |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2009/2011 |
| Reference | Elbaz, et al 2011
|
GOODS Herschel 500 micron, DR1 data release
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSHerschel5, GOODS Herschel 500, GOODS: Herschel 500
Description
GOODS-Herschel is an open time key program of more than 360 hours of observation with the Hershel, SPIRE and PACS, from 100 um and 500.
North and South GOODS data is available for 100 and 160 microns (using PACS) but only the northern field is
available at 250, 350 and 500 microns (using SPIRE).
Note that the scale and resolution of the underlying pixels is different in each band.
| Regime | Infrared |
| Frequency | 600 MHz |
| Bandpass | 510-700 MHz |
| Provenance |
Downloaded from the Herschel Database in Marseille. Release DR1.
|
| Copyright |
All papers using GOODS-Herschel data downloaded from HeDaM should include the following acknowledgements:
The GOODS-Herschel data was accessed through the Herschel Database in Marseille (HeDaM) - http://hedam.lam.fr -
operated by CeSAM and hosted by the Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Marseille.
|
| NSurvey | 5 |
| PixelScale | 7.2" |
| Resolution | 36.6" |
| PixelUnits | Jy/pixel |
| Coverage | Extended North GOODS Fields. 1.6e-5 |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2009/2011 |
| Reference | Elbaz, et al 2011
|
Spitzer IRAC GOODS 3.6 micron data, channel 1
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSIRAC 1, GOODS IRAC 1, GOODS IRAC 3.6, GOODS: Spitzer IRAC 3.6
Description
Spitzer IRAC medium infrared observations taken in all four IRAC channels in both the north
and south GOODS fields.
Spitzer IRAC GOODS 4.5 micron data, channel 2
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSIRAC 2, GOODS IRAC 2, GOODS IRAC 4.5, GOODS: Spitzer IRAC 4.5
Description
Spitzer IRAC medium infrared observations taken in all four IRAC channels in both the north
and south GOODS fields.
Spitzer IRAC GOODS 5.8 micron data, channel 3
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSIRAC 3, GOODS IRAC 3, GOODS IRAC 5.8, GOODS: Spitzer IRAC 5.8
Description
Spitzer IRAC medium infrared observations taken in all four IRAC channels in both the north
and south GOODS fields.
Spitzer IRAC GOODS 8.0 micron data, channel 4
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSIRAC 4, GOODS IRAC 4, GOODS IRAC 8.0, GOODS: Spitzer IRAC 8.0
Description
Spitzer IRAC medium infrared observations taken in all four IRAC channels in both the north
and south GOODS fields.
Southern GOODS Field: VLT ISAAC Observations, H band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODS ISAAC H, GOODS: VLT ISAAC H
Description
As part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS),
near-infrared imaging observations of the Chandra Deep Field South (CDF-S)
were carried out in J, H, Ks bands, using the ISAAC instrument mounted at
the Antu Unit Telescope of the VLT at ESO's Cerro Paranal Observatory, Chile.
These data were obtained as part of the ESO Large Programme 168.A-0485 (PI: C. Cesarsky).
Data covering four ISAAC fields in J and Ks bands were also drawn from the ESO programmes 64.O-0643, 66.A-0572 and 68.A-0544 (PI: E.Giallongo),
which were part of the previous data releases.
This data release covers 172.4, 159.6, and 173.1 arcmin2 of the GOODS/CDF-S
region in J, H and Ks respectively. More than 50% of the images reach a 5-sigma depth
for point sources of at least 25.2 mag (J), 24.7 mag (H and Ks) in the AB system ("median depth").
This final GOODS/ISAAC data release accumulates observational data which have
been acquired in 12814 science integrations between October 1999 and January 2007
totaling 1.3 Msec integration time.
[Above adapted from reference Web site.]
SkyView uses the mosaic files provided in this delivery. The Version 1.5 mosaic
is used for the KS band.
| Regime | Infrared |
| Frequency | 183 THz |
| Bandwidth | 168-202 THz |
| Provenance | Data downloaded from VLT archive |
| Copyright | Data freely available |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Resolution | 0.3-0.6" |
| PixelSize | 0.15" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| PixelUnits | ADU/s |
| Epoch | October 1999 to January 2007 |
| Reference |
Paper and
web site.
|
Southern GOODS Field: VLT ISAAC Observations, J band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODS ISAAC J, GOODS: VLT ISAAC J
Description
As part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS),
near-infrared imaging observations of the Chandra Deep Field South (CDF-S)
were carried out in J, H, Ks bands, using the ISAAC instrument mounted at
the Antu Unit Telescope of the VLT at ESO's Cerro Paranal Observatory, Chile.
These data were obtained as part of the ESO Large Programme 168.A-0485 (PI: C. Cesarsky).
Data covering four ISAAC fields in J and Ks bands were also drawn from the ESO programmes 64.O-0643, 66.A-0572 and 68.A-0544 (PI: E.Giallongo),
which were part of the previous data releases.
This data release covers 172.4, 159.6, and 173.1 arcmin2 of the GOODS/CDF-S
region in J, H and Ks respectively. More than 50% of the images reach a 5-sigma depth
for point sources of at least 25.2 mag (J), 24.7 mag (H and Ks) in the AB system ("median depth").
This final GOODS/ISAAC data release accumulates observational data which have
been acquired in 12814 science integrations between October 1999 and January 2007
totaling 1.3 Msec integration time.
[Above adapted from reference Web site.]
SkyView uses the mosaic files provided in this delivery. The Version 1.5 mosaic
is used for the KS band.
| Regime | Infrared |
| Frequency | 245 THz |
| Bandwidth | 225-270 THz |
| Provenance | Data downloaded from VLT archive |
| Copyright | Data freely available |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Resolution | 0.3-0.6" |
| PixelSize | 0.15" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| PixelUnits | ADU/s |
| Epoch | October 1999 to January 2007 |
| Reference |
Paper and
web site.
|
Southern GOODS Field: VLT ISAAC Observations, KS band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODS ISAAC KS, GOODS: VLT ISAAC KS
Description
As part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS),
near-infrared imaging observations of the Chandra Deep Field South (CDF-S)
were carried out in J, H, Ks bands, using the ISAAC instrument mounted at
the Antu Unit Telescope of the VLT at ESO's Cerro Paranal Observatory, Chile.
These data were obtained as part of the ESO Large Programme 168.A-0485 (PI: C. Cesarsky).
Data covering four ISAAC fields in J and Ks bands were also drawn from the ESO programmes 64.O-0643, 66.A-0572 and 68.A-0544 (PI: E.Giallongo),
which were part of the previous data releases.
This data release covers 172.4, 159.6, and 173.1 arcmin2 of the GOODS/CDF-S
region in J, H and Ks respectively. More than 50% of the images reach a 5-sigma depth
for point sources of at least 25.2 mag (J), 24.7 mag (H and Ks) in the AB system ("median depth").
This final GOODS/ISAAC data release accumulates observational data which have
been acquired in 12814 science integrations between October 1999 and January 2007
totaling 1.3 Msec integration time.
[Above adapted from reference Web site.]
SkyView uses the mosaic files provided in this delivery. The Version 1.5 mosaic
is used for the KS band.
| Regime | Infrared |
| Frequency | 137 THz |
| Bandwidth | 125-150 THz |
| Provenance | Data downloaded from VLT archive |
| Copyright | Data freely available |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Resolution | 0.3-0.6" |
| PixelSize | 0.15" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| PixelUnits | ADU/s |
| Epoch | October 1999 to January 2007 |
| Reference |
Paper and
web site.
|
Spitzer MIPS GOODS 24 Micron Data
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSMIPS, GOODS MIPS, GOODS: Spitzer MIPS, GOODS: Spitzer MIPS 24
Description
Spitzer MIPS observations of the GOODS North and South fields in the
24 micron channel.
| Provenance | IRSA, GOODS team |
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 12.5 THz (24 microns) |
| Bandpass | 10.2-14.7 THz |
| Coverage | GOODS regions, 0.01% of sky |
| PixelScale | 1.2" |
| PixelUnits | DN/s |
| Resolution | 5" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2004-5/2004-8 |
| Reference | See
release documentation for data.
|
GOODS NICMOS Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSNICMOS, GNS, GOODS: HST NICMOS
Description
The GOODS NICMOS Survey (GNS) is a 180 orbit Hubble Space Telescope survey
consisting of 60 pointings with the NICMOS-3 near-infrared camera.
Each pointing is centred on a massive galaxy (M* > 1011 Msun)
in the redshift range 1.7 < z < 3,
selected by their optical-to-infrared colours (Papovich+06,Yan+04,Daddi+07)
from the GOODS (Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey) fields.
The positions of the 60 GNS pointings were optimised to contain as
many massive galaxies as possible and are partly overlapping,
covering a total area of about 45 arcmin2.
The field of view of the NICMOS-3 camera is 51.2 ?? 51.2 arcsec with a
resolution of about 0.1 arcsec/pixel.
The PSF has a width of about 0.3 arcsec FWHM.
The limiting magnitude in H band reached at 5?? is HAB = 26.8,
about 2 magnitudes fainter than in available ground based data of the GOODS fields.
[Taken from reference web site.]
| Provenance | University of Nottingham, GNS group. |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 187 THz |
| Bandpass | 167-214 THz |
| Coverage | About 10% of the GOODS fields or about 3 x 10-7 of the sky |
| Resolution | 0.3" |
| PixelScale | 0.1" |
| CoordinateSystem | J2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2007-02-14/2008-04-27 |
| Reference |
Web site
and reference paper
|
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band I
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Hawaii HDF I, Hawaii: HDF I
Description
The Hawaii-HDF-N is an intensive multi-color imaging survey of 0.2 sq.
degrees centered on the HDF-N. Data were collected on the NOAO 4m Mayall telescope,
the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 8.2m Subaru telescope and the
University of Hawaii 2.2m telescope.
Deep U, B, V, R, I, and z' data were obtained over the whole field and deep HK' data over
the Chandra Deep Field North. Details are available in the references.
[Adapted from reference web site.]
Two different images are given in the V band (V0201 and V0401) from observations
separated by about a month that had substantial differences in seeing.
| Provenance | Data downloaded from the reference web site. A formatting
error in the FITS files was corrected.
|
| Copyright | Public Domain. Users are requested to include a reference to
Capak, et al. 2004 when using these data.
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 8 |
| Frequency | 375 THz |
| Bandpass | 358-395 THz |
| Coverage | 0.000005 |
| Resolution | 0.67-1.26" |
| PixelScale | 0.3" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1999/2002 |
| Reference |
2004AJ....127..180C
or the web site.
|
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band Z
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Hawaii HDF Z, Hawaii: HDF Z
Description
The Hawaii-HDF-N is an intensive multi-color imaging survey of 0.2 sq.
degrees centered on the HDF-N. Data were collected on the NOAO 4m Mayall telescope,
the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 8.2m Subaru telescope and the
University of Hawaii 2.2m telescope.
Deep U, B, V, R, I, and z' data were obtained over the whole field and deep HK' data over
the Chandra Deep Field North. Details are available in the references.
[Adapted from reference web site.]
Two different images are given in the V band (V0201 and V0401) from observations
separated by about a month that had substantial differences in seeing.
| Provenance | Data downloaded from the reference web site. A formatting
error in the FITS files was corrected.
|
| Copyright | Public Domain. Users are requested to include a reference to
Capak, et al. 2004 when using these data.
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 8 |
| Frequency | 330 THz |
| Bandpass | 317-345 THz |
| Coverage | 0.000005 |
| Resolution | 0.67-1.26" |
| PixelScale | 0.3" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1999/2002 |
| Reference |
2004AJ....127..180C
or the web site.
|
VLT ISAAC Ks Observations of the Southern Hubble Ultradeep Field
Short name[s] used to specify survey:HUDFISAAC, HUDF: VLT ISAAC Ks
Description
A very deep Ks observation of the Hubble Ultradeep Field. This observation is
approximately 0.6 magnitudes deeper than the GOODS ISAAC Ks image but covers
only small fraction of the area.
| Regime | Infrared |
| Frequency | 137 THz |
| Bandwidth | 125-150 THz |
| Provenance | Data downloaded from VLT archive |
| Copyright | Data freely available |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Resolution | 0.3-0.6" |
| PixelSize | 0.15" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| PixelUnits | ADU/s |
| Reference |
Paper and
Web site
|
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 100 micron
Short name[s] used to specify survey: IRAS100, IRAS 100 micron, IRAS 100, IRAS 100
Description
The IRAS data include all data distributed as part of the IRAS Sky Survey Atlas. Data from the four IRAS bands are shown as individual surveys in SkyView. Users should be aware that IPAC does not
encourage the use of data near the ecliptic plane as they feel that contribution from local cirrus emission is significant.
The data are distributed in sets of 430 maps. Each map covers approximately 12.5x12.5 degrees, and the map centers are offset by 5 degrees so that there is a 2.5 degree overlap.
IPAC has processed to a uniform standard so that excellent mosaics of the maps can be made. Users should be cautious of data in saturated regions. Known problems in the analysis mean that data
values are unlikely to be correct. Note that IPAC has optimized the processing of these data for features of 5' or more although the resolution of the data is closer to the 1.5' pixel size.
There are occasional pixels in the IRAS maps which are given as NULL values. Unless these are explicitly trapped by user software, these data will appear as large negative values. SkyView ignores
these pixels when determining the color scale to display an image.
Essentially the entire sky is covered by the survey. However there are a few regions not surveyed and the data values in these regions are suspect. These are given to users as delivered from IPAC.
| Provenance |
NASA IPAC/Jet Propulsion Laboratory
|
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 3 THz |
| Bandpass | 2.5-3.6 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.025 deg/pix |
| Units | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | 2' |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic(TAN) |
| Equinox | 1950 |
| Epoch | 1983 |
| Reference |
Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS) Explanatory Supplement
|
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 12 micron
Short name[s] used to specify survey: IRAS12, IRAS 12 micron, IRAS 12, IRAS 12
Description
The IRAS data include all data distributed as part of the IRAS Sky Survey Atlas. Data from the four IRAS bands are shown as individual surveys in SkyView. Users should be aware that IPAC does not
encourage the use of data near the ecliptic plane as they feel that contribution from local cirrus emission is significant.
The data are distributed in sets of 430 maps. Each map covers approximately 12.5x12.5 degrees, and the map centers are offset by 5 degrees so that there is a 2.5 degree overlap.
IPAC has processed to a uniform standard so that excellent mosaics of the maps can be made. Users should be cautious of data in saturated regions. Known problems in the analysis mean that data
values are unlikely to be correct. Note that IPAC has optimized the processing of these data for features of 5' or more although the resolution of the data is closer to the 1.5' pixel size.
There are occasional pixels in the IRAS maps which are given as NULL values. Unless these are explicitly trapped by user software, these data will appear as large negative values. SkyView ignores
these pixels when determining the color scale to display an image.
Essentially the entire sky is covered by the survey. However there are a few regions not surveyed and the data values in these regions are suspect. These are given to users as delivered from IPAC.
| Provenance |
NASA IPAC/Jet Propulsion Laboratory
|
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 25 THz |
| Bandpass | 20-35 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.025 deg/pix |
| Units | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | 2' |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic(TAN) |
| Equinox | 1950 |
| Epoch | 1983 |
| Reference |
Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS) Explanatory Supplement
|
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 25 micron
Short name[s] used to specify survey: IRAS25, IRAS 25 micron, IRAS 25, IRAS 25
Description
The IRAS data include all data distributed as part of the IRAS Sky Survey Atlas. Data from the four IRAS bands are shown as individual surveys in SkyView. Users should be aware that IPAC does not
encourage the use of data near the ecliptic plane as they feel that contribution from local cirrus emission is significant.
The data are distributed in sets of 430 maps. Each map covers approximately 12.5x12.5 degrees, and the map centers are offset by 5 degrees so that there is a 2.5 degree overlap.
IPAC has processed to a uniform standard so that excellent mosaics of the maps can be made. Users should be cautious of data in saturated regions. Known problems in the analysis mean that data
values are unlikely to be correct. Note that IPAC has optimized the processing of these data for features of 5' or more although the resolution of the data is closer to the 1.5' pixel size.
There are occasional pixels in the IRAS maps which are given as NULL values. Unless these are explicitly trapped by user software, these data will appear as large negative values. SkyView ignores
these pixels when determining the color scale to display an image.
Essentially the entire sky is covered by the survey. However there are a few regions not surveyed and the data values in these regions are suspect. These are given to users as delivered from IPAC.
| Provenance |
NASA IPAC/Jet Propulsion Laboratory
|
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 12 THz |
| Bandpass | 10-15.8 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.025 deg/pix |
| Units | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | 2' |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic(TAN) |
| Equinox | 1950 |
| Epoch | 1983 |
| Reference |
Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS) Explanatory Supplement
|
IRAS Sky Survey Atlas: 60 micron
Short name[s] used to specify survey: IRAS60, IRAS 60 micron, IRAS 60, IRAS 60
Description
The IRAS data include all data distributed as part of the IRAS Sky Survey Atlas. Data from the four IRAS bands are shown as individual surveys in SkyView. Users should be aware that IPAC does not
encourage the use of data near the ecliptic plane as they feel that contribution from local cirrus emission is significant.
The data are distributed in sets of 430 maps. Each map covers approximately 12.5x12.5 degrees, and the map centers are offset by 5 degrees so that there is a 2.5 degree overlap.
IPAC has processed to a uniform standard so that excellent mosaics of the maps can be made. Users should be cautious of data in saturated regions. Known problems in the analysis mean that data
values are unlikely to be correct. Note that IPAC has optimized the processing of these data for features of 5' or more although the resolution of the data is closer to the 1.5' pixel size.
There are occasional pixels in the IRAS maps which are given as NULL values. Unless these are explicitly trapped by user software, these data will appear as large negative values. SkyView ignores
these pixels when determining the color scale to display an image.
Essentially the entire sky is covered by the survey. However there are a few regions not surveyed and the data values in these regions are suspect. These are given to users as delivered from IPAC.
| Provenance |
NASA IPAC/Jet Propulsion Laboratory
|
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 5 THz |
| Bandpass | 3.75-6.5 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.025 deg/pix |
| Units | MJy/sr |
| Resolution | 2' |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic(TAN) |
| Equinox | 1950 |
| Epoch | 1983 |
| Reference |
Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS) Explanatory Supplement
|
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 100
Short name[s] used to specify survey: IRIS100, IRIS 100 micron,IRIS 100, IRIS 100
Description
The IRIS data is a reprocessing of the IRAS data set
and has the same geometry as the IRAS Sky Survey Atlas (ISSA,
labeled as IRAS nnn micron in SkyView) surveys.
This new generation of IRAS images, called IRIS,
benefits from a better zodiacal light subtraction,
from a calibration and zero level compatible with DIRBE,
and from a better destriping.
At 100 micron the IRIS product is also a significant improvement
from the Schlegel et al. (1998) maps.
IRIS keeps the full ISSA resolution,
it includes well calibrated point sources and the
diffuse emission calibration at scales smaller
than 1 degree was corrected for the variation of
the IRAS detector responsivity with scale and brightness.
The uncertainty on the IRIS calibration and zero level
are dominated by the uncertainty on the DIRBE calibration
and on the accuracy of the zodiacal light model.
More information about the IRIS dataset is available at
the IRIS Web site
whence most of the preceding description came.
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 12
Short name[s] used to specify survey: IRIS12, IRIS 12 micron,IRIS 12, IRIS 12
Description
The IRIS data is a reprocessing of the IRAS data set
and has the same geometry as the IRAS Sky Survey Atlas (ISSA,
labeled as IRAS nnn micron in SkyView) surveys.
This new generation of IRAS images, called IRIS,
benefits from a better zodiacal light subtraction,
from a calibration and zero level compatible with DIRBE,
and from a better destriping.
At 100 micron the IRIS product is also a significant improvement
from the Schlegel et al. (1998) maps.
IRIS keeps the full ISSA resolution,
it includes well calibrated point sources and the
diffuse emission calibration at scales smaller
than 1 degree was corrected for the variation of
the IRAS detector responsivity with scale and brightness.
The uncertainty on the IRIS calibration and zero level
are dominated by the uncertainty on the DIRBE calibration
and on the accuracy of the zodiacal light model.
More information about the IRIS dataset is available at
the IRIS Web site
whence most of the preceding description came.
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 25
Short name[s] used to specify survey: IRIS25, IRIS 25 micron,IRIS 25, IRIS 25
Description
The IRIS data is a reprocessing of the IRAS data set
and has the same geometry as the IRAS Sky Survey Atlas (ISSA,
labeled as IRAS nnn micron in SkyView) surveys.
This new generation of IRAS images, called IRIS,
benefits from a better zodiacal light subtraction,
from a calibration and zero level compatible with DIRBE,
and from a better destriping.
At 100 micron the IRIS product is also a significant improvement
from the Schlegel et al. (1998) maps.
IRIS keeps the full ISSA resolution,
it includes well calibrated point sources and the
diffuse emission calibration at scales smaller
than 1 degree was corrected for the variation of
the IRAS detector responsivity with scale and brightness.
The uncertainty on the IRIS calibration and zero level
are dominated by the uncertainty on the DIRBE calibration
and on the accuracy of the zodiacal light model.
More information about the IRIS dataset is available at
the IRIS Web site
whence most of the preceding description came.
Improved Reprocessing of the IRAS Survey: 60
Short name[s] used to specify survey: IRIS60, IRIS 60 micron,IRIS 60, IRIS 60
Description
The IRIS data is a reprocessing of the IRAS data set
and has the same geometry as the IRAS Sky Survey Atlas (ISSA,
labeled as IRAS nnn micron in SkyView) surveys.
This new generation of IRAS images, called IRIS,
benefits from a better zodiacal light subtraction,
from a calibration and zero level compatible with DIRBE,
and from a better destriping.
At 100 micron the IRIS product is also a significant improvement
from the Schlegel et al. (1998) maps.
IRIS keeps the full ISSA resolution,
it includes well calibrated point sources and the
diffuse emission calibration at scales smaller
than 1 degree was corrected for the variation of
the IRAS detector responsivity with scale and brightness.
The uncertainty on the IRIS calibration and zero level
are dominated by the uncertainty on the DIRBE calibration
and on the accuracy of the zodiacal light model.
More information about the IRIS dataset is available at
the IRIS Web site
whence most of the preceding description came.
Schlegel, Finkbeiner and Davis 100 Micron survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: SFD100m,SFD 100m, SFD 100 Micron
Description
The full sky 100 micron map is a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE
and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point
sources removed. Artifacts from the IRAS scan pattern were removed.
The result of these manipulations is a map with DIRBE-quality calibration
and IR AS resolution.
Schlegel, Finkbeiner and Davis dust map survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey: SFDdust,SFD dust, SFD dust map
Description
The full sky 100 micron map is a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE
and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point
sources removed. Artifacts from the IRAS scan pattern were removed.
The result of these manipulations is a map with DIRBE-quality calibration
and IR AS resolution.
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey H-band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UKIDSS-H,UKIDSSH,UKIDSS H
Description
The UKIDSS survey is the next generation infrared survey, a successor
to 2MASS. It will ultimately cover 7000 square degrees in the
northern sky at both high and low Galactic latitudes and goes about
three magnitudes deeper than 2MASS in the coverage area. Most data is
taken in the J, H and K bands. A Y band is available in some regions.
UKIDSS is comprised of several distinct surveys in different regions of the
sky. Of primary interest to SkyView users (since they have the largest
sky coverage) are the Large Area Survey, the Galactic Plane Survey, and the
Galactic Clusters Survey. There are deep and ultadeep surveys which cover
much smaller fractions of the sky. The planned coverage for the UKIDSS
surveys may be seen at the
UKIDSS survey page. All UKIDSS data products are published by the Wide-Field
Astronomy Unit (WFAU) at the University of Edinburgh through the
WFCAM Science Archive (WSA) which includes
more detailed coverage information for each data release.
SkyView currently uses the DR8 data release except for the Galactic
Plane Survey region where the DR7 is the latest public release. Many thanks to
the WSA team at WFAU for providing an interface to make all the latest
data easily accessed. Note that coverage is not uniform across the different bands so
that at a given point there might be H and K band data, but nothing in the J band.
| Provenance | UKIDSS Project |
| Copyright |
The UKIDSS team requests that text similar
to the following be included when UKIDSS data is used:
The UKIDSS project is defined in
Lawrence et al (2007).
UKIDSS uses the UKIRT Wide Field Camera (WFCAM;
Hewett et al (2006),
and the calibration is described in
Hodgkin et al. (2009).
The pipeline processing and science
archive are described in Irwin et al (2009, in prep)
and
Hambly et al (2008).
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 184 THz |
| Bandpass | 168-201 THz |
| Coverage | 0.17 (7000 square degrees |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Zenithal Polynomial |
| Epoch | 2005-2012 |
| Reference | See the UKIDSS web site or
Lawrence et al (2007).
|
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey J-band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UKIDSS-J,UKIDSSJ,UKIDSS J
Description
The UKIDSS survey is the next generation infrared survey, a successor
to 2MASS. It will ultimately cover 7000 square degrees in the
northern sky at both high and low Galactic latitudes and goes about
three magnitudes deeper than 2MASS in the coverage area. Most data is
taken in the J, H and K bands. A Y band is available in some regions.
UKIDSS is comprised of several distinct surveys in different regions of the
sky. Of primary interest to SkyView users (since they have the largest
sky coverage) are the Large Area Survey, the Galactic Plane Survey, and the
Galactic Clusters Survey. There are deep and ultadeep surveys which cover
much smaller fractions of the sky. The planned coverage for the UKIDSS
surveys may be seen at the
UKIDSS survey page. All UKIDSS data products are published by the Wide-Field
Astronomy Unit (WFAU) at the University of Edinburgh through the
WFCAM Science Archive (WSA) which includes
more detailed coverage information for each data release.
SkyView currently uses the DR8 data release except for the Galactic
Plane Survey region where the DR7 is the latest public release. Many thanks to
the WSA team at WFAU for providing an interface to make all the latest
data easily accessed. Note that coverage is not uniform across the different bands so
that at a given point there might be H and K band data, but nothing in the J band.
| Provenance | UKIDSS Project |
| Copyright |
The UKIDSS team requests that text similar
to the following be included when UKIDSS data is used:
The UKIDSS project is defined in
Lawrence et al (2007).
UKIDSS uses the UKIRT Wide Field Camera (WFCAM;
Hewett et al (2006),
and the calibration is described in
Hodgkin et al. (2009).
The pipeline processing and science
archive are described in Irwin et al (2009, in prep)
and
Hambly et al (2008).
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 240 THz |
| Bandpass | 225-260 THz |
| Coverage | 0.17 (7000 square degrees |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Zenithal Polynomial |
| Epoch | 2005-2012 |
| Reference | See the UKIDSS web site or
Lawrence et al (2007).
|
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey K-band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UKIDSS-K,UKIDSSK,UKIDSS K
Description
The UKIDSS survey is the next generation infrared survey, a successor
to 2MASS. It will ultimately cover 7000 square degrees in the
northern sky at both high and low Galactic latitudes and goes about
three magnitudes deeper than 2MASS in the coverage area. Most data is
taken in the J, H and K bands. A Y band is available in some regions.
UKIDSS is comprised of several distinct surveys in different regions of the
sky. Of primary interest to SkyView users (since they have the largest
sky coverage) are the Large Area Survey, the Galactic Plane Survey, and the
Galactic Clusters Survey. There are deep and ultadeep surveys which cover
much smaller fractions of the sky. The planned coverage for the UKIDSS
surveys may be seen at the
UKIDSS survey page. All UKIDSS data products are published by the Wide-Field
Astronomy Unit (WFAU) at the University of Edinburgh through the
WFCAM Science Archive (WSA) which includes
more detailed coverage information for each data release.
SkyView currently uses the DR8 data release except for the Galactic
Plane Survey region where the DR7 is the latest public release. Many thanks to
the WSA team at WFAU for providing an interface to make all the latest
data easily accessed. Note that coverage is not uniform across the different bands so
that at a given point there might be H and K band data, but nothing in the J band.
| Provenance | UKIDSS Project |
| Copyright |
The UKIDSS team requests that text similar
to the following be included when UKIDSS data is used:
The UKIDSS project is defined in
Lawrence et al (2007).
UKIDSS uses the UKIRT Wide Field Camera (WFCAM;
Hewett et al (2006),
and the calibration is described in
Hodgkin et al. (2009).
The pipeline processing and science
archive are described in Irwin et al (2009, in prep)
and
Hambly et al (2008).
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 136 THz |
| Bandpass | 126-148 THz |
| Coverage | 0.17 (7000 square degrees |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Zenithal Polynomial |
| Epoch | 2005-2012 |
| Reference | See the UKIDSS web site or
Lawrence et al (2007).
|
UKIRT Infrared Deep Survey Y-band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UKIDSS-Y,UKIDSSY,UKIDSS Y
Description
The UKIDSS survey is the next generation infrared survey, a successor
to 2MASS. It will ultimately cover 7000 square degrees in the
northern sky at both high and low Galactic latitudes and goes about
three magnitudes deeper than 2MASS in the coverage area. Most data is
taken in the J, H and K bands. A Y band is available in some regions.
UKIDSS is comprised of several distinct surveys in different regions of the
sky. Of primary interest to SkyView users (since they have the largest
sky coverage) are the Large Area Survey, the Galactic Plane Survey, and the
Galactic Clusters Survey. There are deep and ultadeep surveys which cover
much smaller fractions of the sky. The planned coverage for the UKIDSS
surveys may be seen at the
UKIDSS survey page. All UKIDSS data products are published by the Wide-Field
Astronomy Unit (WFAU) at the University of Edinburgh through the
WFCAM Science Archive (WSA) which includes
more detailed coverage information for each data release.
SkyView currently uses the DR8 data release except for the Galactic
Plane Survey region where the DR7 is the latest public release. Many thanks to
the WSA team at WFAU for providing an interface to make all the latest
data easily accessed. Note that coverage is not uniform across the different bands so
that at a given point there might be H and K band data, but nothing in the J band.
| Provenance | UKIDSS Project |
| Copyright |
The UKIDSS team requests that text similar
to the following be included when UKIDSS data is used:
The UKIDSS project is defined in
Lawrence et al (2007).
UKIDSS uses the UKIRT Wide Field Camera (WFCAM;
Hewett et al (2006),
and the calibration is described in
Hodgkin et al. (2009).
The pipeline processing and science
archive are described in Irwin et al (2009, in prep)
and
Hambly et al (2008).
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 290 THz |
| Bandpass | 280-310 THz |
| Coverage | 0.17 (7000 square degrees |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Zenithal Polynomial |
| Epoch | 2005-2012 |
| Reference | See the UKIDSS web site or
Lawrence et al (2007).
|
HIPS Survey:Ultradeep survey using the ESO Vista surveys telescope: Band H
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UltraVista-H
Description
UltraVISTA is an Ultra Deep, near-infrared survey with the new VISTA surveys telescope of the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Over the course of 5 years, UltraVISTA will
repeatedly image the COSMOS field in 5 bands covering a 1.5deg^2 field.\n \nESO acknowledgment: Data products from observations made with ESO Telescopes at the La Silla Paranal Observatories under
ESO programme ID 179.A-2005 and on data products produced by TERAPIX and the Cambridge Astronomy Survey Unit on behalf of the UltraVISTA consortium. This survey description was generated
automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | Origin unknown |
| Copyright | ULTRAVISTA consortium - |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Coverage | 4.527 x 10-5 (near J2000 coordinates: [150., 1.58]) |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | see McCracken et al. 2012A&A...544A.156M |
| Epoch | |
HIPS Survey:Ultradeep survey using the ESO Vista surveys telescope: Band J
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UltraVista-J
Description
UltraVISTA is an Ultra Deep, near-infrared survey with the new VISTA surveys telescope of the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Over the course of 5 years, UltraVISTA will
repeatedly image the COSMOS field in 5 bands covering a 1.5deg^2 field.\n \nESO acknowledgment: Data products from observations made with ESO Telescopes at the La Silla Paranal Observatories under
ESO programme ID 179.A-2005 and on data products produced by TERAPIX and the Cambridge Astronomy Survey Unit on behalf of the UltraVISTA consortium. This survey description was generated
automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | Origin unknown |
| Copyright | ULTRAVISTA consortium - |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Coverage | 4.516 x 10-5 (near J2000 coordinates: [150., 1.58]) |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | see McCracken et al. 2012A&A...544A.156M |
| Epoch | |
HIPS Survey:Ultradeep survey using the ESO Vista surveys telescope: Band Ks
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UltraVista-Ks
Description
UltraVISTA is an Ultra Deep, near-infrared survey with the new VISTA surveys telescope of the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Over the course of 5 years, UltraVISTA will
repeatedly image the COSMOS field in 5 bands covering a 1.5deg^2 field.\n \nESO acknowledgment: Data products from observations made with ESO Telescopes at the La Silla Paranal Observatories under
ESO programme ID 179.A-2005 and on data products produced by TERAPIX and the Cambridge Astronomy Survey Unit on behalf of the UltraVISTA consortium. This survey description was generated
automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | Origin unknown |
| Copyright | ULTRAVISTA consortium - |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Coverage | 4.523 x 10-5 (near J2000 coordinates: [150., 1.58]) |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | see McCracken et al. 2012A&A...544A.156M |
| Epoch | |
HIPS Survey:Ultradeep survey using the ESO Vista surveys telescope: Band NB118
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UltraVista-NB118
Description
UltraVISTA is an Ultra Deep, near-infrared survey with the new VISTA surveys telescope of the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Over the course of 5 years, UltraVISTA will
repeatedly image the COSMOS field in 5 bands covering a 1.5deg^2 field.\n \nESO acknowledgment: Data products from observations made with ESO Telescopes at the La Silla Paranal Observatories under
ESO programme ID 179.A-2005 and on data products produced by TERAPIX and the Cambridge Astronomy Survey Unit on behalf of the UltraVISTA consortium. This survey description was generated
automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | Origin unknown |
| Copyright | ULTRAVISTA consortium - |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Coverage | 2.891 x 10-5 (near J2000 coordinates: [150., 1.58]) |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | see McCracken et al. 2012A&A...544A.156M |
| Epoch | |
HIPS Survey:Ultradeep survey using the ESO Vista surveys telescope: Band Y
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UltraVista-Y
Description
UltraVISTA is an Ultra Deep, near-infrared survey with the new VISTA surveys telescope of the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Over the course of 5 years, UltraVISTA will
repeatedly image the COSMOS field in 5 bands covering a 1.5deg^2 field.\n \nESO acknowledgment: Data products from observations made with ESO Telescopes at the La Silla Paranal Observatories under
ESO programme ID 179.A-2005 and on data products produced by TERAPIX and the Cambridge Astronomy Survey Unit on behalf of the UltraVISTA consortium. This survey description was generated
automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | Origin unknown |
| Copyright | ULTRAVISTA consortium - |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Coverage | 4.513 x 10-5 (near J2000 coordinates: [150., 1.58]) |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | see McCracken et al. 2012A&A...544A.156M |
| Epoch | |
WISE 3.4 Micron All-Sky Survey>: All-WISE data release
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Wise W1,Wise 3.4, WiseW1, Wise3.4
Description
From the WISE mission site:.
NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mapped the
sky at 3.4, 4.6, 12 and 22 micrometers in 2010 with an
angular resolution of 6.1", 6.4", 6.5" and 12.0" in the four bands.
WISE achieved a 5 sigma point source sensitivities better and 0.08, 0.11
1 and 6 mJy in unconfused regions on the ecliptic in the four
bands. Sensitivity improves toward the ecliptic poles due to denser
coverage and lower zodaical background.
The WISE All-WISE
includes all data taking during the WISE full cryogenic phase, from January 7, 2010 to August 6, 2010, that were processed
with improved calibrations and reduction algorithms and combines this with the NEOWISE postcryogenic
survey to form the most comprehensive view of the full mid-infrared sky.
bibcode=1995ApJ...451..564V,2010ApJ...713..912W
SkyView includes the four WISE bands as separate surveys. Many non-image
data products are available at the WISE site. Note that WISE data is
distributed in relatively large (>50 MB) image files. When SkyView generates
an image for a part of the sky where it has not yet cached the
data from the IPAC server there may be a delay as full tiles are downloaded
even when only a small fraction of a tile is needed. Images
in cached regions, are generated much faster. Access to
the WISE data uses the VO SIA interface maintained at IPAC. Even when
data is cached, the SIA service must still be available for successful
queries.
| Provenance | WISE Archive (IRSA/IPAC) |
| Copyright |
WISE data is in the public domain but publications are requested to include the
statment:
This publication makes use of data products from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer,
which is a joint project of the University of California, Los Angeles,
and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology,
funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 88 THz (3.4 micrometers) |
| Bandpass | 78-107 THz |
| Coverage | All sky |
| PixelScale | 1.375" |
| PixelUnits | DN |
| Resolution | 6.1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Sine |
| Epoch | January 2010 to February 2011 |
| Reference |
The main All-Sky survey is described in Wright et al (2010)
The NEOWISE data is discussed in Mainzer et al.
|
WISE 4.6 Micron All-Sky Survey>: All-WISE data release
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Wise W2,Wise 4.6, WiseW2, Wise4.6
Description
From the WISE mission site:.
NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mapped the
sky at 3.4, 4.6, 12 and 22 micrometers in 2010 with an
angular resolution of 6.1", 6.4", 6.5" and 12.0" in the four bands.
WISE achieved a 5 sigma point source sensitivities better and 0.08, 0.11
1 and 6 mJy in unconfused regions on the ecliptic in the four
bands. Sensitivity improves toward the ecliptic poles due to denser
coverage and lower zodaical background.
The WISE All-WISE
includes all data taking during the WISE full cryogenic phase, from January 7, 2010 to August 6, 2010, that were processed
with improved calibrations and reduction algorithms and combines this with the NEOWISE postcryogenic
survey to form the most comprehensive view of the full mid-infrared sky.
bibcode=1995ApJ...451..564V,2010ApJ...713..912W
SkyView includes the four WISE bands as separate surveys. Many non-image
data products are available at the WISE site. Note that WISE data is
distributed in relatively large (>50 MB) image files. When SkyView generates
an image for a part of the sky where it has not yet cached the
data from the IPAC server there may be a delay as full tiles are downloaded
even when only a small fraction of a tile is needed. Images
in cached regions, are generated much faster. Access to
the WISE data uses the VO SIA interface maintained at IPAC. Even when
data is cached, the SIA service must still be available for successful
queries.
| Provenance | WISE Archive (IRSA/IPAC) |
| Copyright |
WISE data is in the public domain but publications are requested to include the
statment:
This publication makes use of data products from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer,
which is a joint project of the University of California, Los Angeles,
and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology,
funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 65 THz (4.6 micrometers) |
| Bandpass | 58-74 THz |
| Coverage | All sky |
| PixelScale | 1.375" |
| PixelUnits | DN |
| Resolution | 6.4" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Sine |
| Epoch | January 2010 to February 2011 |
| Reference |
The main All-Sky survey is described in Wright et al (2010)
The NEOWISE data is discussed in Mainzer et al.
|
WISE 12 Micron All-Sky Survey>: All-WISE data release
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Wise W3,Wise 12, WiseW3, Wise12
Description
From the WISE mission site:.
NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mapped the
sky at 3.4, 4.6, 12 and 22 micrometers in 2010 with an
angular resolution of 6.1", 6.4", 6.5" and 12.0" in the four bands.
WISE achieved a 5 sigma point source sensitivities better and 0.08, 0.11
1 and 6 mJy in unconfused regions on the ecliptic in the four
bands. Sensitivity improves toward the ecliptic poles due to denser
coverage and lower zodaical background.
The WISE All-WISE
includes all data taking during the WISE full cryogenic phase, from January 7, 2010 to August 6, 2010, that were processed
with improved calibrations and reduction algorithms and combines this with the NEOWISE postcryogenic
survey to form the most comprehensive view of the full mid-infrared sky.
bibcode=1995ApJ...451..564V,2010ApJ...713..912W
SkyView includes the four WISE bands as separate surveys. Many non-image
data products are available at the WISE site. Note that WISE data is
distributed in relatively large (>50 MB) image files. When SkyView generates
an image for a part of the sky where it has not yet cached the
data from the IPAC server there may be a delay as full tiles are downloaded
even when only a small fraction of a tile is needed. Images
in cached regions, are generated much faster. Access to
the WISE data uses the VO SIA interface maintained at IPAC. Even when
data is cached, the SIA service must still be available for successful
queries.
| Provenance | WISE Archive (IRSA/IPAC) |
| Copyright |
WISE data is in the public domain but publications are requested to include the
statment:
This publication makes use of data products from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer,
which is a joint project of the University of California, Los Angeles,
and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology,
funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 25 THz (12 micrometers) |
| Bandpass | 18-40 THz |
| Coverage | All sky |
| PixelScale | 1.375" |
| PixelUnits | DN |
| Resolution | 6.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Sine |
| Epoch | January 2010 to February 2011 |
| Reference |
The main All-Sky survey is described in Wright et al (2010)
The NEOWISE data is discussed in Mainzer et al.
|
WISE 22 Micron All-Sky Survey>: All-WISE data release
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Wise W4,Wise 22, WiseW4, Wise22
Description
From the WISE mission site:.
NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mapped the
sky at 3.4, 4.6, 12 and 22 micrometers in 2010 with an
angular resolution of 6.1", 6.4", 6.5" and 12.0" in the four bands.
WISE achieved a 5 sigma point source sensitivities better and 0.08, 0.11
1 and 6 mJy in unconfused regions on the ecliptic in the four
bands. Sensitivity improves toward the ecliptic poles due to denser
coverage and lower zodaical background.
The WISE All-WISE
includes all data taking during the WISE full cryogenic phase, from January 7, 2010 to August 6, 2010, that were processed
with improved calibrations and reduction algorithms and combines this with the NEOWISE postcryogenic
survey to form the most comprehensive view of the full mid-infrared sky.
bibcode=1995ApJ...451..564V,2010ApJ...713..912W
SkyView includes the four WISE bands as separate surveys. Many non-image
data products are available at the WISE site. Note that WISE data is
distributed in relatively large (>50 MB) image files. When SkyView generates
an image for a part of the sky where it has not yet cached the
data from the IPAC server there may be a delay as full tiles are downloaded
even when only a small fraction of a tile is needed. Images
in cached regions, are generated much faster. Access to
the WISE data uses the VO SIA interface maintained at IPAC. Even when
data is cached, the SIA service must still be available for successful
queries.
| Provenance | WISE Archive (IRSA/IPAC) |
| Copyright |
WISE data is in the public domain but publications are requested to include the
statment:
This publication makes use of data products from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer,
which is a joint project of the University of California, Los Angeles,
and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology,
funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
|
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 14 THz (22 micrometers) |
| Bandpass | 12-15 THz |
| Coverage | All sky |
| PixelScale | 1.375" |
| PixelUnits | DN |
| Resolution | 12" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Sine |
| Epoch | January 2010 to February 2011 |
| Reference |
The main All-Sky survey is described in Wright et al (2010)
The NEOWISE data is discussed in Mainzer et al.
|
WMAP Nine Year K-Band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:WMAPK,WMAP K,WMAP-K
Description
These data represent the 9 year co-added maps for each of the five frequency bands
in the WMAP dataset.
The original data are available at the LAMBDA archive.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the WMAP data.
| Provenance | WMAP Mission/LAMBDA archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 23 GHz |
| Bandpass | 19-25 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 7.5' |
| PixelUnits | millikelvins |
| Resolution | 0.91 degrees |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2000-2009 |
| Reference |
LAMBDA archive
or Nine year results
|
WMAP Nine Year Ka-Band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:WMAPKa,WMAP Ka,WMAP-Ka
Description
These data represent the 9 year co-added maps for each of the five frequency bands
in the WMAP dataset.
The original data are available at the LAMBDA archive.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the WMAP data.
| Provenance | WMAP Mission/LAMBDA archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 33 GHz |
| Bandpass | 29-37 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 7.5' |
| PixelUnits | millikelvins |
| Resolution | 0.69 degrees |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2000-2009 |
| Reference |
LAMBDA archive
or Nine year results
|
WMAP Nine Year Q-Band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:WMAPQ,WMAP Q,WMAP-Q
Description
These data represent the 9 year co-added maps for each of the five frequency bands
in the WMAP dataset.
The original data are available at the LAMBDA archive.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the WMAP data.
| Provenance | WMAP Mission/LAMBDA archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 40 GHz |
| Bandpass | 35-45 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 7.5' |
| PixelUnits | millikelvins |
| Resolution | 0.54 degrees |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2000-2009 |
| Reference |
LAMBDA archive
or Nine year results
|
WMAP Nine Year V-Band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:WMAPV,WMAP V,WMAP-V
Description
These data represent the 9 year co-added maps for each of the five frequency bands
in the WMAP dataset.
The original data are available at the LAMBDA archive.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the WMAP data.
| Provenance | WMAP Mission/LAMBDA archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 61 GHz |
| Bandpass | 54-68 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 7.5' |
| PixelUnits | millikelvins |
| Resolution | 0.37 degrees |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2000-2009 |
| Reference |
LAMBDA archive
or Nine year results
|
WMAP Nine Year W-Band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:WMAPW,WMAP W,WMAP-W
Description
These data represent the 9 year co-added maps for each of the five frequency bands
in the WMAP dataset.
The original data are available at the LAMBDA archive.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the WMAP data.
| Provenance | WMAP Mission/LAMBDA archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 94 GHz |
| Bandpass | 84-104 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 7.5' |
| PixelUnits | millikelvins |
| Resolution | 0.26 degrees |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2000-2009 |
| Reference |
LAMBDA archive
or Nine year results
|
WMAP Nine Year Galaxy Removed
Short name[s] used to specify survey:WMAPILC,WMAP ILC,WMAP
Description
These survey represents a combination of the 9-year data combined
in a way that is intended
to minimize the contribution from the galaxy. The data measure the temperature deviation
from a uniform black body.
The original data are available at the LAMBDA archive.
The original data are stored in HEALPix pixels. SkyView treats HEALPix as a standard
projection but assumes that the HEALPix data is in a projection plane with a rotation of -45 degrees.
The rotation transforms the HEALPix pixels from diamonds to squares so that the boundaries of the
pixels are treated properly. The special HealPixImage class is used so that SkyView can use
the HEALPix FITS files directly. The HealPixImage simulates a rectangular image but
translates the pixels from that image to the nested HEALPix structure that is used
by the WMAP data.
| Provenance | WMAP Mission/LAMBDA archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Infrared |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 23-200 GHz |
| Coverage | AllSky |
| PixelScale | 7.5' |
| PixelUnits | millikelvins |
| Resolution | 0.88 degree beam size |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | HEALPix |
| Epoch | 2000-2009 |
| Reference |
LAMBDA archive
or Seven year results
|
Optical surveys
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS D g
Short name[s] used to specify survey:CFHTLS-D-g
Description
The Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey is a 5-year program carried out jointly by the Canadian and French agencies. It will use the Megaprime/Megacam instrument mounted at
prime focus of the 3.6m CFH telescope during the period 2003-2008. The Deep survey concerns 4 patchsof 1 square-degree. All will be observed in u,g,r,i and z, with very lon gexposure time
This survey description was generated automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | CFHT
HiPS generated by CDS |
| Copyright | (c) CFH - powered by Terapix - healpixed by CDS
The CFHT Science Archive contains data and meta-data provided by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 647.3 THz |
| Coverage | 1.044E-4 |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | 2.795E-5 Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | 2012yCat.2317....0H, Also |
| Epoch | 2006-06-01 to 2009-01-01 |
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS D i
Short name[s] used to specify survey:CFHTLS-D-i
Description
The Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey is a 5-year program carried out jointly by the Canadian and French agencies. It will use the Megaprime/Megacam instrument mounted at
prime focus of the 3.6m CFH telescope during the period 2003-2008. The Deep survey concerns 4 patchsof 1 square-degree. All will be observed in u,g,r,i and z, with very lon gexposure time
This survey description was generated automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | CFHT
HiPS generated by CDS |
| Copyright | (c) CFH - powered by Terapix - healpixed by CDS
The CFHT Science Archive contains data and meta-data provided by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 401.5 THz |
| Coverage | 1.044E-4 |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | 2.795E-5 Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | 2012yCat.2317....0H, Also |
| Epoch | 2006-06-01 to 2009-01-01 |
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS D r
Short name[s] used to specify survey:CFHTLS-D-r
Description
The Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey is a 5-year program carried out jointly by the Canadian and French agencies. It will use the Megaprime/Megacam instrument mounted at
prime focus of the 3.6m CFH telescope during the period 2003-2008. The Deep survey concerns 4 patchsof 1 square-degree. All will be observed in u,g,r,i and z, with very lon gexposure time
This survey description was generated automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | CFHT
HiPS generated by CDS |
| Copyright | (c) CFH - powered by Terapix - healpixed by CDS
The CFHT Science Archive contains data and meta-data provided by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 486.7 THz |
| Coverage | 1.044E-4 |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | 2.795E-5 Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | 2012yCat.2317....0H, Also |
| Epoch | 2006-06-01 to 2009-01-01 |
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS D u
Short name[s] used to specify survey:CFHTLS-D-u
Description
The Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey is a 5-year program carried out jointly by the Canadian and French agencies. It will use the Megaprime/Megacam instrument mounted at
prime focus of the 3.6m CFH telescope during the period 2003-2008. The Deep survey concerns 4 patchsof 1 square-degree. All will be observed in u,g,r,i and z, with very lon gexposure time
This survey description was generated automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | CFHT
HiPS generated by CDS |
| Copyright | (c) CFH - powered by Terapix - healpixed by CDS
The CFHT Science Archive contains data and meta-data provided by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 803.0 THz |
| Coverage | 1.044E-4 |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | 2.795E-5 Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | 2012yCat.2317....0H, Also |
| Epoch | 2006-06-01 to 2009-01-01 |
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS D z
Short name[s] used to specify survey:CFHTLS-D-z
Description
The Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey is a 5-year program carried out jointly by the Canadian and French agencies. It will use the Megaprime/Megacam instrument mounted at
prime focus of the 3.6m CFH telescope during the period 2003-2008. The Deep survey concerns 4 patchsof 1 square-degree. All will be observed in u,g,r,i and z, with very lon gexposure time
This survey description was generated automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | CFHT
HiPS generated by CDS |
| Copyright | (c) CFH - powered by Terapix - healpixed by CDS
The CFHT Science Archive contains data and meta-data provided by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 337.3 THz |
| Coverage | 1.044E-4 |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | 2.795E-5 Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | 2012yCat.2317....0H, Also |
| Epoch | 2006-06-01 to 2009-01-01 |
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS W g
Short name[s] used to specify survey:CFHTLS-W-g
Description
The Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey is a 5-year program carried out jointly by the Canadian and French agencies. It will use the Megaprime/Megacam instrument mounted at
prime focus of the 3.6m CFH telescope during the period 2003-2008. The WIDE survey concerns 4 patchs, 3 of about 7x7 square-degrees each and 1 of about 4x4 square-degrees. All will be observed in
u,g,r,i and z, with about 1 hr exposure time per filter This survey description was generated automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | CFHT
HiPS generated by CDS |
| Copyright | (c) CFH - powered by Terapix - healpixed by CDS
The CFHT Science Archive contains data and meta-data provided by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 647.3 THz |
| Coverage | 0.003731 |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | 5.591E-5 Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | 2012yCat.2317....0H, Also |
| Epoch | 2006-06-01 to 2009-01-01 |
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS W i
Short name[s] used to specify survey:CFHTLS-W-i
Description
The Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey is a 5-year program carried out jointly by the Canadian and French agencies. It will use the Megaprime/Megacam instrument mounted at
prime focus of the 3.6m CFH telescope during the period 2003-2008. The WIDE survey concerns 4 patchs, 3 of about 7x7 square-degrees each and 1 of about 4x4 square-degrees. All will be observed in
u,g,r,i and z, with about 1 hr exposure time per filter This survey description was generated automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | CFHT
HiPS generated by CDS |
| Copyright | (c) CFH - powered by Terapix - healpixed by CDS
The CFHT Science Archive contains data and meta-data provided by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 401.5 THz |
| Coverage | 0.003731 |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | 5.591E-5 Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | 2012yCat.2317....0H, Also |
| Epoch | 2006-06-01 to 2009-01-01 |
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS W r
Short name[s] used to specify survey:CFHTLS-W-r
Description
The Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey is a 5-year program carried out jointly by the Canadian and French agencies. It will use the Megaprime/Megacam instrument mounted at
prime focus of the 3.6m CFH telescope during the period 2003-2008. The WIDE survey concerns 4 patchs, 3 of about 7x7 square-degrees each and 1 of about 4x4 square-degrees. All will be observed in
u,g,r,i and z, with about 1 hr exposure time per filter This survey description was generated automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | CFHT
HiPS generated by CDS |
| Copyright | (c) CFH - powered by Terapix - healpixed by CDS
The CFHT Science Archive contains data and meta-data provided by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 486.7 THz |
| Coverage | 0.003731 |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | 5.591E-5 Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | 2012yCat.2317....0H, Also |
| Epoch | 2006-06-01 to 2009-01-01 |
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS W u
Short name[s] used to specify survey:CFHTLS-W-u
Description
The Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey is a 5-year program carried out jointly by the Canadian and French agencies. It will use the Megaprime/Megacam instrument mounted at
prime focus of the 3.6m CFH telescope during the period 2003-2008. The WIDE survey concerns 4 patchs, 3 of about 7x7 square-degrees each and 1 of about 4x4 square-degrees. All will be observed in
u,g,r,i and z, with about 1 hr exposure time per filter This survey description was generated automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | CFHT
HiPS generated by CDS |
| Copyright | (c) CFH - powered by Terapix - healpixed by CDS
The CFHT Science Archive contains data and meta-data provided by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 803.0 THz |
| Coverage | 0.003731 |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | 5.591E-5 Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | 2012yCat.2317....0H, Also |
| Epoch | 2006-06-01 to 2009-01-01 |
HIPS Survey:CFHTLS W z
Short name[s] used to specify survey:CFHTLS-W-z
Description
The Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey is a 5-year program carried out jointly by the Canadian and French agencies. It will use the Megaprime/Megacam instrument mounted at
prime focus of the 3.6m CFH telescope during the period 2003-2008. The WIDE survey concerns 4 patchs, 3 of about 7x7 square-degrees each and 1 of about 4x4 square-degrees. All will be observed in
u,g,r,i and z, with about 1 hr exposure time per filter This survey description was generated automatically from the HiPS property file
| Provenance | CFHT
HiPS generated by CDS |
| Copyright | (c) CFH - powered by Terapix - healpixed by CDS
The CFHT Science Archive contains data and meta-data provided by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 337.3 THz |
| Coverage | 0.003731 |
| Resolution | |
| PixelScale | 5.591E-5 Hierarchical |
| PixelUnits | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HiPS |
| Reference | 2012yCat.2317....0H, Also |
| Epoch | 2006-06-01 to 2009-01-01 |
Original Digitized Sky Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:DSSOld,Digitized Sky Survey,DSS
Description
This survey comprises the compressed digitization of the Southern Sky
Survey and the Palomar Sky Survey E plates as distributed on CD ROM
by the Space Telescope Science Institute. Coverage of the entire
sky is included.
This survey consists of the digititized Southern Sky Survey conducted
at the UK Southern Schmidt Survey Group by the Royal Observatory, Edinburgh
(prior to 1988) and the Anglo-Australian Observatory (since 1988)
Additional plates covering regions with bright objects are also
included.
The plates were digitized at the Space Telescope Science Institute
and compressed using algorithms developed by R.White. These
data are distributed on a set of 101 CD-ROMs.
The following data are included:
- Southern hemisphere
-
SERC Southern Sky Survey and the SERC J Equatorial extension.
These are typically deep, 3600s, IIIa-J exposures with a GG395 filter.
Also included are 94 short (1200s) V exposures typically at Galactic
latitudes below 15°. Special exposures are included in
the regions of the Magellenic clouds.
- Northern hemisphere
- The northern hemisphere is covered by 644 plates from the POSS E
survey. A special exposure of the M31 region that is distributed on
the CD ROMs is not used in SkyView .
| Provenance | Data taken by ROE and AAO, CalTech, Compression
and distribution by Space Telescope Science Institute.
|
| Copyright |
STScI, ROE, AAO, UK-PPARC, CalTech, National Geographic Society.
Full copyright notice
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 560 THz (Different plates have different bands: J or E with a few exceptions) |
| Bandpass | 422-965 THz (individual plates have smaller bandpass) |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 1.7" |
| Units | Scaled densities |
| Resolution | Depends on plate. Typically 2" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Schmidt (distorted Tangent plane projection) |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1945-1958 north, 1980-1999 south |
| Reference |
Lasker, et al., 1990, A.J. 99
Characteristics of the DSS surveys are summarized in
this document.
|
First Digitized Sky Survey: Blue Plates
Short name[s] used to specify survey: DSS1B,DSS1 Blue
Description
This survey uses the POSS1 Blue plates.
| Provenance | Data taken by CalTech, Compression
and distribution by Space Telescope Science Institute.
|
| Copyright |
STScI, CalTech, National Geographic Society.
Full copyright notice
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 638 THz |
| Bandpass | 517-967 THz |
| Coverage | North of -30 degrees declination |
| PixelScale | 1.7" |
| Units | Scaled densities |
| Resolution | Depends on plate. Typically 2" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Schmidt (distorted Tangent plane projection) |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1975-1988 |
| Reference |
Lasker, et al., 1990, A.J. 99
|
First Digitized Sky Survey: Red Plates
Short name[s] used to specify survey:DSS1R,DSS1 Red
Description
This survey is the POSS1 Red plates from the original POSS survey.
It covers the sky north of -30 degrees declination.
| Provenance | Data taken by CalTech Compression
and distribution by Space Telescope Science Institute.
|
| Copyright |
CalTech, National Geographic Society.
Full copyright notice
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 461 THz |
| Bandpass | 437-491 THz |
| Coverage | North of -30 degrees declination |
| PixelScale | 1.7" |
| Units | Scaled densities |
| Resolution | Depends on plate. Typically 2" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Schmidt (distorted Tangent plane projection) |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1945-1958 |
| Reference |
Lasker, et al., 1990, A.J. 99
Characteristics of the DSS surveys are summarized in
this document.
|
2nd Digitized Sky Survey (Blue)
Short name[s] used to specify survey:DSS2B, DSS2 Blue
Description
The native projection of these data is described as a high-order polynomial
distortion of a gnomonic projection using the same terms as the DSS.
| Provenance | Data taken by ROE, AAO, and CalTech, Compression
and distribution by Space Telescope Science Institute.
|
| Copyright |
There are multiple copyright holders depending
upon the source plate or plates.
See full copyright
notices The coverage link below describes the
coverage for each element of the surveys when the original plate used is
not included in the SkyView files. |
.
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 637 THz |
| Bandpass | 517-967 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky, but some data not yet be processed. |
| PixelScale | 1" in the north 1.7" in the south |
| PixelUnits | Pixel values are given as scaled densities |
| Resolution | Depends on plate. Typically better than 2". |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Schmidt |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1950-1998 |
| Reference |
Some information on the DSS2 is given in
McLean, 2000, The Second Generation Guide Star Catalog.
Characteristics of the DSS surveys are summarized in
this document.
|
2nd Digitized Sky Survey (Red)
Short name[s] used to specify survey:DSS2R, DSS2 Red
Description
This survey comprises the POSS2 Red data from the north and
rescanned 1" scans of UKSTU red data in the south.
The native projection of these data is described as a high-order polynomial
distortion of a gnomonic projection using the same terms as the DSS.
| Provenance | Data taken by ROE, AAO, and CalTech, Compression
and distribution by Space Telescope Science Institute.
|
| Copyright |
There are multiple copyright holders depending
upon the source plate or plates.
See full copyright
notices The coverage link below describes the
coverage for each element of the surveys when the original plate used is
not included in the SkyView files. |
.
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 445 THz |
| Bandpass | 422-564 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky, but some data not yet be processed. |
| PixelScale | 1" |
| PixelUnits | Pixel values are given as scaled densities |
| Resolution | Depends on plate. Typically 3". |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Schmidt |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1984-1999 |
| Reference |
Some information on the DSS2 is given in
McLean, 2000, The Second Generation Guide Star Catalog.
Characteristics of the DSS surveys are summarized in
this document.
|
GOODS HST ACS B Filter
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODS ACS B,GOODS: HST ACS B,GOODS_ACS_B
Description
This is a SkyView rendering of the HST ACS data as described in
the release
document. This comprises four bands of observations of each both the north and south GOODS regions.
These data are stored in SkyView as a hierarchical image with 7 levels of pixels, each with a factor
of 2 change in scale. Thus the coarsest sampling using pixels 64 times larger than the finest. As we go to
coarser pixels, 4 adjacent pixels forming a square are averaged to create the pixel in the next level. The coarsest pixel
scale that is at least the resolution requested is used.
The exposure times are given as:
| GOODS ACS exposure (s) |
|---|
| Band | North> | South |
|---|
| z850 | 24760 | 18232 |
| i775 | 8530 | 7028 |
| V606 | 5650 | 5450 |
| B435 |
7200| 7200 |
| Provenance | Created by the GOODS team and distributed by MAST |
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 6.93 x 1014
|
| Bandpass | 6.70-7.17 x 1014
|
| Coverage | GOODS regions (0.01% of sky) |
| PixelScale | 0.03" |
| PixelUnits | Counts (of electrons) |
| Resolution | 0.1" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2002-07-04/2005-04-14 |
| Reference |
GOODS Version 2.0 HST ACS Imaging Data
|
GOODS HST ACS I Filter
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODS ACS I,GOODS: HST ACS I,GOODS_ACS_I
Description
This is a SkyView rendering of the HST ACS data as described in
the release
document. This comprises four bands of observations of each both the north and south GOODS regions.
These data are stored in SkyView as a hierarchical image with 7 levels of pixels, each with a factor
of 2 change in scale. Thus the coarsest sampling using pixels 64 times larger than the finest. As we go to
coarser pixels, 4 adjacent pixels forming a square are averaged to create the pixel in the next level. The coarsest pixel
scale that is at least the resolution requested is used.
The exposure times are given as:
| GOODS ACS exposure (s) |
|---|
| Band | North> | South |
|---|
| z850 | 24760 | 18232 |
| i775 | 8530 | 7028 |
| V606 | 5650 | 5450 |
| B435 |
7200| 7200 |
| Provenance | Created by the GOODS team and distributed by MAST |
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 3.90 x 1014
|
| Bandpass | 3.79-4.01 x 1014
|
| Coverage | GOODS regions (0.01% of sky) |
| PixelScale | 0.03" |
| PixelUnits | Counts (of electrons) |
| Resolution | 0.1" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2002-07-04/2005-04-14 |
| Reference |
GOODS Version 2.0 HST ACS Imaging Data
|
GOODS HST ACS V Filter
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODS ACS V,GOODS: HST ACS V,GOODS_ACS_V
Description
This is a SkyView rendering of the HST ACS data as described in
the release
document. This comprises four bands of observations of each both the north and south GOODS regions.
These data are stored in SkyView as a hierarchical image with 7 levels of pixels, each with a factor
of 2 change in scale. Thus the coarsest sampling using pixels 64 times larger than the finest. As we go to
coarser pixels, 4 adjacent pixels forming a square are averaged to create the pixel in the next level. The coarsest pixel
scale that is at least the resolution requested is used.
The exposure times are given as:
| GOODS ACS exposure (s) |
|---|
| Band | North> | South |
|---|
| z850 | 24760 | 18232 |
| i775 | 8530 | 7028 |
| V606 | 5650 | 5450 |
| B435 |
7200| 7200 |
| Provenance | Created by the GOODS team and distributed by MAST |
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 5.06 x 1014
|
| Bandpass | 4.79-5.37 x 1014
|
| Coverage | GOODS regions (0.01% of sky) |
| PixelScale | 0.03" |
| PixelUnits | Counts (of electrons) |
| Resolution | 0.1" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2002-07-04/2005-04-14 |
| Reference |
GOODS Version 2.0 HST ACS Imaging Data
|
GOODS HST ACS Z Filter
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODS ACS Z,GOODS: HST ACS Z,GOODS_ACS_Z
Description
This is a SkyView rendering of the HST ACS data as described in
the release
document. This comprises four bands of observations of each both the north and south GOODS regions.
These data are stored in SkyView as a hierarchical image with 7 levels of pixels, each with a factor
of 2 change in scale. Thus the coarsest sampling using pixels 64 times larger than the finest. As we go to
coarser pixels, 4 adjacent pixels forming a square are averaged to create the pixel in the next level. The coarsest pixel
scale that is at least the resolution requested is used.
The exposure times are given as:
| GOODS ACS exposure (s) |
|---|
| Band | North> | South |
|---|
| z850 | 24760 | 18232 |
| i775 | 8530 | 7028 |
| V606 | 5650 | 5450 |
| B435 |
7200| 7200 |
| Provenance | Created by the GOODS team and distributed by MAST |
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 4 |
| Frequency | 3.32 x 1014
|
| Bandpass | 3.22-3.42 x 1014
|
| Coverage | GOODS regions (0.01% of sky) |
| PixelScale | 0.03" |
| PixelUnits | Counts (of electrons) |
| Resolution | 0.1" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 2002-07-04/2005-04-14 |
| Reference |
GOODS Version 2.0 HST ACS Imaging Data
|
Southern GOODS Field: VLT VIMOS Observations, R band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODS VIMOS R, GOODS: VLT VIMOS R
Description
As part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS),
deep imaging in the Chandra Deep Field South (CDF-S) has been carried out,
using the VIMOS instrument mounted at the Melipal Unit Telescope of
the VLT at ESO's Cerro Paranal Observatory, Chile.
This data release contains the coadded images in U band from the ESO large programme
168.A-0485 (P.I. C. Cesarsky) which have been obtained in
service mode observations between August 2004 and fall 2006.
The 1-sigma depth for VIMOS U band in the area covered by the GOODS-ACS observations
is ~30 AB (within an aperture of 1" radius, ranging from 29.5 and 30.2 AB).
The PSF of the VIMOS U band mosaic is ~0.8" FWHM, but varies over the field.
Also included in this data release is a coadded image in R band obtained from
data retrieved from the ESO archive. Due to the different observing strategies
adopted in the programmes the resulting coverage of the GOODS-ACS
area is more complex than for the U band.
The depth of the VIMOS R band mosaic over the ACS area ranges from ~28 AB to 29 AB
(1-sigma, 1" aperture radius).
The PSF of the VIMOS R band mosaic is ~0".7 FWHM and varies over the field.
[Adapted from reference web site.]
| Regime | Optical |
| Frequency | 455 THz |
| Bandwidth | 412-509 THz |
| Provenance | Data downloaded from VLT archive |
| Copyright |
Data freely available from ESO archive.
When using data products provided in this release, acknowledgement should
be given in the text to the ESO/GOODS programme,
referring to the publication Nonino et al. 2009.
In addition, please also use the following statement in your articles when using these data:
"Based on observations made with ESO Telescopes at the La Silla or Paranal Observatories under programme number 168.A-0485."
|
| NSurvey | 2 |
| Resolution | 0.7-0.8" |
| PixelSize | 0.2" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| PixelUnits | ADU/s |
| Epoch | 2004-8-11 to 2006-10-27 |
| Reference |
Paper and
web site.>
|
H-alpha Full Sky Map
Short name[s] used to specify survey:HAlpha,HALPHA/Comp,H-Alpha Comp,H-Alpha Composite,H-alpha
Description
The full-sky H-alpha map (6' FWHM resolution) is a composite of the
Virginia Tech Spectral line Survey (VTSS) in the north and the
Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas (SHASSA) in the south. Stellar
artifacts and bleed trails have been carefully removed from these maps.
The Wisconsin H-Alpha Mapper (WHAM) survey provides a stable zero-point
over 3/4 of the sky on a one degree scale. This composite map can be used
to provide limits on thermal bremsstrahlung (free-free emission) from
ionized gas known to contaminate microwave-background data. The map
(in Rayleighs; 1R=106/4pi photons/cm2/s/sr), an error map, and a
bitmask are provided in 8640x4320 Cartesian projections as well as
HEALPIX (Nside 256, 512, and 1024) projections on the
H-Alpha Full-Sky Map web site.
| Copyright | Public domain
|
| Regime | Optical |
| Frequency | 456.79 THz |
| Bandpass | 456.2-457.38 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 2.5' |
| PixelUnits | Rayleighs (R) |
| Resolution | 6' FWHM |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Rectangular |
| Epoch | 1997 to 2002 |
| Reference |
"A Full-Sky H-alpha Template for Microwave Foreground Prediction" Douglas P. Finkbeiner 2003. This paper may be downloaded from
ADS.
|
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band B
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Hawaii HDF B, Hawaii: HDF B
Description
The Hawaii-HDF-N is an intensive multi-color imaging survey of 0.2 sq.
degrees centered on the HDF-N. Data were collected on the NOAO 4m Mayall telescope,
the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 8.2m Subaru telescope and the
University of Hawaii 2.2m telescope.
Deep U, B, V, R, I, and z' data were obtained over the whole field and deep HK' data over
the Chandra Deep Field North. Details are available in the references.
[Adapted from reference web site.]
Two different images are given in the V band (V0201 and V0401) from observations
separated by about a month that had substantial differences in seeing.
| Provenance | Data downloaded from the reference web site. A formatting
error in the FITS files was corrected.
|
| Copyright | Public Domain. Users are requested to include a reference to
Capak, et al. 2004 when using these data.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 8 |
| Frequency | 677 THz |
| Bandpass | 632-728 THz |
| Coverage | 0.000005 |
| Resolution | 0.67-1.26" |
| PixelScale | 0.3" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1999/2002 |
| Reference |
2004AJ....127..180C
or the web site.
|
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band R
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Hawaii HDF R, Hawaii: HDF R
Description
The Hawaii-HDF-N is an intensive multi-color imaging survey of 0.2 sq.
degrees centered on the HDF-N. Data were collected on the NOAO 4m Mayall telescope,
the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 8.2m Subaru telescope and the
University of Hawaii 2.2m telescope.
Deep U, B, V, R, I, and z' data were obtained over the whole field and deep HK' data over
the Chandra Deep Field North. Details are available in the references.
[Adapted from reference web site.]
Two different images are given in the V band (V0201 and V0401) from observations
separated by about a month that had substantial differences in seeing.
| Provenance | Data downloaded from the reference web site. A formatting
error in the FITS files was corrected.
|
| Copyright | Public Domain. Users are requested to include a reference to
Capak, et al. 2004 when using these data.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 8 |
| Frequency | 458 THz |
| Bandpass | 436-484 THz |
| Coverage | 0.000005 |
| Resolution | 0.67-1.26" |
| PixelScale | 0.3" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1999/2002 |
| Reference |
2004AJ....127..180C
or the web site.
|
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band V0201
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Hawaii HDF V0201, Hawaii: HDF V0201
Description
The Hawaii-HDF-N is an intensive multi-color imaging survey of 0.2 sq.
degrees centered on the HDF-N. Data were collected on the NOAO 4m Mayall telescope,
the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 8.2m Subaru telescope and the
University of Hawaii 2.2m telescope.
Deep U, B, V, R, I, and z' data were obtained over the whole field and deep HK' data over
the Chandra Deep Field North. Details are available in the references.
[Adapted from reference web site.]
Two different images are given in the V band (V0201 and V0401) from observations
separated by about a month that had substantial differences in seeing.
| Provenance | Data downloaded from the reference web site. A formatting
error in the FITS files was corrected.
|
| Copyright | Public Domain. Users are requested to include a reference to
Capak, et al. 2004 when using these data.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 8 |
| Frequency | 547 THz |
| Bandpass | 520-577 THz |
| Coverage | 0.000005 |
| Resolution | 0.67-1.26" |
| PixelScale | 0.3" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1999/2002 |
| Reference |
2004AJ....127..180C
or the web site.
|
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band V0401
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Hawaii HDF V0401, Hawaii: HDF V0401
Description
The Hawaii-HDF-N is an intensive multi-color imaging survey of 0.2 sq.
degrees centered on the HDF-N. Data were collected on the NOAO 4m Mayall telescope,
the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 8.2m Subaru telescope and the
University of Hawaii 2.2m telescope.
Deep U, B, V, R, I, and z' data were obtained over the whole field and deep HK' data over
the Chandra Deep Field North. Details are available in the references.
[Adapted from reference web site.]
Two different images are given in the V band (V0201 and V0401) from observations
separated by about a month that had substantial differences in seeing.
| Provenance | Data downloaded from the reference web site. A formatting
error in the FITS files was corrected.
|
| Copyright | Public Domain. Users are requested to include a reference to
Capak, et al. 2004 when using these data.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 8 |
| Frequency | 547 THz |
| Bandpass | 520-577 THz |
| Coverage | 0.000005 |
| Resolution | 0.67-1.26" |
| PixelScale | 0.3" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1999/2002 |
| Reference |
2004AJ....127..180C
or the web site.
|
Mellinger All Sky Mosaic: Blue
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Mellinger-B,Mell-B,Mellinger Blue
Description
This all sky mosaic was created by Axel Mellinger and is used
in SkyView with his permission. A fuller description
is available at the
survey web site.
Between October 2007 and August 2009 a digital all-sky mosaic
was assembled from more than 3000 individual CCD frames.
Using an SBIG STL-11000 camera, 70 fields (each covering 40x27 degrees)
were imaged from dark-sky locations in South Africa, Texas and Michigan.
In order to increase the dynamic range beyond the 16 bits of the camera's
analog-to-digital converter (of which approximately 12 bits provide data
above the noise leve) three different exposure times (240s, 15s and 0.5 s)
were used. Five frames were taken for each exposure time and
filter setting. The frames were photometrically calibrated using
standard catalog stars and sky background data
from the Pioneer 10 and 11 space probes. the panorama has an
image scale of 36"/pixel and a limiting magnitude of approximately 14. The
survey has an 18 bit dynamic range.
The processing of these data used a custom data pipeline built using
IRAF, Source Extractor and SWarp.
The data used here were converted to three independent RGB color planes
of 8 bits each and provided to SkyView as a single 36000x18000x3 Cartesian
projection cube.
To allow users to efficiently sample data in a region of the sky,
this cube was broken up into 2100x2100 pixel regions with a 50 pixel overlap
between adjacent images. Tiles at the poles were 2100x2050.
In SkyView each color plane comprises a survey. The individual planes may be
sampled as surveys independently as Mellinger-R, Mellinger-G and Mellinger-B.
The color mosaics can be regenerated by creating an RGB image of all three
surveys. Since SkyView may stretch the intensity values within
each color, linear scaling and a minimum of 0 and maximum of 255 should
be specified to keep the original intensity scalings.
The full spatial resolution data is used for images of less than
30 degrees on a side. If a user requests a larger region, data are sampled
from a lower resolution 3600x1800x3 data cube. Please contact the survey
author if you need to use the higher resolution data for larger regions.
The Mellinger survey is only available in
SkyView through the Web site. SkyView-in-a-Jar cannot access
the underlying data.
| Provenance |
Axel Mellinger
|
| Copyright |
Axel Mellinger. Permission is granted for use in research
and personal, non-commercial use. Please contact
Axel Mellinger
for permission for other use.
Survey web site
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 475 THz |
| Bandpass | 446-535 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelSize | 0.01 deg/pix |
| Units | Byte-scaled intensity |
| Resolution | 0.02 |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 2008-10 to 2009-04 |
| Reference |
PASP 121, 1180, 2009
Survey web site.
|
Mellinger All Sky Mosaic: Green
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Mellinger-G,Mell-G,Mellinger Green
Description
This all sky mosaic was created by Axel Mellinger and is used
in SkyView with his permission. A fuller description
is available at the
survey web site.
Between October 2007 and August 2009 a digital all-sky mosaic
was assembled from more than 3000 individual CCD frames.
Using an SBIG STL-11000 camera, 70 fields (each covering 40x27 degrees)
were imaged from dark-sky locations in South Africa, Texas and Michigan.
In order to increase the dynamic range beyond the 16 bits of the camera's
analog-to-digital converter (of which approximately 12 bits provide data
above the noise leve) three different exposure times (240s, 15s and 0.5 s)
were used. Five frames were taken for each exposure time and
filter setting. The frames were photometrically calibrated using
standard catalog stars and sky background data
from the Pioneer 10 and 11 space probes. the panorama has an
image scale of 36"/pixel and a limiting magnitude of approximately 14. The
survey has an 18 bit dynamic range.
The processing of these data used a custom data pipeline built using
IRAF, Source Extractor and SWarp.
The data used here were converted to three independent RGB color planes
of 8 bits each and provided to SkyView as a single 36000x18000x3 Cartesian
projection cube.
To allow users to efficiently sample data in a region of the sky,
this cube was broken up into 2100x2100 pixel regions with a 50 pixel overlap
between adjacent images. Tiles at the poles were 2100x2050.
In SkyView each color plane comprises a survey. The individual planes may be
sampled as surveys independently as Mellinger-R, Mellinger-G and Mellinger-B.
The color mosaics can be regenerated by creating an RGB image of all three
surveys. Since SkyView may stretch the intensity values within
each color, linear scaling and a minimum of 0 and maximum of 255 should
be specified to keep the original intensity scalings.
The full spatial resolution data is used for images of less than
30 degrees on a side. If a user requests a larger region, data are sampled
from a lower resolution 3600x1800x3 data cube. Please contact the survey
author if you need to use the higher resolution data for larger regions.
The Mellinger survey is only available in
SkyView through the Web site. SkyView-in-a-Jar cannot access
the underlying data.
| Provenance |
Axel Mellinger
|
| Copyright |
Axel Mellinger. Permission is granted for use in research
and personal, non-commercial use. Please contact
Axel Mellinger
for permission for other use.
Survey web site
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 566 THz |
| Bandpass | 491-631 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelSize | 0.01 deg/pix |
| Units | Byte-scaled intensity |
| Resolution | 0.02 |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 2008-10 to 2009-04 |
| Reference |
PASP 121, 1180, 2009
Survey web site.
|
Mellinger All Sky Mosaic: Red
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Mellinger-R,Mell-R,Mellinger Red
Description
This all sky mosaic was created by Axel Mellinger and is used
in SkyView with his permission. A fuller description
is available at the
survey web site.
Between October 2007 and August 2009 a digital all-sky mosaic
was assembled from more than 3000 individual CCD frames.
Using an SBIG STL-11000 camera, 70 fields (each covering 40x27 degrees)
were imaged from dark-sky locations in South Africa, Texas and Michigan.
In order to increase the dynamic range beyond the 16 bits of the camera's
analog-to-digital converter (of which approximately 12 bits provide data
above the noise leve) three different exposure times (240s, 15s and 0.5 s)
were used. Five frames were taken for each exposure time and
filter setting. The frames were photometrically calibrated using
standard catalog stars and sky background data
from the Pioneer 10 and 11 space probes. the panorama has an
image scale of 36"/pixel and a limiting magnitude of approximately 14. The
survey has an 18 bit dynamic range.
The processing of these data used a custom data pipeline built using
IRAF, Source Extractor and SWarp.
The data used here were converted to three independent RGB color planes
of 8 bits each and provided to SkyView as a single 36000x18000x3 Cartesian
projection cube.
To allow users to efficiently sample data in a region of the sky,
this cube was broken up into 2100x2100 pixel regions with a 50 pixel overlap
between adjacent images. Tiles at the poles were 2100x2050.
In SkyView each color plane comprises a survey. The individual planes may be
sampled as surveys independently as Mellinger-R, Mellinger-G and Mellinger-B.
The color mosaics can be regenerated by creating an RGB image of all three
surveys. Since SkyView may stretch the intensity values within
each color, linear scaling and a minimum of 0 and maximum of 255 should
be specified to keep the original intensity scalings.
The full spatial resolution data is used for images of less than
30 degrees on a side. If a user requests a larger region, data are sampled
from a lower resolution 3600x1800x3 data cube. Please contact the survey
author if you need to use the higher resolution data for larger regions.
The Mellinger survey is only available in
SkyView through the Web site. SkyView-in-a-Jar cannot access
the underlying data.
| Provenance |
Axel Mellinger
|
| Copyright |
Axel Mellinger. Permission is granted for use in research
and personal, non-commercial use. Please contact
Axel Mellinger
for permission for other use.
Survey web site
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 697 THz |
| Bandpass | 576-788 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelSize | 0.01 deg/pix |
| Units | Byte-scaled intensity |
| Resolution | 0.02 |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 2008-10 to 2009-04 |
| Reference |
PASP 121, 1180, 2009
Survey web site.
|
Near-Earth Asteriod Tracking System Archive
Short name[s] used to specify survey:NEAT, NEAT/SkyMorph
Description
The NEAT/SkyMorph survey provides access to the archives
of the Near Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT) project. NEAT is
designed to look for potentially hazardous asteroids, i.e., those
whose orbits cross the Earth's. Over 200,000 images are available
in the NEAT archive.
SkyMorph
provides a Web interface to the NEAT
images and allows users to select all images in which a given fixed
or moving object is found.
Unlike most SkyView surveys, the NEAT data are extremely irregular in their
spatial distribution. SkyView's algorithms for mosaicking images
together to form large images are not adequate for the NEAT data, so
mosaicking is surpressed. Only data within a single NEAT image will
be displayed. The system attempts to find the most recent image within
which has a offset in both RA and Dec of less than 0.8 degrees. If no
such image is found, then an image with the minimum offset is returned, or
the search may fail altogether if there are no nearby plates.
The NEAT telescope uses an array of 4 CCDs. The backgrounds of the
CCDs may differ significantly.
The NEAT survey covers approximately 30% of the sky. Extreme southern
and low-Galactic latitude regions are unsurveyed. Coverage is otherwise
particularly dense in the ecliptic plane.
NEAT data consists primarily of groups of three images taken with separations
of 20 minutes and almost identical positions. SkyView will normally
return the last of a 'triplet'. The SkyMorph site can be used to display
an overlay of triplets to look for targets which moved during the interval
between images.
A catalog of objects detected in the NEAT/SkyMorph pages is accessible
through the SkyMorph pages. 'Light-curves' from all images during which
an object was in the NEAT field of view can also be generated.
The NEAT data values are in arbitrary density units. To enhance the display
data are transformed such that all pixels below the median values
are scaled linearly to values 0-20, while all pixels above the median
are shifted (but not scaled) to values greater than 20.
| Provenance |
NEAT project
|
| Copyright |
See the JPL Image Use Policy
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 500 THz |
| Bandpass | 374-750 THz |
| Coverage | Patches of the sky, approximately 30% coverage |
| PixelScale | 1.42" |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | Depends on image. Typically 3" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Radially distorted gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1995-2006 |
| Reference |
href=http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1999AJ...117.1616P> Pravdo, et al. 1999 (ADS)
|
Sloan Digital Sky Survey g-band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SDSSg,SDSS g
Description
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is the deepest large scale survey of the
sky currently available. SkyView dynamically queries the SDSS archive
(currently release DR9) to retrieve information and resample it into the user
requested frame. Further information on the SDSS and many additional services
are available at the SDSS Web site.
| Provenance | Sloan Digital Sky Survey Team |
| Copyright |
See
Sloan usage document for distribution rights and acknowledgements.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 646 THz |
| Bandpass | 567-750 THz |
| Coverage | 14,555 square degrees. The SDDS site provides coverage maps |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | 1998 to 2011 |
| Reference |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey web site
or
ADS
|
Sloan Digital Sky Survey i-band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SDSSi,SDSS i
Description
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is the deepest large scale survey of the
sky currently available. SkyView dynamically queries the SDSS archive
(currently release DR9) to retrieve information and resample it into the user
requested frame. Further information on the SDSS and many additional services
are available at the SDSS Web site.
| Provenance | Sloan Digital Sky Survey Team |
| Copyright |
See
Sloan usage document for distribution rights and acknowledgements.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 403 THz |
| Bandpass | 372-439 THz |
| Coverage | 14,555 square degrees. The SDDS site provides coverage maps |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | 1998 to 2011 |
| Reference |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey web site
or
ADS
|
Sloan Digital Sky Survey r-band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SDSSr,SDSS r
Description
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is the deepest large scale survey of the
sky currently available. SkyView dynamically queries the SDSS archive
(currently release DR9) to retrieve information and resample it into the user
requested frame. Further information on the SDSS and many additional services
are available at the SDSS Web site.
| Provenance | Sloan Digital Sky Survey Team |
| Copyright |
See
Sloan usage document for distribution rights and acknowledgements.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 490 THz |
| Bandpass | 448-540 THz |
| Coverage | 14,555 square degrees. The SDDS site provides coverage maps |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | 1998 to 2011 |
| Reference |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey web site
or
ADS
|
Sloan Digital Sky Survey u-band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SDSSu,SDSS u
Description
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is the deepest large scale survey of the
sky currently available. SkyView dynamically queries the SDSS archive
(currently release DR9) to retrieve information and resample it into the user
requested frame. Further information on the SDSS and many additional services
are available at the SDSS Web site.
| Provenance | Sloan Digital Sky Survey Team |
| Copyright |
See
Sloan usage document for distribution rights and acknowledgements.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 834 THz |
| Bandpass | 772-934 THz |
| Coverage | 14,555 square degrees. The SDDS site provides coverage maps |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | 1998 to 2011 |
| Reference |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey web site
or
ADS
|
Sloan Digital Sky Survey z-band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SDSSz,SDSS z
Description
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is the deepest large scale survey of the
sky currently available. SkyView dynamically queries the SDSS archive
(currently release DR9) to retrieve information and resample it into the user
requested frame. Further information on the SDSS and many additional services
are available at the SDSS Web site.
| Provenance | Sloan Digital Sky Survey Team |
| Copyright |
See
Sloan usage document for distribution rights and acknowledgements.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 337 THz |
| Bandpass | 327-348 THz |
| Coverage | 14,555 square degrees. The SDDS site provides coverage maps |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | 1998 to 2011 |
| Reference |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey web site
or
ADS
|
Sloan Digital Sky Survey g-band DR7
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SDSSdr7g,SDSSdr7 g
Description
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is the deepest large scale survey of the
sky currently available. SkyView dynamically queries the SDSS archive
to retrieve information and resample it into the user
requested frame. Further information on the SDSS and many additional services
are available at the SDSS Web site.
| Provenance | Sloan Digital Sky Survey Team |
| Copyright |
See
Sloan usage document for distribution rights and acknowledgements.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 646 THz |
| Bandpass | 567-750 THz |
| Coverage | 9,583 square degrees. The SDDS site provides coverage maps |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | ADUs |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | ca. 2000 |
| Reference |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey web site
|
Sloan Digital Sky Survey i-band DR7
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SDSSdr7i,SDSSdr7 i
Description
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is the deepest large scale survey of the
sky currently available. SkyView dynamically queries the SDSS archive
to retrieve information and resample it into the user
requested frame. Further information on the SDSS and many additional services
are available at the SDSS Web site.
| Provenance | Sloan Digital Sky Survey Team |
| Copyright |
See
Sloan usage document for distribution rights and acknowledgements.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 403 THz |
| Bandpass | 372-439 THz |
| Coverage | 9,583 square degrees. The SDDS site provides coverage maps |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | ADUs |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | ca. 2000 |
| Reference |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey web site
|
Sloan Digital Sky Survey r-band DR7
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SDSSdr7r,SDSSdr7 r
Description
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is the deepest large scale survey of the
sky currently available. SkyView dynamically queries the SDSS archive
to retrieve information and resample it into the user
requested frame. Further information on the SDSS and many additional services
are available at the SDSS Web site.
| Provenance | Sloan Digital Sky Survey Team |
| Copyright |
See
Sloan usage document for distribution rights and acknowledgements.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 490 THz |
| Bandpass | 448-540 THz |
| Coverage | 9,583 square degrees. The SDDS site provides coverage maps |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | ADUs |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | ca. 2000 |
| Reference |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey web site
|
Sloan Digital Sky Survey u-band DR7
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SDSSdr7u,SDSSdr7 u
Description
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is the deepest large scale survey of the
sky currently available. SkyView dynamically queries the SDSS archive
to retrieve information and resample it into the user
requested frame. Further information on the SDSS and many additional services
are available at the SDSS Web site.
| Provenance | Sloan Digital Sky Survey Team |
| Copyright |
See
Sloan usage document for distribution rights and acknowledgements.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 834 THz |
| Bandpass | 772-934 THz |
| Coverage | 9,583 square degrees. The SDDS site provides coverage maps |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | ADUs |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | ca. 2000 |
| Reference |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey web site
|
Sloan Digital Sky Survey z-band DR7
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SDSSdr7z,SDSSdr7 z
Description
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is the deepest large scale survey of the
sky currently available. SkyView dynamically queries the SDSS archive
to retrieve information and resample it into the user
requested frame. Further information on the SDSS and many additional services
are available at the SDSS Web site.
| Provenance | Sloan Digital Sky Survey Team |
| Copyright |
See
Sloan usage document for distribution rights and acknowledgements.
|
| Regime | Optical |
| NSurvey | 5 |
| Frequency | 337 THz |
| Bandpass | 327-348 THz |
| Coverage | 9,583 square degrees. The SDDS site provides coverage maps |
| PixelScale | 0.4" |
| PixelUnits | ADUs |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | ca. 2000 |
| Reference |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey web site
|
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: Continuum
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SHASSA-C,SHASSA_C,SHASSA C
Description
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas is the product of a wide-angle
digital imaging survey of the H-alpha emission from the warm ionized
interstellar gas of our Galaxy. This atlas covers the southern hemisphere
sky (declinations less than +15 degrees). The observations were taken with
a robotic camera operating at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO)
in Chile. The atlas consists of 2168 images covering 542 fields. There are four
images available for each field: H-alpha, Continuum, Continuum-Corrected
(the difference of the H-alpha and Continuum images), and Smoothed (median filtered to 5 pixel, or 4.0 arcminute, resolution to remove star residuals better). The SHASSA web site has more details of the data and the status of this and related projects. Images can also be
obtained from the Download Images section at the SHASSA site.
| Provenance | John E. Gaustad (Swarthmore College), Peter R. McCullough (University of Illinois), Wayne Rosing (Las Cumbres Observatory), and Dave Van Buren (Extrasolar Research Corporation)
|
| Copyright |
Las Cumbres Observatory, Inc. See the Acknowledgement/Guidelines for Use of Images
|
| Regime | Optical |
| Frequency | 457 THz |
| Bandpass | 456-458 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky south of 15 |
| Resolution | 3.2' |
| PixelScale | 0.79' |
| PixelUnits | decirayleighs (dR) or 105/4pi photons/cm2/s/sr |
| CoordinateSystem | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1997-2000 |
| Reference | "A Robotic Wide-Angle H-alpha Survey of the Southern Sky" by J.E. Gaustad, P.R. McCullough, W. Rosing, and D. Van Buren 2001, PASP, 113, 1326. This paper may be downloaded in PDF (2.5 Mb) or Postscript (12.7 Mb) format.
or
ADS
|
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: Continuum-Corrected
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SHASSA-CC,SHASSA_CC,SHASSA CC
Description
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas is the product of a wide-angle
digital imaging survey of the H-alpha emission from the warm ionized
interstellar gas of our Galaxy. This atlas covers the southern hemisphere
sky (declinations less than +15 degrees). The observations were taken with
a robotic camera operating at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO)
in Chile. The atlas consists of 2168 images covering 542 fields. There are four
images available for each field: H-alpha, Continuum, Continuum-Corrected
(the difference of the H-alpha and Continuum images), and Smoothed (median filtered to 5 pixel, or 4.0 arcminute, resolution to remove star residuals better). The SHASSA web site has more details of the data and the status of this and related projects. Images can also be
obtained from the Download Images section at the SHASSA site.
| Provenance | John E. Gaustad (Swarthmore College), Peter R. McCullough (University of Illinois), Wayne Rosing (Las Cumbres Observatory), and Dave Van Buren (Extrasolar Research Corporation)
|
| Copyright |
Las Cumbres Observatory, Inc. See the Acknowledgement/Guidelines for Use of Images
|
| Regime | Optical |
| Frequency | 457 THz |
| Bandpass | 456-458 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky south of 15 |
| Resolution | 3.2' |
| PixelScale | 0.79' |
| PixelUnits | decirayleighs (dR) or 105/4pi photons/cm2/s/sr |
| CoordinateSystem | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1997-2000 |
| Reference | "A Robotic Wide-Angle H-alpha Survey of the Southern Sky" by J.E. Gaustad, P.R. McCullough, W. Rosing, and D. Van Buren 2001, PASP, 113, 1326. This paper may be downloaded in PDF (2.5 Mb) or Postscript (12.7 Mb) format.
or
ADS
|
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: H-Alpha
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SHASSA-H,SHASSA_H,SHASSA H
Description
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas is the product of a wide-angle
digital imaging survey of the H-alpha emission from the warm ionized
interstellar gas of our Galaxy. This atlas covers the southern hemisphere
sky (declinations less than +15 degrees). The observations were taken with
a robotic camera operating at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO)
in Chile. The atlas consists of 2168 images covering 542 fields. There are four
images available for each field: H-alpha, Continuum, Continuum-Corrected
(the difference of the H-alpha and Continuum images), and Smoothed (median filtered to 5 pixel, or 4.0 arcminute, resolution to remove star residuals better). The SHASSA web site has more details of the data and the status of this and related projects. Images can also be
obtained from the Download Images section at the SHASSA site.
| Provenance | John E. Gaustad (Swarthmore College), Peter R. McCullough (University of Illinois), Wayne Rosing (Las Cumbres Observatory), and Dave Van Buren (Extrasolar Research Corporation)
|
| Copyright |
Las Cumbres Observatory, Inc. See the Acknowledgement/Guidelines for Use of Images
|
| Regime | Optical |
| Frequency | 457 THz |
| Bandpass | 456-458 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky south of 15 |
| Resolution | 3.2' |
| PixelScale | 0.79' |
| PixelUnits | decirayleighs (dR) or 105/4pi photons/cm2/s/sr |
| CoordinateSystem | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1997-2000 |
| Reference | "A Robotic Wide-Angle H-alpha Survey of the Southern Sky" by J.E. Gaustad, P.R. McCullough, W. Rosing, and D. Van Buren 2001, PASP, 113, 1326. This paper may be downloaded in PDF (2.5 Mb) or Postscript (12.7 Mb) format.
or
ADS
|
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas: Smoothed
Short name[s] used to specify survey:SHASSA-Sm,SHASSA_Sm,SHASSA Sm
Description
The Southern H-Alpha Sky Survey Atlas is the product of a wide-angle
digital imaging survey of the H-alpha emission from the warm ionized
interstellar gas of our Galaxy. This atlas covers the southern hemisphere
sky (declinations less than +15 degrees). The observations were taken with
a robotic camera operating at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO)
in Chile. The atlas consists of 2168 images covering 542 fields. There are four
images available for each field: H-alpha, Continuum, Continuum-Corrected
(the difference of the H-alpha and Continuum images), and Smoothed (median filtered to 5 pixel, or 4.0 arcminute, resolution to remove star residuals better). The SHASSA web site has more details of the data and the status of this and related projects. Images can also be
obtained from the Download Images section at the SHASSA site.
| Provenance | John E. Gaustad (Swarthmore College), Peter R. McCullough (University of Illinois), Wayne Rosing (Las Cumbres Observatory), and Dave Van Buren (Extrasolar Research Corporation)
|
| Copyright |
Las Cumbres Observatory, Inc. See the Acknowledgement/Guidelines for Use of Images
|
| Regime | Optical |
| Frequency | 457 THz |
| Bandpass | 456-458 THz |
| Coverage | All-sky south of 15 |
| Resolution | 3.2' |
| PixelScale | 0.79' |
| PixelUnits | decirayleighs (dR) or 105/4pi photons/cm2/s/sr |
| CoordinateSystem | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1997-2000 |
| Reference | "A Robotic Wide-Angle H-alpha Survey of the Southern Sky" by J.E. Gaustad, P.R. McCullough, W. Rosing, and D. Van Buren 2001, PASP, 113, 1326. This paper may be downloaded in PDF (2.5 Mb) or Postscript (12.7 Mb) format.
or
ADS
|
Ultraviolet surveys
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 171 A
Short name[s] used to specify survey:euve171, EUVE 171 A
Description
The EUVE satellite surveyed the entire sky in the extreme ultraviolet
through a set of four filters. The filters include:
- Lexan/Boron filter: peak at 83A (full range 50-180)
- Aluminium/Carbon/Titanium : 171A (160-240)
- Aluminium/Titanium/Antimony: 405A (345-605)
- Tin/SiO: 555A (500-740)
The data currently in SkyView is direct from the Center for EUVE.
| Provenance | Center for Extreme UV Astronomy, UCB |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Frequency | 17.3 PHz |
| Bandpass | 8.1-17.6 PHz |
| PixelScale | 0.025 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | counts |
| Resolution | ca. 3' |
| CoordinateSystem | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic/Tan |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1992-07 to 1993-01 |
| Reference |
Boywer et al 1996 (ADS)
|
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 405 A
Short name[s] used to specify survey:euve405, EUVE 405 A
Description
The EUVE satellite surveyed the entire sky in the extreme ultraviolet
through a set of four filters. The filters include:
- Lexan/Boron filter: peak at 83A (full range 50-180)
- Aluminium/Carbon/Titanium : 171A (160-240)
- Aluminium/Titanium/Antimony: 405A (345-605)
- Tin/SiO: 555A (500-740)
The data currently in SkyView is direct from the Center for EUVE.
| Provenance | Center for Extreme UV Astronomy, UCB |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Frequency | 7.4 PHz |
| Bandpass | 5.0-7.9 PHz |
| PixelScale | 0.025 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | counts |
| Resolution | ca. 3' |
| CoordinateSystem | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic/Tan |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1992-07 to 1993-01 |
| Reference |
Boywer et al 1996 (ADS)
|
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 555 A
Short name[s] used to specify survey:euve555, EUVE 555 A
Description
The EUVE satellite surveyed the entire sky in the extreme ultraviolet
through a set of four filters. The filters include:
- Lexan/Boron filter: peak at 83A (full range 50-180)
- Aluminium/Carbon/Titanium : 171A (160-240)
- Aluminium/Titanium/Antimony: 405A (345-605)
- Tin/SiO: 555A (500-740)
The data currently in SkyView is direct from the Center for EUVE.
| Provenance | Center for Extreme UV Astronomy, UCB |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Frequency | 5.4 PHz |
| Bandpass | 3.75-6 PHz |
| PixelScale | 0.025 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | counts |
| Resolution | ca. 3' |
| CoordinateSystem | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic/Tan |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1992-07 to 1993-01 |
| Reference |
Boywer et al 1996 (ADS)
|
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer: 83 A
Short name[s] used to specify survey:euve83, EUVE 83 A
Description
The EUVE satellite surveyed the entire sky in the extreme ultraviolet
through a set of four filters. The filters include:
- Lexan/Boron filter: peak at 83A (full range 50-180)
- Aluminium/Carbon/Titanium : 171A (160-240)
- Aluminium/Titanium/Antimony: 405A (345-605)
- Tin/SiO: 555A (500-740)
The data currently in SkyView is direct from the Center for EUVE.
| Provenance | Center for Extreme UV Astronomy, UCB |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Frequency | 36 PHz |
| Bandpass | 15-43 PHz |
| PixelScale | 0.025 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | counts |
| Resolution | ca. 3' |
| CoordinateSystem | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic/Tan |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Epoch | 1992-07 to 1993-01 |
| Reference |
Boywer et al 1996 (ADS)
|
Galaxy Explorer All Sky Survey: Far UV
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GalexFar,GALEX Far UV
Description
The GALEX, Galaxy Explorer, mission
was launched by a Pegasus-XL vehicle on April 28 2003 into
a 690km altitude, 29 degree inclination, circular orbit with a 98.6
minute period. The GALEX instrument allows imaging and spectroscopic
observations to be made in two ultraviolet bands,
Far UV (FUV) 1350-1780A and Near UV (NUV) 1770-2730A.
The instrument provides simultaneous co-aligned FUV and NUV
images with spatial resolution 4.3 and 5.3 arcseconds respectively.
Details of the performance of the instrument and detectors can be found in
Morrissey et al. (2007) ApJS, 173, 682.
The SkyView GALEX surveys mosaic the intensity images of
All-Sky Survey images. For a given pixel only the nearest image is used.
Since a given GALEX observation is circular, this maximizes the coverage
compared with default image finding algorithms which use the distance from
edge of the image.
As of February 10, 2011 SkyView uses the GR6 data release for the entire sky.
| Provenance |
All data is downloaded from the
MAST GALEX archive.
|
| Copyright |
Public domain.
|
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 2 |
| Frequency | 1.96 PHz
|
| Bandpass | 1.68-2.23 PHz |
| Coverage | All sky/patchy |
| PixelScale | 1.5" |
| PixelUnits | Intensity |
| Resolution | 4.3" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | 2003 to 2009 |
| Reference |
The GALEX Guest Invesitigator and
MAST Archive sites provide documentation and
characteristics of the GALEX observatory and archive. The
technical document
provides instrument details.
|
Galaxy Explorer All Sky Survey: Near UV
Short name[s] used to specify survey: GalexNear,GALEX NEAR UV
Description
The GALEX, Galaxy Explorer, mission
was launched by a Pegasus-XL vehicle on April 28 2003 into
a 690km altitude, 29 degree inclination, circular orbit with a 98.6
minute period. The GALEX instrument allows imaging and spectroscopic
observations to be made in two ultraviolet bands,
Far UV (FUV) 1350-1780A and Near UV (NUV) 1770-2730A.
The instrument provides simultaneous co-aligned FUV and NUV
images with spatial resolution 4.3 and 5.3 arcseconds respectively.
Details of the performance of the instrument and detectors can be found in
Morrissey et al. (2007) ApJS, 173, 682.
The SkyView GALEX surveys mosaic the intensity images of
All-Sky Survey images. For a given pixel only the nearest image is used.
Since a given GALEX observation is circular, this maximizes the coverage
compared with default image finding algorithms which use the distance from
edge of the image.
As of February 10, 2011, SkyView uses the GALEX GR6 data release.
| Provenance |
All data is downloaded from the
MAST GALEX archive.
|
| Copyright |
Public domain.
|
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 2 |
| Frequency | 1.32 PHz |
| Bandpass | 1.05-1.69 PHz |
| Coverage | All sky/patchy |
| PixelScale | 1.5" |
| PixelUnits | Intensity |
| Resolution | 5.3" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Tangent |
| Epoch | 2003 to 2009 |
| Reference |
The GALEX Guest Invesitigator and
MAST Archive sites provide documentation and
characteristics of the GALEX observatory and archive. The
technical document provides instrument details.
|
Southern GOODS Field: VLT VIMOS Observations, U band
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODS VIMOS U, GOODS: VLT VIMOS U
Description
As part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS),
deep imaging in the Chandra Deep Field South (CDF-S) has been carried out,
using the VIMOS instrument mounted at the Melipal Unit Telescope of
the VLT at ESO's Cerro Paranal Observatory, Chile.
This data release contains the coadded images in U band from the ESO large programme
168.A-0485 (P.I. C. Cesarsky) which have been obtained in
service mode observations between August 2004 and fall 2006.
The 1-sigma depth for VIMOS U band in the area covered by the GOODS-ACS observations
is ~30 AB (within an aperture of 1" radius, ranging from 29.5 and 30.2 AB).
The PSF of the VIMOS U band mosaic is ~0.8" FWHM, but varies over the field.
Also included in this data release is a coadded image in R band obtained from
data retrieved from the ESO archive. Due to the different observing strategies
adopted in the programmes the resulting coverage of the GOODS-ACS
area is more complex than for the U band.
The depth of the VIMOS R band mosaic over the ACS area ranges from ~28 AB to 29 AB
(1-sigma, 1" aperture radius).
The PSF of the VIMOS R band mosaic is ~0".7 FWHM and varies over the field.
[Adapted from reference web site.]
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| Frequency | 821 THz |
| Bandwidth | 753-903 THz |
| Provenance | Data downloaded from VLT archive |
| Copyright |
Data freely available from ESO archive.
When using data products provided in this release, acknowledgement should
be given in the text to the ESO/GOODS programme,
referring to the publication Nonino et al. 2009.
In addition, please also use the following statement in your articles when using these data:
"Based on observations made with ESO Telescopes at the La Silla or Paranal Observatories under programme number 168.A-0485."
|
| NSurvey | 2 |
| Resolution | 0.7-0.8" |
| PixelSize | 0.2" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| PixelUnits | ADU/s |
| Epoch | 2004-8-11 to 2006-10-27 |
| Reference |
Paper and
web site.>
|
The Hawaii Hubble Deep Field North: Band U
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Hawaii HDF U, Hawaii: HDF U
Description
The Hawaii-HDF-N is an intensive multi-color imaging survey of 0.2 sq.
degrees centered on the HDF-N. Data were collected on the NOAO 4m Mayall telescope,
the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan 8.2m Subaru telescope and the
University of Hawaii 2.2m telescope.
Deep U, B, V, R, I, and z' data were obtained over the whole field and deep HK' data over
the Chandra Deep Field North. Details are available in the references.
[Adapted from reference web site.]
Two different images are given in the V band (V0201 and V0401) from observations
separated by about a month that had substantial differences in seeing.
| Provenance | Data downloaded from the reference web site. A formatting
error in the FITS files was corrected.
|
| Copyright | Public Domain. Users are requested to include a reference to
Capak, et al. 2004 when using these data.
|
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 8 |
| Frequency | 822 THz |
| Bandpass | 780-868 THz |
| Coverage | 0.000005 |
| Resolution | 0.67-1.26" |
| PixelScale | 0.3" |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1999/2002 |
| Reference |
2004AJ....127..180C
or the web site.
|
Swift UVOT Combined B Counts Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTBcnt,UVOT B Counts, SwiftUVOTBcnt
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 865 THz (4392 A) |
| Bandpass | 774-975 THz (3904-4880 ?) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0112 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined U Counts Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUcnt,UVOT U Counts, SwiftUVOTUcnt
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 865 THz (3465 A) |
| Bandpass | 774-975 THz (3072-3875 ?) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0287 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined UVM2 Counts Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUVM2cnt,UVOT UVM2 Counts, SwiftUVOTUVM2cnt
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 1334 THz (2246 A) |
| Bandpass | 1200-1500 THz (1997-2495 ?) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0314 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined UVW1 Counts Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUVW1cnt,UVOT UVW1 Counts, SwiftUVOTUVW1cnt
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 1154 THz (2600 A) |
| Bandpass | 1017-1330 THz (2253-2946 ?) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0277 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined UVW2 Counts Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUVW2cnt,UVOT UVW2 Counts, SwiftUVOTUVW2cnt
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 1554 THz (1928 A) |
| Bandpass | 1328-1874 THz (1600-2256 ?) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0260 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined V Counts Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTVcnt,UVOT V Counts, SwiftUVOTVcnt
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 548 THz (5468 A) |
| Bandpass | 512-590 THz (5083-5852 ?) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0171 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined WHITE Counts Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTWHITEcnt,UVOT WHITE Counts, SwiftUVOTWHITEcnt
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 832 THz (3600 A) |
| Bandpass | 500-1874 THz (1600-6000 ?) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0017 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined B Exposure Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTBexp,UVOT B Exposure, SwiftUVOTBexp
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 865 THz (4392 A) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0112 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined U Exposure Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUexp,UVOT U Exposure, SwiftUVOTUexp
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 865 THz (3465 A) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0287 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined UVM2 Exposure Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUVM2exp,UVOT UVM2 Exposure, SwiftUVOTUVM2exp
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 1334 THz (2246 A) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0314 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined UVW1 Exposure Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUVW1exp,UVOT UVW1 Exposure, SwiftUVOTUVW1exp
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 1154 THz (2600 A) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0277 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined UVW2 Exposure Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUVW2exp,UVOT UVW2 Exposure, SwiftUVOTUVW2exp
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 1554 THz ( A) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0260 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined V Exposure Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTVexp,UVOT V Exposure, SwiftUVOTVexp
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 548 THz (5468 A) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0171 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined WHITE Exposure Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTWHITEexp,UVOT WHITE Exposure, SwiftUVOTWHITEexp
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 832 THz (3600 A) |
| Bandpass | 500-1874 THz (1600-6000 ?) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0017 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined B Intensity Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTBint,UVOT B Intensity, SwiftUVOTBint
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 865 THz (4392 A) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0112 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts/s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined U Intensity Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUint,UVOT U Intensity, SwiftUVOTUint
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 865 THz (3465 A) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0287 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts/s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined UVM2 Intensity Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUVM2int,UVOT UVM2 Intensity, SwiftUVOTUVM2int
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 1334 THz (2246 A) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0314 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts/s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined UVW1 Intensity Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUVW1int,UVOT UVW1 Intensity, SwiftUVOTUVW1int
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 1154 THz (2600 A) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0277 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts/s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined UVW2 Intensity Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTUVW2int,UVOT UVW2 Intensity, SwiftUVOTUVW2int
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 1554 THz (1928 A) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0260 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts/s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined V Intensity Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTVint,UVOT V Intensity, SwiftUVOTVint
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 548 THz (5468 A) |
| Bandpass | 512-590 THz (5083-5852 ?) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0171 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts/s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
Swift UVOT Combined WHITE Intensity Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:UVOTWHITEint,UVOT WHITE Intensity, SwiftUVOTWHITEint
Description
The Swift UVOT instrument is a 30 cm modified Ritchey-Chretien reflecting telescope launched on
board the Swift satellite on November 20, 2004.
The range of optical and UV filters can accomodate wavebands between 1700 and 6500 Angstroms.
A full field image covers 17x17 arcminutes and at maximum spatial sampling is imaged onto 2048x2048 0.5"
pixels. A 1000 second observation can detect point sources to m=22.3 when no filter is used.
The Swift Serendipitous Source Catalog (Page et al., 2015) detects sources down to m=23-26 for
the six filters in very deep observations, but the typical limits are substantially brighter (~20-23 magnitude).
These surveys are mosaics of all Swift UVOT observations released between the start of the mission and July 2017.
Data were extracted from the HEASARC archive from the UVOT products directory. Mosaics are provided
in six filters and also with no filter, i.e., WHITE. The table below gives the number of
observations and bandpasses for each of the filters. For each UVOT observation standard processing generates a
counts and exposure file as a single multi-extension FITS file with a separate extension for each filter. To aid
processing, these extensions were copied into separate files in directory trees for each filter.
Four observations in which the exposure and counts maps did not agree on the filters
used were omitted from the processing.
Some observations were recorded with 0.5" pixels while others were binned to 1". All 0.5" observations
(typically fewer than 10%) were rebinned to the larger pixels for the counts maps since the counts
data scales with the pixel size.
Since the exposure values are intensive and do not vary significantly based upon the resolution, these data were
not generally rebinned unless it was needed to ensure that Order 9 Hips data were produced.
The CDS Hipsgen software was used to generate Order 9 HiPS data (~0.8" pixels) for both the Counts and
Exposure images. The HiPS (Hierarchical Progressive Survey VO standard) supports multi-resolution mosaics.
Any quantitative use of these images should note that the rebinning increases the
total counts by a factor of ~(1.0/0.8)^2 ~ 1.56. This software uses a bilinear interpolation to generate HEALPix tiles of an appropriate
order (18 in this case). SkyView developed software was used to divide the level 9 counts maps
tiles by the corresponding exposure maps to create intensity tiles.
Pixels where the exposure was less than 5 seconds were left as NaNs.
The lower order (8 to 3) order intensity tiles were then generated by averaging
2x2 sets of the higher order maps treating any missing maps or pixels as NaNs.
A HiPS all-sky image was generated by averaged the Order 3 tiles.
Only the Intensity HIPS files are presented in the SkyView web page directly, but intensity, counts and
exposure maps are available for all seven filters. Note that unlike the XRT HiPS data, the exposure
and counts maps have not been clipped. I.e., the source FITS files have been aligned with the
coordinate system and thus contain large numbers of unexposed pixels with 0 values.
These 0's are simply propogated to HiPS tiles.
NaNs are returned in regions which lie outside any of the original source images. For the Intensity map,
any pixel for which the exposure was less than 5s is returned as a NaN.
| Filter | Count | Central Wavelength (Å) | Bandpass (Å) | Central Frequency(THz) | Bandpass (THz) | Coverage |
|---|
| WHITE | 3,000 | 3600 | 1600-6000 | 832 | 500-1874 | 0.0017 |
|---|
| V | 30,557 | 5468 | 5083-5852 | < 548 | 512-590 | 0.0171 |
|---|
| B | 28,347 | 4392 | 3904-4880 | 683 | 614-768 | 0.0112 | |
|---|
| U | 49,954 | 3465 | 3072-3875 | 865 | 774-975 | 0.0287 |
|---|
| UVW1 | 60,690 | 2600 | 2253-2946 | 1154 | 1017-1330 | 0.0277 |
|---|
| UVM2 | 56,977 | 2246 | 1997-2495 | 1334 | 1201-1501 | >td>0.0314
|---|
| UVW2 | 54,590 | 1928 | 1600-2256 | 1554 | 1328-1874 | 0.0260 |
|---|
Observation counts and bandpasses for UVOT Filters
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 21 |
| Frequency | 832 THz (3600 A) |
| Bandpass | 500-1874 THz (1600-6000 ?) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~0.0017 of the sky |
| PixelScale | 0.8" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts/s |
| Resolution | 2.5" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to July 2017 |
| Reference |
Web site
|
ROSAT Wide Field Camera: F1
Short name[s] used to specify survey:wfcf1, ROSAT WFC F1
Description
This survey is a mosaic of images taken by the ROSAT Wide Field Camera and
comprises of 12,743 seperates fields in each of two filters. Each field
covers a region 2.6° x 2.6° with a
0.3° overlap. Currently, this data is not a complete coverage of
the sky; regions near the northern ecliptic pole are currently not
included.
| Provenance | University of Leicester |
| Copyright | University of Leicester used by permission (no
restrictions on not for profit use) |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 2 |
| Frequency | 19.3 PHz |
| Bandpass | 15-27 PHz |
| Coverage | all-sky |
| PixelScale | 1 arcminute/pixel |
| PixelUnit | Counts |
| Resolution | 3' |
| Coordinates | Ecliptic |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-01 |
| Reference |
ADS
|
ROSAT Wide Field Camera: F2
Short name[s] used to specify survey:wfcf2, ROSAT WFC F2
Description
This survey is a mosaic of images taken by the ROSAT Wide Field Camera and
comprises of 12,743 seperates fields in each of two filters. Each field
covers a region 2.6° x 2.6° with a
0.3° overlap. Currently, this data is not a complete coverage of
the sky; regions near the northern ecliptic pole are currently not
included.
| Provenance | University of Leicester |
| Copyright | University of Leicester used by permission (no
restrictions on not for profit use) |
| Regime | Ultraviolet |
| NSurvey | 2 |
| Frequency | 30 PHz |
| Bandpass | 21-50 PHz |
| Coverage | all-sky |
| PixelScale | 1 arcminute/pixel |
| PixelUnit | Counts |
| Resolution | 3' |
| Coordinates | Ecliptic |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-01 |
| Reference |
ADS
|
X-ray surveys
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 14-20 keV: flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-flux-1, BAT flux 1, BAT flux 14-20
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
| Provenance |
NASA BAT Team
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 4.04 EHz |
| Bandpass | 3.38-4.84 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 2.8' |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/det |
| Resolution | 20' |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 2005-2010 |
| Reference |
The 70-Month Swift-BAT Hard X-ray Survey,
(Baumgartner et al 2013)
|
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 14-20 keV: snr
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-snr-1, BAT snr 1, BAT snr 14-20
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 20-24 keV: flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-flux-2, BAT flux 2, BAT flux 20-24
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
| Provenance |
NASA BAT Team
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 5.29 EHz |
| Bandpass | 4.84-5.80 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 2.8' |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/det |
| Resolution | 20' |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 2005-2010 |
| Reference |
The 70-Month Swift-BAT Hard X-ray Survey,
(Baumgartner et al 2013)
|
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 20-24 keV: snr
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-snr-2, BAT snr 2, BAT snr 20-24
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 24-35 keV: flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-flux-3, BAT flux 3, BAT flux 24-35
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
| Provenance |
NASA BAT Team
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 7.00 EHz |
| Bandpass | 5.80-8.46 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 2.8' |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/det |
| Resolution | 20' |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 2005-2010 |
| Reference |
The 70-Month Swift-BAT Hard X-ray Survey,
(Baumgartner et al 2013)
|
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 24-35 keV: snr
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-snr-3, BAT snr 3, BAT snr 24-35
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 35-50 keV: flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-flux-4, BAT flux 4, BAT flux 35-50
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
| Provenance |
NASA BAT Team
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 10.1 EHz |
| Bandpass | 8.46-12.1 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 2.8' |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/det |
| Resolution | 20' |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 2005-2010 |
| Reference |
The 70-Month Swift-BAT Hard X-ray Survey,
(Baumgartner et al 2013)
|
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 35-50 keV: snr
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-snr-4, BAT snr 4, BAT snr 35-50
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 50-75 keV: flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-flux-5, BAT flux 5, BAT flux 50-75
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
| Provenance |
NASA BAT Team
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 14.8 EHz |
| Bandpass | 12.1-18.1 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 2.8' |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/det |
| Resolution | 20' |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 2005-2010 |
| Reference |
The 70-Month Swift-BAT Hard X-ray Survey,
(Baumgartner et al 2013)
|
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 50-75 keV: snr
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-snr-5, BAT snr 5, BAT snr 50-75
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 75-100 keV: flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-flux-6, BAT flux 6, BAT flux 75-100
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
| Provenance |
NASA BAT Team
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 20.9 EHz |
| Bandpass | 18.1-24.2 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 2.8' |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/det |
| Resolution | 20' |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 2005-2010 |
| Reference |
The 70-Month Swift-BAT Hard X-ray Survey,
(Baumgartner et al 2013)
|
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 75-100 keV: snr
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-snr-6, BAT snr 6, BAT snr 75-100
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 100-150 keV: flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-flux-7, BAT flux 7, BAT flux 100-150
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
| Provenance |
NASA BAT Team
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 29.6 EHz |
| Bandpass | 24.2-36.3 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 2.8' |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/det |
| Resolution | 20' |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 2005-2010 |
| Reference |
The 70-Month Swift-BAT Hard X-ray Survey,
(Baumgartner et al 2013)
|
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 100-150 keV: snr
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-snr-7, BAT snr 7, BAT snr 100-150
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 150-195 keV: flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-flux-8, BAT flux 8, BAT flux 150-195
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
| Provenance |
NASA BAT Team
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 9 |
| Frequency | 41.4 EHz |
| Bandpass | 36.3-48.2 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 2.8' |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/det |
| Resolution | 20' |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 2005-2010 |
| Reference |
The 70-Month Swift-BAT Hard X-ray Survey,
(Baumgartner et al 2013)
|
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 150-195 keV: snr
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-snr-8, BAT snr 8, BAT snr 150-195
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
Swift BAT 70 Month All-Sky Survey: 14-195 keV: snr
Short name[s] used to specify survey:BAT-snr-sum, BAT snr sum, BAT snr 14-195
Description
This BAT Hard X-ray Survey data is the 70-month survey product of the BAT instrument on
the Swift observatory. Swift/BAT is a wide field-of-view (70x100
degrees) hard X-ray imager consisting of a coded mask and a large array
of CdZnTe detectors (with an effective area of ~ 5000 cm2).
BAT is sensitive in the energy range 14-195 keV. The data are divided
into 8 energy bands
| Band | Energy (keV) | Frequency (EHz) |
|---|
| 1 | 14-20 | 3.38-4.84 |
| 2 | 20-24 | 4.84-5.80 |
| 3 | 24-35 | 5.80-8.46 |
| 4 | 35-50 | 8.46-12.1 |
| 5 | 50-75 | 12.1-18.1 |
| 6 | 75-100 | 18.1-24.2 |
| 7 | 100-150 | 24.2-36.3 |
| 8 | 150-195 | 36.3-47.2 |
| Sum (SNR only) | 14-195 | 3.38-47.2 |
Each band is represented as as two separate surveys, a signal-to-noise (SNR) map and a flux map.
(e.g., BAT-snr-1 or BAT SNR 1 or BAT SNR 14-20, or BAT-Flux-1, ...).
An additional summed survey, BAT-SNR-SUM or BAT SNR SUM or BAT SNR 14-195, is also available, but there
is no summed flux survey. In our Web interface only the SNR surveys are
shown in the Web form. Users can get flux maps corresponding to a given SNR image
from the results pages. The batch interfaces may directly query any of the surveys since
the user chooses the names explicitly rather than from a selection box.
The values displayed in the significance
maps are the local signal to noise ratio in each pixel. The noise in
these coded-mask images follows a Gaussian distribution with center at
zero and a characteristic width (sigma) of 1.0. The noise is
calculated locally for each pixel by measuring the RMS value of all
pixel values in an annulus around each pixel and hence includs both
statistical and systematic components. Known sources are excluded from
the annuli.
The signal in each pixel is taken from the flux maps.
The flux values are in the native BAT survey units of
counts/sec/detector. The detector is an individual piece of CZT in
the BAT array with an area of 1.6 x 10-7m2.
While the Swift mission is primarily designed to follow gamma-ray bursts,
the random distribution of bursts in the sky means that these survey's sky coverage
is relatively uniform with the exposure at any point varying between about 6 to 16 megaseconds.
The survey limits for source detection are about 10-11 ergs/s/cm2
over about half the sky and 1.3x10-11 ergs/s/cm2 over 90%.
These data replace the 9-month BAT datasets which we have retired. If you wish access to the older data please let us know.
Note that for the 9-month data we provided access through the web page to the flux data
and gave links to the signal-to-noise maps. Since the existence of sources is most
easily seen in the SNR maps, we decided to invert that for this release.
For the 8 band data, the source data were provided by the BAT team as 6 FITS files. Each of these contained the 8 bands in separate image
extensions for a region centered at l=0,b=+/-90 or l=0,90,180,270,b=0, the centers of 6 cubic facets. However these data are not the classical
cube-faced projections, e.g., as used in COBE data. The data on the facets overlap, so that this is just a convenient way to tile the sky.
SkyView separated each of the FITS image extensions into a separate file, but no other modifications were made to the data. The summed image was
provided as six separate files.
GOODS Chandra ACIS: Full band (0.5-8 keV)
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSACISFB,GOODS: Chandra ACIS FB, GOODS ACIS FB
Description
This survey comprises the 2 Ms Chandra Deep Field North and 4 Ms Deep Field South ACIS observations.
All observations are co-added into two fields in the north and south. Data are provided in three bands,
the soft 0.5-2 keV band, the hard 2.0-8.0 keV and the full 0.5 to 8 keV band.
| Provenance |
Taken from the Neil Brandt's PSU web sites for the the
north
and
south.
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 480 PHz |
| Bandpass | 121-1900 PHz |
| Coverage | Approximately 10.e-5 around two goods regions (roughly 0.4 square degrees) |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| PixelScale | 0.5" |
| PixelUnits | Counts |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1999/2010 |
| Reference |
Published descriptions of the North and
South field observations.
|
GOODS Chandra ACIS: Hard band (2-8 keV)
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSACISHB,GOODS: Chandra ACIS HB, GOODS ACIS HB
Description
This survey comprises the 2 Ms Chandra Deep Field North and 4 Ms Deep Field South ACIS observations.
All observations are co-added into two fields in the north and south. Data are provided in three bands,
the soft 0.5-2 keV band, the hard 2.0-8.0 keV and the full 0.5 to 8 keV band.
| Provenance |
Taken from the Neil Brandt's PSU web sites for the the
north
and
south.
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 960 PHz |
| Bandpass | 480-1900 PHz |
| Coverage | Approximately 10.e-5 around two goods regions (roughly 0.4 square degrees) |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| PixelScale | 0.5" |
| PixelUnits | Counts |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1999/2010 |
| Reference |
Published descriptions of the North and
South field observations.
|
GOODS Chandra ACIS: Soft band (0.5-2 keV)
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GOODSACISSB,GOODS: Chandra ACIS SB, GOODS ACIS SB
Description
This survey comprises the 2 Ms Chandra Deep Field North and 4 Ms Deep Field South ACIS observations.
All observations are co-added into two fields in the north and south. Data are provided in three bands,
the soft 0.5-2 keV band, the hard 2.0-8.0 keV and the full 0.5 to 8 keV band.
| Provenance |
Taken from the Neil Brandt's PSU web sites for the the
north
and
south.
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 121-480 PHz |
| Coverage | Approximately 10.e-5 around two goods regions (roughly 0.4 square degrees) |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| PixelScale | 0.5" |
| PixelUnits | Counts |
| CoordinateSystem | ICRS |
| Resolution | 1" |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1999/2010 |
| Reference |
Published descriptions of the North and
South field observations.
|
GRANAT/SIGMA Flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GRANAT_SIGMA_Flux,GRANAT/SIGMA Flux,
Description
The Soviet orbital observatory GRANAT was launched in December 1989 and
was operational till November 1998. One of the main instruments
of the observatory was the French-Soviet hard X-ray coded mask telescope SIGMA
(Paul et al.1 1991, Adv.Space Res., 11, 279). It was the first
space telescope that used coded aperture technique for reconstruction of
sky images in hard X-rays (35-1300 keV). The angular
resolution of the telescope was approximately 12' and the accuracy of a source
localization is approximately 2-3'.
SIGMA discovered numerous interesting hard X-ray sources including
GRS 1758-258, which is located
only 40' from bright soft X-ray source GX 5-1. It
detected hard X-ray flux from X-ray burster A1742-294, which is very
near to bright black hole binary 1E1740.7-2942. SIGMA set an upper
limit on the hard X-ray flux of from the central supermassive black hole in
our Galaxy.
During the period 1990-1998 SIGMA observed more that one quarter of the sky
with sensitivity better than 100 mCrab. The Galactic Center region
had the deepest exposure ( approximately 9 million sec), with the
sensitivity to a source discovery (S/N > ~ 5) or approximately
10 mCrab.
A list of all detected sources with references to publications
on them is presented in the paper of Revnivtsev et al. 2004, Astr. Lett. v.6.
In these survey images (40-100 keV) all performed observations are
averaged together. Transient sources that were discovered by
SIGMA may not visible in the averaged image.
This survey has some features that users should
keep in mind. The SIGMA telescope is a complicated instrument and
is strongly dominated by the accuracy of the background subtraction.
The presence of a very bright source in the field of view of the telescope
sometimes cannot be fully accounted for and as a result of it some 'ghost'
sources can appear. Such features can be seen in the regions near
very bright sources like Crab Nebula, Cyg X-1, Nova Per 1992,
Nova Mus 1991, Nova Oph 1993, and in the Galactic Center region.
In addition to its nominal field of view (~17x17 deg)
located around the optical axis of the telescope, SIGMA had another
window of relatively high transparency of its shield,
approximately 20-30° apart from the optical axis.
Becuase of this a very bright sources like Cyg X-1 can
cause non zero illumination of the SIGMA
detector if they are located approximately 20-30° from the optical axis.
The ring-like features caused by this effect, can be seen around Cyg X-1,
and Nova Per 1992.
The count rate of detected sources (or upper limits)
can be roughly translated into mCrab using the fact that
that Crab nebula gives the count rate approximately 2.8e-3 cnts/s in the units, provided in 'flux' maps
| Provenance |
High Energy Astrophysics Department,
Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia; CEA, Centre d'Etudes de
Saclay Orme des Merisiers, France; Centre d'Etude Spatiale
des Rayonnements, Toulouse, France; Fédération de
Recherche Astroparticule et Cosmologie Université de Paris, France
|
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 2 (significance and flux) |
| Frequency | 16 EHz |
| Bandpass | 10-24 EHz |
| Coverage | Approximately one quarter of the sky |
| PixelScale | 3.24 arc minutes/pix |
| Units | Statistical significance, Flux |
| Resolution | 12 arc minutes |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Equinox | 1950 |
| Epoch | 1983-1989 |
| Reference |
Hard X-ray sky survey with the SIGMA telescope aboard
GRANAT observatory,
Revnivtsev M., Sunyaev R., Gilfanov M., Churazov E., Goldwurm A., Paul J.,
Mandrou P., Roques J.-P., Astronomy Letters 2004, v.30 (ADS)
|
GRANAT/SIGMA Significance
Short name[s] used to specify survey:GRANAT_SIGMA_Sig,GRANAT/SIGMA Sig,
GRANAT/SIGMA
Description
The Soviet orbital observatory GRANAT was launched in December 1989 and
was operational till November 1998. One of the main instruments
of the observatory was the French-Soviet hard X-ray coded mask telescope SIGMA
(Paul et al.1 1991, Adv.Space Res., 11, 279). It was the first
space telescope that used coded aperture technique for reconstruction of
sky images in hard X-rays (35-1300 keV). The angular
resolution of the telescope was approximately 12' and the accuracy of a source
localization is approximately 2-3'.
SIGMA discovered numerous interesting hard X-ray sources including
GRS 1758-258, which is located
only 40' from bright soft X-ray source GX 5-1. It
detected hard X-ray flux from X-ray burster A1742-294, which is very
near to bright black hole binary 1E1740.7-2942. SIGMA set an upper
limit on the hard X-ray flux of from the central supermassive black hole in
our Galaxy.
During the period 1990-1998 SIGMA observed more that one quarter of the sky
with sensitivity better than 100 mCrab. The Galactic Center region
had the deepest exposure ( approximately 9 million sec), with the
sensitivity to a source discovery (S/N > ~ 5) or approximately
10 mCrab.
A list of all detected sources with references to publications
on them is presented in the paper of Revnivtsev et al. 2004, Astr. Lett. v.6.
In these survey images (40-100 keV) all performed observations are
averaged together. Transient sources that were discovered by
SIGMA may not visible in the averaged image.
This survey has some features that users should
keep in mind. The SIGMA telescope is a complicated instrument and
is strongly dominated by the accuracy of the background subtraction.
The presence of a very bright source in the field of view of the telescope
sometimes cannot be fully accounted for and as a result of it some 'ghost'
sources can appear. Such features can be seen in the regions near
very bright sources like Crab Nebula, Cyg X-1, Nova Per 1992,
Nova Mus 1991, Nova Oph 1993, and in the Galactic Center region.
In addition to its nominal field of view (~17x17 deg)
located around the optical axis of the telescope, SIGMA had another
window of relatively high transparency of its shield,
approximately 20-30° apart from the optical axis.
Becuase of this a very bright sources like Cyg X-1 can
cause non zero illumination of the SIGMA
detector if they are located approximately 20-30° from the optical axis.
The ring-like features caused by this effect, can be seen around Cyg X-1,
and Nova Per 1992.
The count rate of detected sources (or upper limits)
can be roughly translated into mCrab using the fact that
that Crab nebula gives the count rate approximately 2.8e-3 cnts/s in the units, provided in 'flux' maps
| Provenance |
High Energy Astrophysics Department,
Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia; CEA, Centre d'Etudes de
Saclay Orme des Merisiers, France; Centre d'Etude Spatiale
des Rayonnements, Toulouse, France; Fédération de
Recherche Astroparticule et Cosmologie Université de Paris, France
|
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 2 (significance and flux) |
| Frequency | 16 EHz |
| Bandpass | 10-24 EHz |
| Coverage | Approximately one quarter of the sky |
| PixelScale | 3.24 arc minutes/pix |
| Units | Statistical significance, Flux |
| Resolution | 12 arc minutes |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Equinox | 1950 |
| Epoch | 1983-1989 |
| Reference |
Hard X-ray sky survey with the SIGMA telescope aboard
GRANAT observatory,
Revnivtsev M., Sunyaev R., Gilfanov M., Churazov E., Goldwurm A., Paul J.,
Mandrou P., Roques J.-P., Astronomy Letters 2004, v.30 (ADS)
|
HEAO 1A
Short name[s] used to specify survey:HEAO1A, HEAO 1 A-2
Description
These data were generated at the HEASARC in 1994. Certain
gaps and streaks in the image have been fixed by interpolating
over the the gap. Typically these gaps are no more than a pixel
or two wide. A brief description of the satellite and the
data analysis follows. The map used in SkyView
is the map designated 322_15_tot_ecl_samp.img in the
HEASARC FTP area. Many other maps are available. These differ
in epoch, resolution, energy band,
coordinate system and projection, and sampling methods.
Details are given in the README file in the archive.
See Allen, Jahoda, and Whitlock (1994) for full details about the
available maps, their processing, and methods for converting the
map intensities into familiar physical units.
| Provenance | NASA, HEASARC |
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 2.4 EHz |
| Bandpass | 0.48-14.5 EHz |
| CoordinateSystem | Ecliptic |
| Projection | Cartesion |
| PixelScale | 0.5x0.25 degrees |
| Units | Counts/Secont |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Resolution | Approxmately 2 degrees |
| Epoch | 1978 to 1979 |
| Reference |
Shafer, R.A. 1983, Spatial Fluctuations in the
Diffuse X-Ray Background, University of Maryland Ph.D. thesis.
Allen, J., Jahoda, K., and Whitlock, L. 1994, HEAO-1 and the A2 experiment,
Legacy, 5.
also
HEAO1
|
ROSAT High Resolution Image Pointed Observations Mosaic: Intensity
Short name[s] used to specify survey:HRIint, HRI
Description
This survey was generated from all available ROSAT HRI observations. Data
were mosaicked into 1.1 degree tiles by SkyView. Exposure maps were
generated for each HRI observation using the hriexpmap FTOOL. For each
tile, all observations that might contribute to that tile were located and
added to count and exposure map tiles. Exposures for each observation were
calculated using a nearest neighbor interpolation of the center of the tile
pixels to the exposure map pixels. Counts were computed by projecting the
RA and Decs of each eligible photon into the appropriate tile pixel.
Only photons with a PHA > 3 were included in the mosaic and within each
observation only counts within the region where the exposure was greater
than half the maximum exposure were included.
| Provenance |
Data from GSFC and MPE. SkyView mosaic generated by SkyView.
|
| Copyright |
Public Domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 260 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-480 PHz |
| Coverage | Observation patches covering ~1.8% of the sky. |
| PixelScale | 5" |
| PixelUnits | |
| Resolution | 10" |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1991 to 1999 |
| Reference |
The ROSAT High Resolution Imager (HRI) Calibration Report
|
INTEGRAL/Spectral Imager Galactic Center Survey
Short name[s] used to specify survey:INTEGRALSPI_gc, INTEGRAL/SPI GC
Description
The INTEGRAL observatory (Winkler et al. 2003, A&A, 411, L1) was
launched in October 2002. The spectrograph SPI (Vedrenne et al. 2003,
A&A, 411, L63) consists of 19 Germanium detectors and is capable of
imaging in the 20 - 8000 keV band because of a coded mask. Part of the
core program of the INTEGRAL mission is a study of the Galactic Centre,
the Galactic Centre Deep Exposure (GCDE).
The SPI significance map is based on the public GCDE data and
uses data in the 20 - 40 keV energy range. The analysis of the data was
done using the SPIROS software (Skinner & Connell 2003, A&A, 411, L123).
This software uses the 'Iterative Removal of Sources' technique in order
to find the most significant sources. In the output significance map the
sources found in this process are put on top of the residual map as
points with a FWHM of 1 degree.
Current data respresent the combination of all public observations as of
September 1, 2004.
| Provenance |
INTEGRAL Science Data Center, Geneva, Switzerland
|
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 6.8 EHz |
| Bandpass | 2.9-4.8 EHz |
| Coverage |
|
| PixelScale | 6 arc minutes/pix |
| Units | Statistical significance |
| Resolution | approximately 1 degree |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Aitoff |
| Epoch | March 2002 - May 2003 |
| Reference |
INTEGRAL Guest Observer Facility
SPI Reference at (ADS)
|
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-35 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Exposure
Short name[s] used to specify survey:INT GAL 17-35 Exp, INTGAL1735E
Description
This survey combines 9 years of INTEGRAL IBIS observations from December 2002
through January 2011 into a single Galactic Plane image. A total of 135 megaseconds
of exposure is included in the observations used. Survey data is generated for
the Galactic plane in the region |b| <= 17.5. The original flux data has been convolved with
5' seeing kernel. To minimize loss of resolution in transformations, the Lanczos sampler is
suggested as the default, but may be overriden by the user.
Both the preconvolved and standard
convolved maps are available at the Web site.
The exposure and sensitivity vary considerably over the coverage region, but 90% of the field
has a limiting sensitivity better than 2.2 x 10-11ergs s-1cm-2
or about 1.56 mCrab. Further details of the survey construction are given in the reference.
The flux and significance maps use the PSF convolved maps from the survey. The flux maps are in millicrab units.
Exposure maps (with exposures in seconds) were from the exposure extension in the MAPDLD files and
give the dead-time corrected exposure in seconds.
Links to the exposure and significance maps corresponding to the requested region will
be given in the Web output. These maps can be generated directly in the CLI interface.
For each waveband the flux, significance and exposure maps are available with just the
end of the survey names distinguishing them (e.g., INT Gal 17-35 [Flux|Sig|Exp] or
INTGal1735[F|S|E])
| Provenance |
Krivonos et al., 2012
Based on observations with INTEGRAL, an ESA project with instruments and
science data centre funded by ESA member states (especially the PI countries:
Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and Spain), Poland, and participation
of Russia and the USA.
|
| Copyright | Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 6 EHz |
| Bandpass | 4.4-8.5 EHz |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| PixelScale | 4' |
| Units | Flux (milliCrabs), Exposure (s) and Significance |
| Coverage | Galactic plane, |b| < 17.5 (30% of the sky) |
| NSurvey | 9 [(Flux,Significance,Exposure) x 3 bands] |
| Resolution | Gaussian 5' |
| Epoch | December 2002 to January 2011 |
| Reference |
Survey paper: Krivonos et al., 2012
Web site
|
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-35 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:INT GAL 17-35 Flux, INTGAL1735F
Description
This survey combines 9 years of INTEGRAL IBIS observations from December 2002
through January 2011 into a single Galactic Plane image. A total of 135 megaseconds
of exposure is included in the observations used. Survey data is generated for
the Galactic plane in the region |b| <= 17.5. The original flux data has been convolved with
5' seeing kernel. To minimize loss of resolution in transformations, the Lanczos sampler is
suggested as the default, but may be overriden by the user.
Both the preconvolved and standard
convolved maps are available at the Web site.
The exposure and sensitivity vary considerably over the coverage region, but 90% of the field
has a limiting sensitivity better than 2.2 x 10-11ergs s-1cm-2
or about 1.56 mCrab. Further details of the survey construction are given in the reference.
The flux and significance maps use the PSF convolved maps from the survey. The flux maps are in millicrab units.
Exposure maps (with exposures in seconds) were from the exposure extension in the MAPDLD files and
give the dead-time corrected exposure in seconds.
Links to the exposure and significance maps corresponding to the requested region will
be given in the Web output. These maps can be generated directly in the CLI interface.
For each waveband the flux, significance and exposure maps are available with just the
end of the survey names distinguishing them (e.g., INT Gal 17-35 [Flux|Sig|Exp] or
INTGal1735[F|S|E])
| Provenance |
Krivonos et al., 2012
Based on observations with INTEGRAL, an ESA project with instruments and
science data centre funded by ESA member states (especially the PI countries:
Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and Spain), Poland, and participation
of Russia and the USA.
|
| Copyright | Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 6 EHz |
| Bandpass | 4.4-8.5 EHz |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| PixelScale | 4' |
| Units | Flux (milliCrabs), Exposure (s) and Significance |
| Coverage | Galactic plane, |b| < 17.5 (30% of the sky) |
| NSurvey | 9 [(Flux,Significance,Exposure) x 3 bands] |
| Resolution | Gaussian 5' |
| Epoch | December 2002 to January 2011 |
| Reference |
Survey paper: Krivonos et al., 2012
Web site
|
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-35 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Significance
Short name[s] used to specify survey:INT GAL 17-35 Sig, INTGAL1735S
Description
This survey combines 9 years of INTEGRAL IBIS observations from December 2002
through January 2011 into a single Galactic Plane image. A total of 135 megaseconds
of exposure is included in the observations used. Survey data is generated for
the Galactic plane in the region |b| <= 17.5. The original flux data has been convolved with
5' seeing kernel. To minimize loss of resolution in transformations, the Lanczos sampler is
suggested as the default, but may be overriden by the user.
Both the preconvolved and standard
convolved maps are available at the Web site.
The exposure and sensitivity vary considerably over the coverage region, but 90% of the field
has a limiting sensitivity better than 2.2 x 10-11ergs s-1cm-2
or about 1.56 mCrab. Further details of the survey construction are given in the reference.
The flux and significance maps use the PSF convolved maps from the survey. The flux maps are in millicrab units.
Exposure maps (with exposures in seconds) were from the exposure extension in the MAPDLD files and
give the dead-time corrected exposure in seconds.
Links to the exposure and significance maps corresponding to the requested region will
be given in the Web output. These maps can be generated directly in the CLI interface.
For each waveband the flux, significance and exposure maps are available with just the
end of the survey names distinguishing them (e.g., INT Gal 17-35 [Flux|Sig|Exp] or
INTGal1735[F|S|E])
| Provenance |
Krivonos et al., 2012
Based on observations with INTEGRAL, an ESA project with instruments and
science data centre funded by ESA member states (especially the PI countries:
Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and Spain), Poland, and participation
of Russia and the USA.
|
| Copyright | Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 6 EHz |
| Bandpass | 4.4-8.5 EHz |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| PixelScale | 4' |
| Units | Flux (milliCrabs), Exposure (s) and Significance |
| Coverage | Galactic plane, |b| < 17.5 (30% of the sky) |
| NSurvey | 9 [(Flux,Significance,Exposure) x 3 bands] |
| Resolution | Gaussian 5' |
| Epoch | December 2002 to January 2011 |
| Reference |
Survey paper: Krivonos et al., 2012
Web site
|
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-60 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Exposure
Short name[s] used to specify survey:INT GAL 17-60 Exp, INTGAL1760E
Description
This survey combines 9 years of INTEGRAL IBIS observations from December 2002
through January 2011 into a single Galactic Plane image. A total of 135 megaseconds
of exposure is included in the observations used. Survey data is generated for
the Galactic plane in the region |b| <= 17.5. The original flux data has been convolved with
5' seeing kernel. To minimize loss of resolution in transformations, the Lanczos sampler is
suggested as the default, but may be overriden by the user.
Both the preconvolved and standard
convolved maps are available at the Web site.
The exposure and sensitivity vary considerably over the coverage region, but 90% of the field
has a limiting sensitivity better than 2.2 x 10-11ergs s-1cm-2
or about 1.56 mCrab. Further details of the survey construction are given in the reference.
The flux and significance maps use the PSF convolved maps from the survey. The flux maps are in millicrab units.
Exposure maps (with exposures in seconds) were from the exposure extension in the MAPDLD files and
give the dead-time corrected exposure in seconds.
Links to the exposure and significance maps corresponding to the requested region will
be given in the Web output. These maps can be generated directly in the CLI interface.
For each waveband the flux, significance and exposure maps are available with just the
end of the survey names distinguishing them (e.g., INT Gal 17-35 [Flux|Sig|Exp] or
INTGal1735[F|S|E])
| Provenance |
Krivonos et al., 2012
Based on observations with INTEGRAL, an ESA project with instruments and
science data centre funded by ESA member states (especially the PI countries:
Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and Spain), Poland, and participation
of Russia and the USA.
|
| Copyright | Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 8 EHz |
| Bandpass | 4.4-14 EHz |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| PixelScale | 4' |
| Units | Flux (milliCrabs), Exposure (s) and Significance |
| Coverage | Galactic plane, |b| < 17.5 (30% of the sky) |
| NSurvey | 9 [(Flux,Significance,Exposure) x 3 bands] |
| Resolution | Gaussian 5' |
| Epoch | December 2002 to January 2011 |
| Reference |
Survey paper: Krivonos et al., 2012
Web site
|
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-60 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:INT GAL 17-60 Flux, INTGAL1760F
Description
This survey combines 9 years of INTEGRAL IBIS observations from December 2002
through January 2011 into a single Galactic Plane image. A total of 135 megaseconds
of exposure is included in the observations used. Survey data is generated for
the Galactic plane in the region |b| <= 17.5. The original flux data has been convolved with
5' seeing kernel. To minimize loss of resolution in transformations, the Lanczos sampler is
suggested as the default, but may be overriden by the user.
Both the preconvolved and standard
convolved maps are available at the Web site.
The exposure and sensitivity vary considerably over the coverage region, but 90% of the field
has a limiting sensitivity better than 2.2 x 10-11ergs s-1cm-2
or about 1.56 mCrab. Further details of the survey construction are given in the reference.
The flux and significance maps use the PSF convolved maps from the survey. The flux maps are in millicrab units.
Exposure maps (with exposures in seconds) were from the exposure extension in the MAPDLD files and
give the dead-time corrected exposure in seconds.
Links to the exposure and significance maps corresponding to the requested region will
be given in the Web output. These maps can be generated directly in the CLI interface.
For each waveband the flux, significance and exposure maps are available with just the
end of the survey names distinguishing them (e.g., INT Gal 17-35 [Flux|Sig|Exp] or
INTGal1735[F|S|E])
| Provenance |
Krivonos et al., 2012
Based on observations with INTEGRAL, an ESA project with instruments and
science data centre funded by ESA member states (especially the PI countries:
Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and Spain), Poland, and participation
of Russia and the USA.
|
| Copyright | Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 8 EHz |
| Bandpass | 4.4-14 EHz |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| PixelScale | 4' |
| Units | Flux (milliCrabs), Exposure (s) and Significance |
| Coverage | Galactic plane, |b| < 17.5 (30% of the sky) |
| NSurvey | 9 [(Flux,Significance,Exposure) x 3 bands] |
| Resolution | Gaussian 5' |
| Epoch | December 2002 to January 2011 |
| Reference |
Survey paper: Krivonos et al., 2012
Web site
|
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 17-60 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Significance
Short name[s] used to specify survey:INT GAL 17-60 Sig, INTGAL1760S
Description
This survey combines 9 years of INTEGRAL IBIS observations from December 2002
through January 2011 into a single Galactic Plane image. A total of 135 megaseconds
of exposure is included in the observations used. Survey data is generated for
the Galactic plane in the region |b| <= 17.5. The original flux data has been convolved with
5' seeing kernel. To minimize loss of resolution in transformations, the Lanczos sampler is
suggested as the default, but may be overriden by the user.
Both the preconvolved and standard
convolved maps are available at the Web site.
The exposure and sensitivity vary considerably over the coverage region, but 90% of the field
has a limiting sensitivity better than 2.2 x 10-11ergs s-1cm-2
or about 1.56 mCrab. Further details of the survey construction are given in the reference.
The flux and significance maps use the PSF convolved maps from the survey. The flux maps are in millicrab units.
Exposure maps (with exposures in seconds) were from the exposure extension in the MAPDLD files and
give the dead-time corrected exposure in seconds.
Links to the exposure and significance maps corresponding to the requested region will
be given in the Web output. These maps can be generated directly in the CLI interface.
For each waveband the flux, significance and exposure maps are available with just the
end of the survey names distinguishing them (e.g., INT Gal 17-35 [Flux|Sig|Exp] or
INTGal1735[F|S|E])
| Provenance |
Krivonos et al., 2012
Based on observations with INTEGRAL, an ESA project with instruments and
science data centre funded by ESA member states (especially the PI countries:
Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and Spain), Poland, and participation
of Russia and the USA.
|
| Copyright | Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 8 EHz |
| Bandpass | 4.4-14 EHz |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| PixelScale | 4' |
| Units | Flux (milliCrabs), Exposure (s) and Significance |
| Coverage | Galactic plane, |b| < 17.5 (30% of the sky) |
| NSurvey | 9 [(Flux,Significance,Exposure) x 3 bands] |
| Resolution | Gaussian 5' |
| Epoch | December 2002 to January 2011 |
| Reference |
Survey paper: Krivonos et al., 2012
Web site
|
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 35-80 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Exposure
Short name[s] used to specify survey:INT GAL 35-80 Exp, INTGAL3580E
Description
This survey combines 9 years of INTEGRAL IBIS observations from December 2002
through January 2011 into a single Galactic Plane image. A total of 135 megaseconds
of exposure is included in the observations used. Survey data is generated for
the Galactic plane in the region |b| <= 17.5. The original flux data has been convolved with
5' seeing kernel. To minimize loss of resolution in transformations, the Lanczos sampler is
suggested as the default, but may be overriden by the user.
Both the preconvolved and standard
convolved maps are available at the Web site.
The exposure and sensitivity vary considerably over the coverage region, but 90% of the field
has a limiting sensitivity better than 2.2 x 10-11ergs s-1cm-2
or about 1.56 mCrab. Further details of the survey construction are given in the reference.
The flux and significance maps use the PSF convolved maps from the survey. The flux maps are in millicrab units.
Exposure maps (with exposures in seconds) were from the exposure extension in the MAPDLD files and
give the dead-time corrected exposure in seconds.
Links to the exposure and significance maps corresponding to the requested region will
be given in the Web output. These maps can be generated directly in the CLI interface.
For each waveband the flux, significance and exposure maps are available with just the
end of the survey names distinguishing them (e.g., INT Gal 17-35 [Flux|Sig|Exp] or
INTGal1735[F|S|E])
| Provenance |
Krivonos et al., 2012
Based on observations with INTEGRAL, an ESA project with instruments and
science data centre funded by ESA member states (especially the PI countries:
Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and Spain), Poland, and participation
of Russia and the USA.
|
| Copyright | Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 12 EHz |
| Bandpass | 7.2-20 EHz |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| PixelScale | 4' |
| Units | Flux (milliCrabs), Exposure (s) and Significance |
| Coverage | Galactic plane, |b| < 17.5 (30% of the sky) |
| NSurvey | 9 [(Flux,Significance,Exposure) x 3 bands] |
| Resolution | Gaussian 5' |
| Epoch | December 2002 to January 2011 |
| Reference |
Survey paper: Krivonos et al., 2012
Web site
|
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 35-80 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:INT GAL 35-80 Flux, INTGAL3580F
Description
This survey combines 9 years of INTEGRAL IBIS observations from December 2002
through January 2011 into a single Galactic Plane image. A total of 135 megaseconds
of exposure is included in the observations used. Survey data is generated for
the Galactic plane in the region |b| <= 17.5. The original flux data has been convolved with
5' seeing kernel. To minimize loss of resolution in transformations, the Lanczos sampler is
suggested as the default, but may be overriden by the user.
Both the preconvolved and standard
convolved maps are available at the Web site.
The exposure and sensitivity vary considerably over the coverage region, but 90% of the field
has a limiting sensitivity better than 2.2 x 10-11ergs s-1cm-2
or about 1.56 mCrab. Further details of the survey construction are given in the reference.
The flux and significance maps use the PSF convolved maps from the survey. The flux maps are in millicrab units.
Exposure maps (with exposures in seconds) were from the exposure extension in the MAPDLD files and
give the dead-time corrected exposure in seconds.
Links to the exposure and significance maps corresponding to the requested region will
be given in the Web output. These maps can be generated directly in the CLI interface.
For each waveband the flux, significance and exposure maps are available with just the
end of the survey names distinguishing them (e.g., INT Gal 17-35 [Flux|Sig|Exp] or
INTGal1735[F|S|E])
| Provenance |
Krivonos et al., 2012
Based on observations with INTEGRAL, an ESA project with instruments and
science data centre funded by ESA member states (especially the PI countries:
Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and Spain), Poland, and participation
of Russia and the USA.
|
| Copyright | Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 12 EHz |
| Bandpass | 7.2-20 EHz |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| PixelScale | 4' |
| Units | Flux (milliCrabs), Exposure (s) and Significance |
| Coverage | Galactic plane, |b| < 17.5 (30% of the sky) |
| NSurvey | 9 [(Flux,Significance,Exposure) x 3 bands] |
| Resolution | Gaussian 5' |
| Epoch | December 2002 to January 2011 |
| Reference |
Survey paper: Krivonos et al., 2012
Web site
|
Nine Year INTEGRAL IBIS 35-80 keV Galactic Plane Survey: Significance
Short name[s] used to specify survey:INT GAL 35-80 Sig, INTGAL3580S
Description
This survey combines 9 years of INTEGRAL IBIS observations from December 2002
through January 2011 into a single Galactic Plane image. A total of 135 megaseconds
of exposure is included in the observations used. Survey data is generated for
the Galactic plane in the region |b| <= 17.5. The original flux data has been convolved with
5' seeing kernel. To minimize loss of resolution in transformations, the Lanczos sampler is
suggested as the default, but may be overriden by the user.
Both the preconvolved and standard
convolved maps are available at the Web site.
The exposure and sensitivity vary considerably over the coverage region, but 90% of the field
has a limiting sensitivity better than 2.2 x 10-11ergs s-1cm-2
or about 1.56 mCrab. Further details of the survey construction are given in the reference.
The flux and significance maps use the PSF convolved maps from the survey. The flux maps are in millicrab units.
Exposure maps (with exposures in seconds) were from the exposure extension in the MAPDLD files and
give the dead-time corrected exposure in seconds.
Links to the exposure and significance maps corresponding to the requested region will
be given in the Web output. These maps can be generated directly in the CLI interface.
For each waveband the flux, significance and exposure maps are available with just the
end of the survey names distinguishing them (e.g., INT Gal 17-35 [Flux|Sig|Exp] or
INTGal1735[F|S|E])
| Provenance |
Krivonos et al., 2012
Based on observations with INTEGRAL, an ESA project with instruments and
science data centre funded by ESA member states (especially the PI countries:
Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and Spain), Poland, and participation
of Russia and the USA.
|
| Copyright | Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia |
| Regime | X-ray |
| Frequency | 12 EHz |
| Bandpass | 7.2-20 EHz |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Cartesian |
| PixelScale | 4' |
| Units | Flux (milliCrabs), Exposure (s) and Significance |
| Coverage | Galactic plane, |b| < 17.5 (30% of the sky) |
| NSurvey | 9 [(Flux,Significance,Exposure) x 3 bands] |
| Resolution | Gaussian 5' |
| Epoch | December 2002 to January 2011 |
| Reference |
Survey paper: Krivonos et al., 2012
Web site
|
PSPC summed pointed observations, 1 degree cutoff, Counts
Short name[s] used to specify survey:PSPC1Cnt, PSPC 1.0 Deg-Cnt, PSPC 1.0 Deg-Counts
Description
The ROSAT PSPC surveys were generated by SkyView as
mosaics from publically available PSPC observations.
The surveys include
all data available through March 1, 1997. This includes the vast majority
of ROSAT PSPC observations. Filter observations and observations taken
during the verification phase in 1991 were not included in either
set. The details of the generation of the surveys are discussed
in a
companion document.
Basically the counts and
exposure from all observations were added and then an intensity
map was generated as the ratio of the two.
The smaller
cut-offs allow users to distinguish point sources in fields where
a bright source may have been towards the edge of one observation
and near the center of another. In these cases the source appears
fuzzy due to the poor resolution of ROSAT near the edge of the field
of view. This comes at the cost of a substantial reduction in
the fraction of the sky covered. Counts and exposure maps are
included for users who may need this information (e.g., to do
statistical analysis).
The global organization of the surveys is similar
to the IRAS survey. Each map covers an area of 2.5°x2.5° with a
minimum overlap of 0.25°. To cover the entire sky would require over
10,000 maps. However due to lack of coverage only approximately 4000-6000 maps
are actually populated. Users asking for reqions where there is no ROSAT
coverage may get a blank region returned.
Detailed information regarding the creation of the ROSAT suveys
can be found in the
ROSAT PSPC Generation Document.
| Provenance |
Observational data from NASA Goddard Space
Flight Center, mosaicking of images done by SkyView.
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-580 PHz |
| Coverage |
Isolated pointings in the sky. Total
coverage < 14%
|
| PixelScale | 15" |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/pixel |
| Resolution | 30" but variable across the field of view |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1991-1994 |
| Reference |
ROSAT Mission Description and Data Products Guide, available through the ROSAT Guest Observer Facility, NASA GSFC.
SkyView Rosat Survey Generation description.
|
PSPC summed pointed observations, 1 degree cutoff, Exposure
Short name[s] used to specify survey:PSPC1Exp, PSPC 1.0 Deg-Exp, PSPC 1.0 Deg-Expos
Description
The ROSAT PSPC surveys were generated by SkyView as
mosaics from publically available PSPC observations.
The surveys include
all data available through March 1, 1997. This includes the vast majority
of ROSAT PSPC observations. Filter observations and observations taken
during the verification phase in 1991 were not included in either
set. The details of the generation of the surveys are discussed
in a
companion document.
Basically the counts and
exposure from all observations were added and then an intensity
map was generated as the ratio of the two.
The smaller
cut-offs allow users to distinguish point sources in fields where
a bright source may have been towards the edge of one observation
and near the center of another. In these cases the source appears
fuzzy due to the poor resolution of ROSAT near the edge of the field
of view. This comes at the cost of a substantial reduction in
the fraction of the sky covered. Counts and exposure maps are
included for users who may need this information (e.g., to do
statistical analysis).
The global organization of the surveys is similar
to the IRAS survey. Each map covers an area of 2.5°x2.5° with a
minimum overlap of 0.25°. To cover the entire sky would require over
10,000 maps. However due to lack of coverage only approximately 4000-6000 maps
are actually populated. Users asking for reqions where there is no ROSAT
coverage may get a blank region returned.
Detailed information regarding the creation of the ROSAT suveys
can be found in the
ROSAT PSPC Generation Document.
| Provenance |
Observational data from NASA Goddard Space
Flight Center, mosaicking of images done by SkyView.
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-580 PHz |
| Coverage |
Isolated pointings in the sky. Total
coverage < 14%
|
| PixelScale | 15" |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/pixel |
| Resolution | 30" but variable across the field of view |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1991-1994 |
| Reference |
ROSAT Mission Description and Data Products Guide, available through the ROSAT Guest Observer Facility, NASA GSFC.
SkyView Rosat Survey Generation description.
|
PSPC summed pointed observations, 1 degree cutoff, Intensity
Short name[s] used to specify survey:PSPC1Int, PSPC 1.0 Deg-Int, PSPC 1.0 Deg-Inten
Description
The ROSAT PSPC surveys were generated by SkyView as
mosaics from publically available PSPC observations.
The surveys include
all data available through March 1, 1997. This includes the vast majority
of ROSAT PSPC observations. Filter observations and observations taken
during the verification phase in 1991 were not included in either
set. The details of the generation of the surveys are discussed
in a
companion document.
Basically the counts and
exposure from all observations were added and then an intensity
map was generated as the ratio of the two.
The smaller
cut-offs allow users to distinguish point sources in fields where
a bright source may have been towards the edge of one observation
and near the center of another. In these cases the source appears
fuzzy due to the poor resolution of ROSAT near the edge of the field
of view. This comes at the cost of a substantial reduction in
the fraction of the sky covered. Counts and exposure maps are
included for users who may need this information (e.g., to do
statistical analysis).
The global organization of the surveys is similar
to the IRAS survey. Each map covers an area of 2.5°x2.5° with a
minimum overlap of 0.25°. To cover the entire sky would require over
10,000 maps. However due to lack of coverage only approximately 4000-6000 maps
are actually populated. Users asking for reqions where there is no ROSAT
coverage may get a blank region returned.
Detailed information regarding the creation of the ROSAT suveys
can be found in the
ROSAT PSPC Generation Document.
| Provenance |
Observational data from NASA Goddard Space
Flight Center, mosaicking of images done by SkyView.
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-580 PHz |
| Coverage |
Isolated pointings in the sky. Total
coverage < 14%
|
| PixelScale | 15" |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/pixel |
| Resolution | 30" but variable across the field of view |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1991-1994 |
| Reference |
ROSAT Mission Description and Data Products Guide, available through the ROSAT Guest Observer Facility, NASA GSFC.
SkyView Rosat Survey Generation description.
|
PSPC summed pointed observations, 2 degree cutoff, Counts
Short name[s] used to specify survey:PSPC2Cnt, PSPC 2.0 Deg-Cnt, PSPC 2.0 Deg-Counts
Description
The ROSAT PSPC surveys were generated by SkyView as
mosaics from publically available PSPC observations.
The surveys include
all data available through March 1, 1997. This includes the vast majority
of ROSAT PSPC observations. Filter observations and observations taken
during the verification phase in 1991 were not included in either
set. The details of the generation of the surveys are discussed
in a
companion document.
Basically the counts and
exposure from all observations were added and then an intensity
map was generated as the ratio of the two.
The smaller
cut-offs allow users to distinguish point sources in fields where
a bright source may have been towards the edge of one observation
and near the center of another. In these cases the source appears
fuzzy due to the poor resolution of ROSAT near the edge of the field
of view. This comes at the cost of a substantial reduction in
the fraction of the sky covered. Counts and exposure maps are
included for users who may need this information (e.g., to do
statistical analysis).
The global organization of the surveys is similar
to the IRAS survey. Each map covers an area of 2.5°x2.5° with a
minimum overlap of 0.25°. To cover the entire sky would require over
10,000 maps. However due to lack of coverage only approximately 4000-6000 maps
are actually populated. Users asking for reqions where there is no ROSAT
coverage may get a blank region returned.
Detailed information regarding the creation of the ROSAT suveys
can be found in the
ROSAT PSPC Generation Document.
| Provenance |
Observational data from NASA Goddard Space
Flight Center, mosaicking of images done by SkyView.
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-580 PHz |
| Coverage |
Isolated pointings in the sky. Total
coverage < 14%
|
| PixelScale | 15" |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/pixel |
| Resolution | 30" but variable across the field of view |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1991-1994 |
| Reference |
ROSAT Mission Description and Data Products Guide, available through the ROSAT Guest Observer Facility, NASA GSFC.
SkyView Rosat Survey Generation description.
|
PSPC summed pointed observations, 2 degree cutoff, Exposure
Short name[s] used to specify survey:PSPC2Exp, PSPC 2.0 Deg-Exp, PSPC 2.0 Deg-Expos
Description
The ROSAT PSPC surveys were generated by SkyView as
mosaics from publically available PSPC observations.
The surveys include
all data available through March 1, 1997. This includes the vast majority
of ROSAT PSPC observations. Filter observations and observations taken
during the verification phase in 1991 were not included in either
set. The details of the generation of the surveys are discussed
in a
companion document.
Basically the counts and
exposure from all observations were added and then an intensity
map was generated as the ratio of the two.
The smaller
cut-offs allow users to distinguish point sources in fields where
a bright source may have been towards the edge of one observation
and near the center of another. In these cases the source appears
fuzzy due to the poor resolution of ROSAT near the edge of the field
of view. This comes at the cost of a substantial reduction in
the fraction of the sky covered. Counts and exposure maps are
included for users who may need this information (e.g., to do
statistical analysis).
The global organization of the surveys is similar
to the IRAS survey. Each map covers an area of 2.5°x2.5° with a
minimum overlap of 0.25°. To cover the entire sky would require over
10,000 maps. However due to lack of coverage only approximately 4000-6000 maps
are actually populated. Users asking for reqions where there is no ROSAT
coverage may get a blank region returned.
Detailed information regarding the creation of the ROSAT suveys
can be found in the
ROSAT PSPC Generation Document.
| Provenance |
Observational data from NASA Goddard Space
Flight Center, mosaicking of images done by SkyView.
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-580 PHz |
| Coverage |
Isolated pointings in the sky. Total
coverage < 14%
|
| PixelScale | 15" |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/pixel |
| Resolution | 30" but variable across the field of view |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1991-1994 |
| Reference |
ROSAT Mission Description and Data Products Guide, available through the ROSAT Guest Observer Facility, NASA GSFC.
SkyView Rosat Survey Generation description.
|
PSPC summed pointed observations, 2 degree cutoff, Intensity
Short name[s] used to specify survey:PSPC2Int, PSPC 2.0 Deg-Int, PSPC 2.0 Deg-Inten
Description
The ROSAT PSPC surveys were generated by SkyView as
mosaics from publically available PSPC observations.
The surveys include
all data available through March 1, 1997. This includes the vast majority
of ROSAT PSPC observations. Filter observations and observations taken
during the verification phase in 1991 were not included in either
set. The details of the generation of the surveys are discussed
in a
companion document.
Basically the counts and
exposure from all observations were added and then an intensity
map was generated as the ratio of the two.
The smaller
cut-offs allow users to distinguish point sources in fields where
a bright source may have been towards the edge of one observation
and near the center of another. In these cases the source appears
fuzzy due to the poor resolution of ROSAT near the edge of the field
of view. This comes at the cost of a substantial reduction in
the fraction of the sky covered. Counts and exposure maps are
included for users who may need this information (e.g., to do
statistical analysis).
The global organization of the surveys is similar
to the IRAS survey. Each map covers an area of 2.5°x2.5° with a
minimum overlap of 0.25°. To cover the entire sky would require over
10,000 maps. However due to lack of coverage only approximately 4000-6000 maps
are actually populated. Users asking for reqions where there is no ROSAT
coverage may get a blank region returned.
Detailed information regarding the creation of the ROSAT suveys
can be found in the
ROSAT PSPC Generation Document.
| Provenance |
Observational data from NASA Goddard Space
Flight Center, mosaicking of images done by SkyView.
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-580 PHz |
| Coverage |
Isolated pointings in the sky. Total
coverage < 14%
|
| PixelScale | 15" |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/pixel |
| Resolution | 30" but variable across the field of view |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1991-1994 |
| Reference |
ROSAT Mission Description and Data Products Guide, available through the ROSAT Guest Observer Facility, NASA GSFC.
SkyView Rosat Survey Generation description.
|
PSPC summed pointed observations, 0.6 degree cutoff, Counts
Short name[s] used to specify survey:PSPC0.6Cnt, PSPC 0.6 Deg-Cnt, PSPC 0.6 Deg-Counts
Description
The ROSAT PSPC surveys were generated by SkyView as
mosaics from publically available PSPC observations.
The surveys include
all data available through March 1, 1997. This includes the vast majority
of ROSAT PSPC observations. Filter observations and observations taken
during the verification phase in 1991 were not included in either
set. The details of the generation of the surveys are discussed
in a
companion document.
Basically the counts and
exposure from all observations were added and then an intensity
map was generated as the ratio of the two.
The smaller
cut-offs allow users to distinguish point sources in fields where
a bright source may have been towards the edge of one observation
and near the center of another. In these cases the source appears
fuzzy due to the poor resolution of ROSAT near the edge of the field
of view. This comes at the cost of a substantial reduction in
the fraction of the sky covered. Counts and exposure maps are
included for users who may need this information (e.g., to do
statistical analysis).
The global organization of the surveys is similar
to the IRAS survey. Each map covers an area of 2.5°x2.5° with a
minimum overlap of 0.25°. To cover the entire sky would require over
10,000 maps. However due to lack of coverage only approximately 4000-6000 maps
are actually populated. Users asking for reqions where there is no ROSAT
coverage may get a blank region returned.
Detailed information regarding the creation of the ROSAT suveys
can be found in the
ROSAT PSPC Generation Document.
| Provenance |
Observational data from NASA Goddard Space
Flight Center, mosaicking of images done by SkyView.
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-580 PHz |
| Coverage |
Isolated pointings in the sky. Total
coverage < 14%
|
| PixelScale | 15" |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/pixel |
| Resolution | 30" but variable across the field of view |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1991-1994 |
| Reference |
ROSAT Mission Description and Data Products Guide, available through the ROSAT Guest Observer Facility, NASA GSFC.
SkyView Rosat Survey Generation description.
|
PSPC summed pointed observations, 0.6 degree cutoff, Exposure
Short name[s] used to specify survey:PSPC0.6Exp, PSPC 0.6 Deg-Exp, PSPC 0.6 Deg-Expos
Description
The ROSAT PSPC surveys were generated by SkyView as
mosaics from publically available PSPC observations.
The surveys include
all data available through March 1, 1997. This includes the vast majority
of ROSAT PSPC observations. Filter observations and observations taken
during the verification phase in 1991 were not included in either
set. The details of the generation of the surveys are discussed
in a
companion document.
Basically the counts and
exposure from all observations were added and then an intensity
map was generated as the ratio of the two.
The smaller
cut-offs allow users to distinguish point sources in fields where
a bright source may have been towards the edge of one observation
and near the center of another. In these cases the source appears
fuzzy due to the poor resolution of ROSAT near the edge of the field
of view. This comes at the cost of a substantial reduction in
the fraction of the sky covered. Counts and exposure maps are
included for users who may need this information (e.g., to do
statistical analysis).
The global organization of the surveys is similar
to the IRAS survey. Each map covers an area of 2.5°x2.5° with a
minimum overlap of 0.25°. To cover the entire sky would require over
10,000 maps. However due to lack of coverage only approximately 4000-6000 maps
are actually populated. Users asking for reqions where there is no ROSAT
coverage may get a blank region returned.
Detailed information regarding the creation of the ROSAT suveys
can be found in the
ROSAT PSPC Generation Document.
| Provenance |
Observational data from NASA Goddard Space
Flight Center, mosaicking of images done by SkyView.
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-580 PHz |
| Coverage |
Isolated pointings in the sky. Total
coverage < 14%
|
| PixelScale | 15" |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/pixel |
| Resolution | 30" but variable across the field of view |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1991-1994 |
| Reference |
ROSAT Mission Description and Data Products Guide, available through the ROSAT Guest Observer Facility, NASA GSFC.
SkyView Rosat Survey Generation description.
|
PSPC summed pointed observations, 0.6 degree cutoff, Intensity
Short name[s] used to specify survey:PSPC0.6Int, PSPC 0.6 Deg-Int, PSPC 0.6 Deg-Inten
Description
The ROSAT PSPC surveys were generated by SkyView as
mosaics from publically available PSPC observations.
The surveys include
all data available through March 1, 1997. This includes the vast majority
of ROSAT PSPC observations. Filter observations and observations taken
during the verification phase in 1991 were not included in either
set. The details of the generation of the surveys are discussed
in a
companion document.
Basically the counts and
exposure from all observations were added and then an intensity
map was generated as the ratio of the two.
The smaller
cut-offs allow users to distinguish point sources in fields where
a bright source may have been towards the edge of one observation
and near the center of another. In these cases the source appears
fuzzy due to the poor resolution of ROSAT near the edge of the field
of view. This comes at the cost of a substantial reduction in
the fraction of the sky covered. Counts and exposure maps are
included for users who may need this information (e.g., to do
statistical analysis).
The global organization of the surveys is similar
to the IRAS survey. Each map covers an area of 2.5°x2.5° with a
minimum overlap of 0.25°. To cover the entire sky would require over
10,000 maps. However due to lack of coverage only approximately 4000-6000 maps
are actually populated. Users asking for reqions where there is no ROSAT
coverage may get a blank region returned.
Detailed information regarding the creation of the ROSAT suveys
can be found in the
ROSAT PSPC Generation Document.
| Provenance |
Observational data from NASA Goddard Space
Flight Center, mosaicking of images done by SkyView.
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 1 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-580 PHz |
| Coverage |
Isolated pointings in the sky. Total
coverage < 14%
|
| PixelScale | 15" |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/pixel |
| Resolution | 30" but variable across the field of view |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1991-1994 |
| Reference |
ROSAT Mission Description and Data Products Guide, available through the ROSAT Guest Observer Facility, NASA GSFC.
SkyView Rosat Survey Generation description.
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Hard Band: Counts
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASShbC, RASSCnt hb, RASS-Cnt Hard
,RASS Hard, RASS3hb, RASShb
Description
The ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey was obtained during 1990/1991 using the
ROSAT Position Sensitive Proportional Counter (PSPC) in combination with
the ROSAT X-ray Telescope (XRT). More than 60,000 X-ray sources
were detected during this time.
SkyView has multiple surveys derived from the RASS data. The surveys whose
RASS are counts and exposure maps from the survey. Previously
The RASSBCK maps have had the point sources removed to show the diffuse X-ray background
and are presended at lower resolution.
The full-resolution RASS surveys
data are organized in 1378 fields each
6.4° x 6.4° covering the whole sky. Neighboring fields
overlap by at least 0.23°.
Three bands are available through SkyView
- broad band (0.1-2.4 keV)
- hard band (0.5-2.0 keV)
- soft band (0.1-0.4 keV)
Data was dowloaded from the
MPE FTP site.
The intensity maps are created from the exposure maps using the single exposure map available which
is appropriate for the broad
band images, so the intensities of the hard and soft bands are only approximate.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPE but data may be used for scientific purposes so long as
appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 120-480 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 45" |
| PixelUnits | Counts,Flux |
| Resolution | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-98 |
| Reference |
The ROSAT All-Sky Survey
(ADS)
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Broad Band: Counts
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASSbbC, RASSCnt bb, RASS-Cnt Broad
,RASS Broad, RASS3bb, RASSbb
,RASS
Description
The ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey was obtained during 1990/1991 using the
ROSAT Position Sensitive Proportional Counter (PSPC) in combination with
the ROSAT X-ray Telescope (XRT). More than 60,000 X-ray sources
were detected during this time.
SkyView has multiple surveys derived from the RASS data. The surveys whose
RASS are counts and exposure maps from the survey. Previously
The RASSBCK maps have had the point sources removed to show the diffuse X-ray background
and are presended at lower resolution.
The full-resolution RASS surveys
data are organized in 1378 fields each
6.4° x 6.4° covering the whole sky. Neighboring fields
overlap by at least 0.23°.
Three bands are available through SkyView
- broad band (0.1-2.4 keV)
- hard band (0.5-2.0 keV)
- soft band (0.1-0.4 keV)
Data was dowloaded from the
MPE FTP site.
The intensity maps are created from the exposure maps using the single exposure map available which
is appropriate for the broad
band images, so the intensities of the hard and soft bands are only approximate.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPE but data may be used for scientific purposes so long as
appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-580 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 45" |
| PixelUnits | Counts,Flux |
| Resolution | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-98 |
| Reference |
The ROSAT All-Sky Survey
(ADS)
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Soft Band: Counts
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASSsbC, RASSCnt sb, RASS-Cnt Soft
,RASS Soft, RASS3sb, RASSsb
Description
The ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey was obtained during 1990/1991 using the
ROSAT Position Sensitive Proportional Counter (PSPC) in combination with
the ROSAT X-ray Telescope (XRT). More than 60,000 X-ray sources
were detected during this time.
SkyView has multiple surveys derived from the RASS data. The surveys whose
RASS are counts and exposure maps from the survey. Previously
The RASSBCK maps have had the point sources removed to show the diffuse X-ray background
and are presended at lower resolution.
The full-resolution RASS surveys
data are organized in 1378 fields each
6.4° x 6.4° covering the whole sky. Neighboring fields
overlap by at least 0.23°.
Three bands are available through SkyView
- broad band (0.1-2.4 keV)
- hard band (0.5-2.0 keV)
- soft band (0.1-0.4 keV)
Data was dowloaded from the
MPE FTP site.
The intensity maps are created from the exposure maps using the single exposure map available which
is appropriate for the broad
band images, so the intensities of the hard and soft bands are only approximate.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPE but data may be used for scientific purposes so long as
appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 73 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-120 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 45" |
| PixelUnits | Counts,Flux |
| Resolution | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-98 |
| Reference |
The ROSAT All-Sky Survey
(ADS)
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Hard Band: Intensity
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASShbI, RASSInt hb, RASS-Int Hard
Description
The ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey was obtained during 1990/1991 using the
ROSAT Position Sensitive Proportional Counter (PSPC) in combination with
the ROSAT X-ray Telescope (XRT). More than 60,000 X-ray sources
were detected during this time.
SkyView has multiple surveys derived from the RASS data. The surveys whose
RASS are counts and exposure maps from the survey. Previously
The RASSBCK maps have had the point sources removed to show the diffuse X-ray background
and are presended at lower resolution.
The full-resolution RASS surveys
data are organized in 1378 fields each
6.4° x 6.4° covering the whole sky. Neighboring fields
overlap by at least 0.23°.
Three bands are available through SkyView
- broad band (0.1-2.4 keV)
- hard band (0.5-2.0 keV)
- soft band (0.1-0.4 keV)
Data was dowloaded from the
MPE FTP site.
The intensity maps are created from the exposure maps using the single exposure map available which
is appropriate for the broad
band images, so the intensities of the hard and soft bands are only approximate.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPE but data may be used for scientific purposes so long as
appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 120-480 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 45" |
| PixelUnits | Counts,Flux |
| Resolution | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-98 |
| Reference |
The ROSAT All-Sky Survey
(ADS)
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Broad Band: Intensity
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASSbbI, RASSInt bb, RASS-Int Broad
Description
The ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey was obtained during 1990/1991 using the
ROSAT Position Sensitive Proportional Counter (PSPC) in combination with
the ROSAT X-ray Telescope (XRT). More than 60,000 X-ray sources
were detected during this time.
SkyView has multiple surveys derived from the RASS data. The surveys whose
RASS are counts and exposure maps from the survey. Previously
The RASSBCK maps have had the point sources removed to show the diffuse X-ray background
and are presended at lower resolution.
The full-resolution RASS surveys
data are organized in 1378 fields each
6.4° x 6.4° covering the whole sky. Neighboring fields
overlap by at least 0.23°.
Three bands are available through SkyView
- broad band (0.1-2.4 keV)
- hard band (0.5-2.0 keV)
- soft band (0.1-0.4 keV)
Data was dowloaded from the
MPE FTP site.
The intensity maps are created from the exposure maps using the single exposure map available which
is appropriate for the broad
band images, so the intensities of the hard and soft bands are only approximate.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPE but data may be used for scientific purposes so long as
appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 240 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-580 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 45" |
| PixelUnits | Counts,Flux |
| Resolution | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-98 |
| Reference |
The ROSAT All-Sky Survey
(ADS)
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey Soft Band: Intensity
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASSsbI, RASSInt sb, RASS-Int Soft
Description
The ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Survey was obtained during 1990/1991 using the
ROSAT Position Sensitive Proportional Counter (PSPC) in combination with
the ROSAT X-ray Telescope (XRT). More than 60,000 X-ray sources
were detected during this time.
SkyView has multiple surveys derived from the RASS data. The surveys whose
RASS are counts and exposure maps from the survey. Previously
The RASSBCK maps have had the point sources removed to show the diffuse X-ray background
and are presended at lower resolution.
The full-resolution RASS surveys
data are organized in 1378 fields each
6.4° x 6.4° covering the whole sky. Neighboring fields
overlap by at least 0.23°.
Three bands are available through SkyView
- broad band (0.1-2.4 keV)
- hard band (0.5-2.0 keV)
- soft band (0.1-0.4 keV)
Data was dowloaded from the
MPE FTP site.
The intensity maps are created from the exposure maps using the single exposure map available which
is appropriate for the broad
band images, so the intensities of the hard and soft bands are only approximate.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPE but data may be used for scientific purposes so long as
appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 73 PHz |
| Bandpass | 24-120 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 45" |
| PixelUnits | Counts,Flux |
| Resolution | |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-98 |
| Reference |
The ROSAT All-Sky Survey
(ADS)
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 1
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASSBck1,rassback1,RASS Background 1
Description
These maps present maps of
ROSAT soft X-ray all-sky survey as presented in Snowden et al, ApJ 485, 125 (1997).
The maps cover approximately 98% of the sky. These maps have had all point sources
removed
These surveys supercede the RASS0.25, RASS0.75 and RASS1.5 Kev surveys
previously provided. Those surveys may still be invoked in SkyView using
batch and jar tools but are not accessible on the Web page.
The seven maps correspond to ranges in the pulse height analysis of the photons
detected. Since the energy resolution of the PSPC is poor, there is consider
overlap between adjacent bands.
The energy range for the bands corresponds to:
| Band | Energy range (keV) |
|---|
| Band 1 | 0.11 - 0.284 |
| Band 2 | 0.14 - 0.284 |
| Band 3 | 0.2 - 0.83 |
| Band 4 | 0.44 - 1.01 |
| Band 5 | 0.56 - 1.21 |
| Band 6 | 0.73 - 1.56 |
| Band 7 | 1.05 - 2.04 |
Note the substantial overlap between bands. Each photon detected is assigned to
a band based on the pulse height analysis for that photon, but the energy resolution
of the detectors is relatively poor. Also note that Band 3 was not
included in the reference paper due to poor statistics and background modeling.
SkyView has several other sets of surveys derived from ROSAT data
with substantially higher resolution and which include point sources.
The RASS surveys are derived from the RASS all sky survey. These include count
and intensity maps. The PSPC maps are dervived from the PSPC pointed observations
which were combined by SkyView. The HRI survey is derived from a similar mosaicking
of all HRI observations.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPI but data may be used for scientific
purposes so long as appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 41 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.2 |
| PixelUnits | 10-6counts/s |
| Resolution | ca. 2° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-8 |
| Reference |
S.L. Snowden, et al.,
Ap,J, Vol.485 (1997), pp.125
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 2
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASSBck2,rassback2,RASS Background 2
Description
These maps present maps of
ROSAT soft X-ray all-sky survey as presented in Snowden et al, ApJ 485, 125 (1997).
The maps cover approximately 98% of the sky. These maps have had all point sources
removed
These surveys supercede the RASS0.25, RASS0.75 and RASS1.5 Kev surveys
previously provided. Those surveys may still be invoked in SkyView using
batch and jar tools but are not accessible on the Web page.
The seven maps correspond to ranges in the pulse height analysis of the photons
detected. Since the energy resolution of the PSPC is poor, there is consider
overlap between adjacent bands.
The energy range for the bands corresponds to:
| Band | Energy range (keV) |
|---|
| Band 1 | 0.11 - 0.284 |
| Band 2 | 0.14 - 0.284 |
| Band 3 | 0.2 - 0.83 |
| Band 4 | 0.44 - 1.01 |
| Band 5 | 0.56 - 1.21 |
| Band 6 | 0.73 - 1.56 |
| Band 7 | 1.05 - 2.04 |
Note the substantial overlap between bands. Each photon detected is assigned to
a band based on the pulse height analysis for that photon, but the energy resolution
of the detectors is relatively poor. Also note that Band 3 was not
included in the reference paper due to poor statistics and background modeling.
SkyView has several other sets of surveys derived from ROSAT data
with substantially higher resolution and which include point sources.
The RASS surveys are derived from the RASS all sky survey. These include count
and intensity maps. The PSPC maps are dervived from the PSPC pointed observations
which were combined by SkyView. The HRI survey is derived from a similar mosaicking
of all HRI observations.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPI but data may be used for scientific
purposes so long as appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 51 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.2 |
| PixelUnits | 10-6counts/s |
| Resolution | ca. 2° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-8 |
| Reference |
S.L. Snowden, et al.,
Ap,J, Vol.485 (1997), pp.125
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 3
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASSBck3,rassback3,RASS Background 3
Description
These maps present maps of
ROSAT soft X-ray all-sky survey as presented in Snowden et al, ApJ 485, 125 (1997).
The maps cover approximately 98% of the sky. These maps have had all point sources
removed
These surveys supercede the RASS0.25, RASS0.75 and RASS1.5 Kev surveys
previously provided. Those surveys may still be invoked in SkyView using
batch and jar tools but are not accessible on the Web page.
The seven maps correspond to ranges in the pulse height analysis of the photons
detected. Since the energy resolution of the PSPC is poor, there is consider
overlap between adjacent bands.
The energy range for the bands corresponds to:
| Band | Energy range (keV) |
|---|
| Band 1 | 0.11 - 0.284 |
| Band 2 | 0.14 - 0.284 |
| Band 3 | 0.2 - 0.83 |
| Band 4 | 0.44 - 1.01 |
| Band 5 | 0.56 - 1.21 |
| Band 6 | 0.73 - 1.56 |
| Band 7 | 1.05 - 2.04 |
Note the substantial overlap between bands. Each photon detected is assigned to
a band based on the pulse height analysis for that photon, but the energy resolution
of the detectors is relatively poor. Also note that Band 3 was not
included in the reference paper due to poor statistics and background modeling.
SkyView has several other sets of surveys derived from ROSAT data
with substantially higher resolution and which include point sources.
The RASS surveys are derived from the RASS all sky survey. These include count
and intensity maps. The PSPC maps are dervived from the PSPC pointed observations
which were combined by SkyView. The HRI survey is derived from a similar mosaicking
of all HRI observations.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPI but data may be used for scientific
purposes so long as appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 100 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.2 |
| PixelUnits | 10-6counts/s |
| Resolution | ca. 2° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-8 |
| Reference |
S.L. Snowden, et al.,
Ap,J, Vol.485 (1997), pp.125
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 4
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASSBck4,rassback4,RASS Background 4
Description
These maps present maps of
ROSAT soft X-ray all-sky survey as presented in Snowden et al, ApJ 485, 125 (1997).
The maps cover approximately 98% of the sky. These maps have had all point sources
removed
These surveys supercede the RASS0.25, RASS0.75 and RASS1.5 Kev surveys
previously provided. Those surveys may still be invoked in SkyView using
batch and jar tools but are not accessible on the Web page.
The seven maps correspond to ranges in the pulse height analysis of the photons
detected. Since the energy resolution of the PSPC is poor, there is consider
overlap between adjacent bands.
The energy range for the bands corresponds to:
| Band | Energy range (keV) |
|---|
| Band 1 | 0.11 - 0.284 |
| Band 2 | 0.14 - 0.284 |
| Band 3 | 0.2 - 0.83 |
| Band 4 | 0.44 - 1.01 |
| Band 5 | 0.56 - 1.21 |
| Band 6 | 0.73 - 1.56 |
| Band 7 | 1.05 - 2.04 |
Note the substantial overlap between bands. Each photon detected is assigned to
a band based on the pulse height analysis for that photon, but the energy resolution
of the detectors is relatively poor. Also note that Band 3 was not
included in the reference paper due to poor statistics and background modeling.
SkyView has several other sets of surveys derived from ROSAT data
with substantially higher resolution and which include point sources.
The RASS surveys are derived from the RASS all sky survey. These include count
and intensity maps. The PSPC maps are dervived from the PSPC pointed observations
which were combined by SkyView. The HRI survey is derived from a similar mosaicking
of all HRI observations.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPI but data may be used for scientific
purposes so long as appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 170 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.2 |
| PixelUnits | 10-6counts/s |
| Resolution | ca. 2° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-8 |
| Reference |
S.L. Snowden, et al.,
Ap,J, Vol.485 (1997), pp.125
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 5
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASSBck5,rassback5,RASS Background 5
Description
These maps present maps of
ROSAT soft X-ray all-sky survey as presented in Snowden et al, ApJ 485, 125 (1997).
The maps cover approximately 98% of the sky. These maps have had all point sources
removed
These surveys supercede the RASS0.25, RASS0.75 and RASS1.5 Kev surveys
previously provided. Those surveys may still be invoked in SkyView using
batch and jar tools but are not accessible on the Web page.
The seven maps correspond to ranges in the pulse height analysis of the photons
detected. Since the energy resolution of the PSPC is poor, there is consider
overlap between adjacent bands.
The energy range for the bands corresponds to:
| Band | Energy range (keV) |
|---|
| Band 1 | 0.11 - 0.284 |
| Band 2 | 0.14 - 0.284 |
| Band 3 | 0.2 - 0.83 |
| Band 4 | 0.44 - 1.01 |
| Band 5 | 0.56 - 1.21 |
| Band 6 | 0.73 - 1.56 |
| Band 7 | 1.05 - 2.04 |
Note the substantial overlap between bands. Each photon detected is assigned to
a band based on the pulse height analysis for that photon, but the energy resolution
of the detectors is relatively poor. Also note that Band 3 was not
included in the reference paper due to poor statistics and background modeling.
SkyView has several other sets of surveys derived from ROSAT data
with substantially higher resolution and which include point sources.
The RASS surveys are derived from the RASS all sky survey. These include count
and intensity maps. The PSPC maps are dervived from the PSPC pointed observations
which were combined by SkyView. The HRI survey is derived from a similar mosaicking
of all HRI observations.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPI but data may be used for scientific
purposes so long as appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 190 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.2 |
| PixelUnits | 10-6counts/s |
| Resolution | ca. 2° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-8 |
| Reference |
S.L. Snowden, et al.,
Ap,J, Vol.485 (1997), pp.125
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 6
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASSBck6,rassback6,RASS Background 6
Description
These maps present maps of
ROSAT soft X-ray all-sky survey as presented in Snowden et al, ApJ 485, 125 (1997).
The maps cover approximately 98% of the sky. These maps have had all point sources
removed
These surveys supercede the RASS0.25, RASS0.75 and RASS1.5 Kev surveys
previously provided. Those surveys may still be invoked in SkyView using
batch and jar tools but are not accessible on the Web page.
The seven maps correspond to ranges in the pulse height analysis of the photons
detected. Since the energy resolution of the PSPC is poor, there is consider
overlap between adjacent bands.
The energy range for the bands corresponds to:
| Band | Energy range (keV) |
|---|
| Band 1 | 0.11 - 0.284 |
| Band 2 | 0.14 - 0.284 |
| Band 3 | 0.2 - 0.83 |
| Band 4 | 0.44 - 1.01 |
| Band 5 | 0.56 - 1.21 |
| Band 6 | 0.73 - 1.56 |
| Band 7 | 1.05 - 2.04 |
Note the substantial overlap between bands. Each photon detected is assigned to
a band based on the pulse height analysis for that photon, but the energy resolution
of the detectors is relatively poor. Also note that Band 3 was not
included in the reference paper due to poor statistics and background modeling.
SkyView has several other sets of surveys derived from ROSAT data
with substantially higher resolution and which include point sources.
The RASS surveys are derived from the RASS all sky survey. These include count
and intensity maps. The PSPC maps are dervived from the PSPC pointed observations
which were combined by SkyView. The HRI survey is derived from a similar mosaicking
of all HRI observations.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPI but data may be used for scientific
purposes so long as appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 250 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.2 |
| PixelUnits | 10-6counts/s |
| Resolution | ca. 2° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-8 |
| Reference |
S.L. Snowden, et al.,
Ap,J, Vol.485 (1997), pp.125
|
ROSAT All-Sky X-ray Background Survey: Band 7
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RASSBck7,rassback7,RASS Background 7
Description
These maps present maps of
ROSAT soft X-ray all-sky survey as presented in Snowden et al, ApJ 485, 125 (1997).
The maps cover approximately 98% of the sky. These maps have had all point sources
removed
These surveys supercede the RASS0.25, RASS0.75 and RASS1.5 Kev surveys
previously provided. Those surveys may still be invoked in SkyView using
batch and jar tools but are not accessible on the Web page.
The seven maps correspond to ranges in the pulse height analysis of the photons
detected. Since the energy resolution of the PSPC is poor, there is consider
overlap between adjacent bands.
The energy range for the bands corresponds to:
| Band | Energy range (keV) |
|---|
| Band 1 | 0.11 - 0.284 |
| Band 2 | 0.14 - 0.284 |
| Band 3 | 0.2 - 0.83 |
| Band 4 | 0.44 - 1.01 |
| Band 5 | 0.56 - 1.21 |
| Band 6 | 0.73 - 1.56 |
| Band 7 | 1.05 - 2.04 |
Note the substantial overlap between bands. Each photon detected is assigned to
a band based on the pulse height analysis for that photon, but the energy resolution
of the detectors is relatively poor. Also note that Band 3 was not
included in the reference paper due to poor statistics and background modeling.
SkyView has several other sets of surveys derived from ROSAT data
with substantially higher resolution and which include point sources.
The RASS surveys are derived from the RASS all sky survey. These include count
and intensity maps. The PSPC maps are dervived from the PSPC pointed observations
which were combined by SkyView. The HRI survey is derived from a similar mosaicking
of all HRI observations.
| Provenance |
Max Planck Institute for Exterrestrial Physics (Garching FRG)
|
| Copyright |
MPI but data may be used for scientific
purposes so long as appropriate reference is included.
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 6 |
| Frequency | 370 PHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 0.2 |
| PixelUnits | 10-6counts/s |
| Resolution | ca. 2° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Zenithal Equal Area |
| Epoch | 1990-07 to 1991-02, 1991-8 |
| Reference |
S.L. Snowden, et al.,
Ap,J, Vol.485 (1997), pp.125
|
RXTE Allsky 3-8 keV Flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RXTE3_8k_flux, RXTE AllSky 3-8keV flux
Description
Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer was launched at the end
of 1995 and up to now (2004) it has been successfully operating for more
than 7 years. The mission was primarily designed to study the variability of
X-ray sources on time scales from sub-milliseconds to years.
The maneuvering capability of the satellite combined with the high
photon throughput of its main
detector (PCA) and high quality of background prediction (thanks to
PCA intrumental group of LHEA, GSFC) has also made it possible to
construct maps of the sky in energy band 3-20 keV. During its life time
RXTE/PCA has collected a large amount of data from slew observations
covering almost the entire sky.
We have utilized the slew parts of all RXTE/PCA
observations performed from April 15, 1996-July 16, 2002 which
amounts in total to approximately 50,000 observations. The exposure
time at a given point in the map is typically between 200-500 seconds.
The observational period before April 15, 1996
(High Voltage Epochs 1 and 2) was
excluded from the analysis because during that time the PCA had
significantly different gain and dependence of the effective area on
energy. The data reduction was done using standard tools of the
LHEASOFT with a set of packages written by M. Revnivtsev
(HEAD/IKI, Moscow; MPA, Garching).
The survey has several features. It has strongly different exposure times
at different points on the sky that lead to strong variability of the
statistical noise on images. Because of that the only meaningful
representation of images is the map in units of statistical significance.
After the detection of a source flux can be determined from the map
in the 'flux' units. Map resolution is determined mainly by
the slew rate of the RXTE (<0.05-0.1°/sec) and the time resolution of
used data (16 sec, Std2 mode of the PCA). Sources can be detected down
to the level of ~6e-12 erg/s/cm2, but at this level the
confusion starts to play an important role. Details of the survey are
presented in the paper of Revnivtsev et al. (2004).
| Provenance |
High Energy Astrophysics Department, Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia; M
PA, Garching, Germany
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 1.2 EHz |
| Bandpass | 0.72-1.9 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |b| > 3 |
| PixelScale | .5x.5° pixel |
| PixelUnits | Flux |
| Resolution | 1° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1996-2002 |
| Reference |
RXTE all-sky slew survey. Catalog of X-ray sources at |b|>10 &#
176;, M. Revnivtsev, S. Sazonov, M. Gilfanov, K. Jahoda 2004, A&A, 418, 92
7
|
RXTE Allsky 3-8 keV Significance
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RXTE3_8k_sig, RXTE AllSky 3-8keV sig
,RXTE AllSky 3-8keV
Description
Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer was launched at the end
of 1995 and up to now (2004) it has been successfully operating for more
than 7 years. The mission was primarily designed to study the variability of
X-ray sources on time scales from sub-milliseconds to years.
The maneuvering capability of the satellite combined with the high
photon throughput of its main
detector (PCA) and high quality of background prediction (thanks to
PCA intrumental group of LHEA, GSFC) has also made it possible to
construct maps of the sky in energy band 3-20 keV. During its life time
RXTE/PCA has collected a large amount of data from slew observations
covering almost the entire sky.
We have utilized the slew parts of all RXTE/PCA
observations performed from April 15, 1996-July 16, 2002 which
amounts in total to approximately 50,000 observations. The exposure
time at a given point in the map is typically between 200-500 seconds.
The observational period before April 15, 1996
(High Voltage Epochs 1 and 2) was
excluded from the analysis because during that time the PCA had
significantly different gain and dependence of the effective area on
energy. The data reduction was done using standard tools of the
LHEASOFT with a set of packages written by M. Revnivtsev
(HEAD/IKI, Moscow; MPA, Garching).
The survey has several features. It has strongly different exposure times
at different points on the sky that lead to strong variability of the
statistical noise on images. Because of that the only meaningful
representation of images is the map in units of statistical significance.
After the detection of a source flux can be determined from the map
in the 'flux' units. Map resolution is determined mainly by
the slew rate of the RXTE (<0.05-0.1°/sec) and the time resolution of
used data (16 sec, Std2 mode of the PCA). Sources can be detected down
to the level of ~6e-12 erg/s/cm2, but at this level the
confusion starts to play an important role. Details of the survey are
presented in the paper of Revnivtsev et al. (2004).
| Provenance |
High Energy Astrophysics Department, Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia; M
PA, Garching, Germany
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 1.2 EHz |
| Bandpass | 0.72-1.9 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |b| > 3 |
| PixelScale | .5x.5° pixel |
| PixelUnits | Significance |
| Resolution | 1° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1996-2002 |
| Reference |
RXTE all-sky slew survey. Catalog of X-ray sources at |b|>10 &#
176;, M. Revnivtsev, S. Sazonov, M. Gilfanov, K. Jahoda 2004, A&A, 418, 92
7
|
RXTE Allsky 8-20 keV Flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RXTE8_20k_flux, RXTE AllSky 8-20keV flux
Description
Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer was launched at the end
of 1995 and up to now (2004) it has been successfully operating for more
than 7 years. The mission was primarily designed to study the variability of
X-ray sources on time scales from sub-milliseconds to years.
The maneuvering capability of the satellite combined with the high
photon throughput of its main
detector (PCA) and high quality of background prediction (thanks to
PCA intrumental group of LHEA, GSFC) has also made it possible to
construct maps of the sky in energy band 3-20 keV. During its life time
RXTE/PCA has collected a large amount of data from slew observations
covering almost the entire sky.
We have utilized the slew parts of all RXTE/PCA
observations performed from April 15, 1996-July 16, 2002 which
amounts in total to approximately 50,000 observations. The exposure
time at a given point in the map is typically between 200-500 seconds.
The observational period before April 15, 1996
(High Voltage Epochs 1 and 2) was
excluded from the analysis because during that time the PCA had
significantly different gain and dependence of the effective area on
energy. The data reduction was done using standard tools of the
LHEASOFT with a set of packages written by M. Revnivtsev
(HEAD/IKI, Moscow; MPA, Garching).
The survey has several features. It has strongly different exposure times
at different points on the sky that lead to strong variability of the
statistical noise on images. Because of that the only meaningful
representation of images is the map in units of statistical significance.
After the detection of a source flux can be determined from the map
in the 'flux' units. Map resolution is determined mainly by
the slew rate of the RXTE (<0.05-0.1°/sec) and the time resolution of
used data (16 sec, Std2 mode of the PCA). Sources can be detected down
to the level of ~6e-12 erg/s/cm2, but at this level the
confusion starts to play an important role. Details of the survey are
presented in the paper of Revnivtsev et al. (2004).
| Provenance |
High Energy Astrophysics Department, Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia; M
PA, Garching, Germany
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 2.9 EHz |
| Bandpass | 1.9-4.8 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |b| > 3 |
| PixelScale | .5x.5° pixel |
| PixelUnits | Flux |
| Resolution | 1° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1996-2002 |
| Reference |
RXTE all-sky slew survey. Catalog of X-ray sources at |b|>10 &#
176;, M. Revnivtsev, S. Sazonov, M. Gilfanov, K. Jahoda 2004, A&A, 418, 92
7
|
RXTE Allsky 8-20 keV Significance
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RXTE8_20k_sig, RXTE AllSky 8-20keV sig
,RXTE AllSky 8-20keV
Description
Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer was launched at the end
of 1995 and up to now (2004) it has been successfully operating for more
than 7 years. The mission was primarily designed to study the variability of
X-ray sources on time scales from sub-milliseconds to years.
The maneuvering capability of the satellite combined with the high
photon throughput of its main
detector (PCA) and high quality of background prediction (thanks to
PCA intrumental group of LHEA, GSFC) has also made it possible to
construct maps of the sky in energy band 3-20 keV. During its life time
RXTE/PCA has collected a large amount of data from slew observations
covering almost the entire sky.
We have utilized the slew parts of all RXTE/PCA
observations performed from April 15, 1996-July 16, 2002 which
amounts in total to approximately 50,000 observations. The exposure
time at a given point in the map is typically between 200-500 seconds.
The observational period before April 15, 1996
(High Voltage Epochs 1 and 2) was
excluded from the analysis because during that time the PCA had
significantly different gain and dependence of the effective area on
energy. The data reduction was done using standard tools of the
LHEASOFT with a set of packages written by M. Revnivtsev
(HEAD/IKI, Moscow; MPA, Garching).
The survey has several features. It has strongly different exposure times
at different points on the sky that lead to strong variability of the
statistical noise on images. Because of that the only meaningful
representation of images is the map in units of statistical significance.
After the detection of a source flux can be determined from the map
in the 'flux' units. Map resolution is determined mainly by
the slew rate of the RXTE (<0.05-0.1°/sec) and the time resolution of
used data (16 sec, Std2 mode of the PCA). Sources can be detected down
to the level of ~6e-12 erg/s/cm2, but at this level the
confusion starts to play an important role. Details of the survey are
presented in the paper of Revnivtsev et al. (2004).
| Provenance |
High Energy Astrophysics Department, Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia; M
PA, Garching, Germany
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 2.9 EHz |
| Bandpass | 1.9-4.8 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |b| > 3 |
| PixelScale | .5x.5° pixel |
| PixelUnits | Significance |
| Resolution | 1° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1996-2002 |
| Reference |
RXTE all-sky slew survey. Catalog of X-ray sources at |b|>10 &#
176;, M. Revnivtsev, S. Sazonov, M. Gilfanov, K. Jahoda 2004, A&A, 418, 92
7
|
RXTE Allsky 3-20 keV Flux
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RXTE3_20k_flux, RXTE AllSky 3-20keV flux
Description
Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer was launched at the end
of 1995 and up to now (2004) it has been successfully operating for more
than 7 years. The mission was primarily designed to study the variability of
X-ray sources on time scales from sub-milliseconds to years.
The maneuvering capability of the satellite combined with the high
photon throughput of its main
detector (PCA) and high quality of background prediction (thanks to
PCA intrumental group of LHEA, GSFC) has also made it possible to
construct maps of the sky in energy band 3-20 keV. During its life time
RXTE/PCA has collected a large amount of data from slew observations
covering almost the entire sky.
We have utilized the slew parts of all RXTE/PCA
observations performed from April 15, 1996-July 16, 2002 which
amounts in total to approximately 50,000 observations. The exposure
time at a given point in the map is typically between 200-500 seconds.
The observational period before April 15, 1996
(High Voltage Epochs 1 and 2) was
excluded from the analysis because during that time the PCA had
significantly different gain and dependence of the effective area on
energy. The data reduction was done using standard tools of the
LHEASOFT with a set of packages written by M. Revnivtsev
(HEAD/IKI, Moscow; MPA, Garching).
The survey has several features. It has strongly different exposure times
at different points on the sky that lead to strong variability of the
statistical noise on images. Because of that the only meaningful
representation of images is the map in units of statistical significance.
After the detection of a source flux can be determined from the map
in the 'flux' units. Map resolution is determined mainly by
the slew rate of the RXTE (<0.05-0.1°/sec) and the time resolution of
used data (16 sec, Std2 mode of the PCA). Sources can be detected down
to the level of ~6e-12 erg/s/cm2, but at this level the
confusion starts to play an important role. Details of the survey are
presented in the paper of Revnivtsev et al. (2004).
| Provenance |
High Energy Astrophysics Department, Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia; M
PA, Garching, Germany
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 1.9 EHz |
| Bandpass | 0.72-4.8 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |b| > 3 |
| PixelScale | .5x.5° pixel |
| PixelUnits | Flux |
| Resolution | 1° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1996-2002 |
| Reference |
RXTE all-sky slew survey. Catalog of X-ray sources at |b|>10 &#
176;, M. Revnivtsev, S. Sazonov, M. Gilfanov, K. Jahoda 2004, A&A, 418, 92
7
|
RXTE Allsky 3-20 keV Significance
Short name[s] used to specify survey:RXTE3_20k_sig, RXTE AllSky 3-20keV sig
,RXTE AllSky 3-20keV
Description
Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer was launched at the end
of 1995 and up to now (2004) it has been successfully operating for more
than 7 years. The mission was primarily designed to study the variability of
X-ray sources on time scales from sub-milliseconds to years.
The maneuvering capability of the satellite combined with the high
photon throughput of its main
detector (PCA) and high quality of background prediction (thanks to
PCA intrumental group of LHEA, GSFC) has also made it possible to
construct maps of the sky in energy band 3-20 keV. During its life time
RXTE/PCA has collected a large amount of data from slew observations
covering almost the entire sky.
We have utilized the slew parts of all RXTE/PCA
observations performed from April 15, 1996-July 16, 2002 which
amounts in total to approximately 50,000 observations. The exposure
time at a given point in the map is typically between 200-500 seconds.
The observational period before April 15, 1996
(High Voltage Epochs 1 and 2) was
excluded from the analysis because during that time the PCA had
significantly different gain and dependence of the effective area on
energy. The data reduction was done using standard tools of the
LHEASOFT with a set of packages written by M. Revnivtsev
(HEAD/IKI, Moscow; MPA, Garching).
The survey has several features. It has strongly different exposure times
at different points on the sky that lead to strong variability of the
statistical noise on images. Because of that the only meaningful
representation of images is the map in units of statistical significance.
After the detection of a source flux can be determined from the map
in the 'flux' units. Map resolution is determined mainly by
the slew rate of the RXTE (<0.05-0.1°/sec) and the time resolution of
used data (16 sec, Std2 mode of the PCA). Sources can be detected down
to the level of ~6e-12 erg/s/cm2, but at this level the
confusion starts to play an important role. Details of the survey are
presented in the paper of Revnivtsev et al. (2004).
| Provenance |
High Energy Astrophysics Department, Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia; M
PA, Garching, Germany
|
| Copyright |
Public domain
|
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 1.9 EHz |
| Bandpass | 0.72-4.8 EHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |b| > 3 |
| PixelScale | .5x.5° pixel |
| PixelUnits | Significance |
| Resolution | 1° |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Equinox | |
| Projection | Gnomonic |
| Epoch | 1996-2002 |
| Reference |
RXTE all-sky slew survey. Catalog of X-ray sources at |b|>10 &#
176;, M. Revnivtsev, S. Sazonov, M. Gilfanov, K. Jahoda 2004, A&A, 418, 92
7
|
Swift XRT Combined Counts Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:XRTCnt, Swift XRT Counts, SwiftXRTCnt
Description
The Swift XRT (Burrows et al 2005, SSRv, 120, 165)
is a sensitive, broad-band (0.2 - 10 keV) X-ray imager
with an effective area of about 125 cm**2 at 1.5 keV.
The 600 x 600 pixel CCD at the focus provides
a 23.6' x 23.6' field of view with a pixel scale
of 2.36". The point spread function
is 18" (HPD) at 1.5 keV.
These XRT surveys represent the data from the first 12.5 years of Swift X-ray observations.
They include all data taken in photon counting mode. A total of just over 8% of the sky
has some non-zero exposure. The fraction of sky exposed as a function of the exposure is given
in the following table:
| Exposure | >0 | 10 | 30 | 100 | 300 | 1000 | 3000 |
1000 | 30000 | 100000 | 300000 |
|---|
| Coverage |
8.42 | 8.37 | 8.29 | 7.67 | 7.29 | 5.68 |
3.40 | 1.26 | 0.35 | 0.044 | 0.00118 |
|---|
The individual exposure and counts maps have been combined
into a Hierarchical Progressive Survey (HiPS) where the data are stored in tiles
in the HEALPix projection at a number of different resulutions. The highest resolution
pixels (HEALPix order 17) have a size of roughly 1.6". Data are also stored at lower
resolutions at factors of 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, and 1/32, and in an all sky image with a resolution
1/256 of the higest resolution. An intensity map has been created as the ratio
of the counts and exposure maps.
These surveys combine the basic count and exposure maps provided as standard products
in the Swift XRT archive in obsid/xrt/products/*xpc_(sk|ex).img.gz. The surveys were created as follows:
- All of the exposure maps available in the archive in mid-May 2017 were combined
using the CDS-developed Hipsgen tool. This includes 129,063 observations for which
both count and exposure files were found in PC mode. Three exposures where there was
a counts map but no exposure map were ignored. A few exposure files had more than
one exposure extension. 1,082 files had two extensions and 1 file had 3 extensions.
The 1084 HDUs in extensions were extracted as separate files and included in the total exposure.
The value of 0 was given to the Hipsgen software as the null value for the FITS files.
This caused the CDS software to treat such pixels as missing rather than 0 exposure.
-
The counts data was extracted from the counts maps for each observation using SkyView
developed software. For any pixel in which a count was recorded, the corresponding
exposure file was checked and if there was any exposure (in any of the associated
extensions), then the count was retained. If there was no exposure in any of the extensions
of the corresponding exposure file, the counts in the pixel were omitted. Once a count
was accepted, the overlap between the counts map pixel and the pixels of the corresponding
HiPS tile (or tiles) was computed. Each count was then assigned entirely to a single
pixel in the HiPS tile randomly but with the destination pixel probabilities weighted by area of
the overlap. Thus if several pixels were found in a given counts map pixel they
might be assigned to different pixels in the output image. The HiPS pixels (~1.6") used were
of substantially higher resolution than the XRT resolution of 18" and somewhat higher than
the counts map resolution of 2.36".
A total of 183,750,428 photons were extracted from the counts maps while 15,226 were rejected
as being from pixels with 0 exposure. There were 501 pixels which required special
treatment as straddling the boundaries of the HEALPix projection.
-
The resulting counts tiles were then clipped using the exposure tiles that had been
previously generated. Basically this transferred the coverage of the exposure tiles
to the counts tiles. Any counts pixel where the corresponding exposure pixel was a NaN
was changed to a NaN to indicate that there was no coverage in this region.
During the clipping process 137,730 HiPS level 8 were clipped (of 786,432 over the entire sky). There were
12,236 tiles for which there was some exposure but no counts found. During the clipping process
2 photons were found on pixels where there was no corresponding exposure in the exposure tiles.
This can happen when the pixel assignment process noted above shifts a photon just outside the
exposed region but should be -- as it was -- rare. These photons were deleted.
-
After creating the clipped level 8 counts maps, level 7 to 3 tiles and an all sky map
where generated by averaging pixels 2x2 to decrease each level.
When adding the four pixels in the level N map together
only pixels whose value was not NaN were considered.
-
Finally an intensity map was created by dividing the counts tiles by the exposure tiles.
To eliminate gross fluctuations due to rare counts in regions with very low exposure, only
regions with exposure > 1 second were retained. A total of 30 photons were deleted due to
this criterion.
Note that while any sampler may in principle be used with these data, the Spline sampler may
give unexpected results. The spline computation propogates NaNs thought the image and
means that even occasional NaNs can corrupt the
output image completely. NaNs are very common in this dataset.
Also, if the region straddles a boundary in the HEALPix projection,
the size of the requested input region is likely to exceed memory limits since the HiPS
data are considered a single very large image.
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 360 PHz (1.5 keV) |
| Bandpass | 48 PHz - 2,400 PHz (0.2-10 keV) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~6% of the sky |
| PixelScale | 1.6" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts |
| Resolution | 18" (HPD) |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to May 2017 |
| Reference |
The XRT Web Site or
Burrows et al 2005, instrument reference
|
Swift XRT Combined Exposure Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:XRTExp, Swift XRT Exposure, SwiftXRTExp
Description
The Swift XRT (Burrows et al 2005, SSRv, 120, 165)
is a sensitive, broad-band (0.2 - 10 keV) X-ray imager
with an effective area of about 125 cm**2 at 1.5 keV.
The 600 x 600 pixel CCD at the focus provides
a 23.6' x 23.6' field of view with a pixel scale
of 2.36". The point spread function
is 18" (HPD) at 1.5 keV.
These XRT surveys represent the data from the first 12.5 years of Swift X-ray observations.
They include all data taken in photon counting mode. A total of just over 8% of the sky
has some non-zero exposure. The fraction of sky exposed as a function of the exposure is given
in the following table:
| Exposure | >0 | 10 | 30 | 100 | 300 | 1000 | 3000 |
1000 | 30000 | 100000 | 300000 |
|---|
| Coverage |
8.42 | 8.37 | 8.29 | 7.67 | 7.29 | 5.68 |
3.40 | 1.26 | 0.35 | 0.044 | 0.00118 |
|---|
The individual exposure and counts maps have been combined
into a Hierarchical Progressive Survey (HiPS) where the data are stored in tiles
in the HEALPix projection at a number of different resulutions. The highest resolution
pixels (HEALPix order 17) have a size of roughly 1.6". Data are also stored at lower
resolutions at factors of 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, and 1/32, and in an all sky image with a resolution
1/256 of the higest resolution. An intensity map has been created as the ratio
of the counts and exposure maps.
These surveys combine the basic count and exposure maps provided as standard products
in the Swift XRT archive in obsid/xrt/products/*xpc_(sk|ex).img.gz. The surveys were created as follows:
- All of the exposure maps available in the archive in mid-May 2017 were combined
using the CDS-developed Hipsgen tool. This includes 129,063 observations for which
both count and exposure files were found in PC mode. Three exposures where there was
a counts map but no exposure map were ignored. A few exposure files had more than
one exposure extension. 1,082 files had two extensions and 1 file had 3 extensions.
The 1084 HDUs in extensions were extracted as separate files and included in the total exposure.
The value of 0 was given to the Hipsgen software as the null value for the FITS files.
This caused the CDS software to treat such pixels as missing rather than 0 exposure.
-
The counts data was extracted from the counts maps for each observation using SkyView
developed software. For any pixel in which a count was recorded, the corresponding
exposure file was checked and if there was any exposure (in any of the associated
extensions), then the count was retained. If there was no exposure in any of the extensions
of the corresponding exposure file, the counts in the pixel were omitted. Once a count
was accepted, the overlap between the counts map pixel and the pixels of the corresponding
HiPS tile (or tiles) was computed. Each count was then assigned entirely to a single
pixel in the HiPS tile randomly but with the destination pixel probabilities weighted by area of
the overlap. Thus if several pixels were found in a given counts map pixel they
might be assigned to different pixels in the output image. The HiPS pixels (~1.6") used were
of substantially higher resolution than the XRT resolution of 18" and somewhat higher than
the counts map resolution of 2.36".
A total of 183,750,428 photons were extracted from the counts maps while 15,226 were rejected
as being from pixels with 0 exposure. There were 501 pixels which required special
treatment as straddling the boundaries of the HEALPix projection.
-
The resulting counts tiles were then clipped using the exposure tiles that had been
previously generated. Basically this transferred the coverage of the exposure tiles
to the counts tiles. Any counts pixel where the corresponding exposure pixel was a NaN
was changed to a NaN to indicate that there was no coverage in this region.
During the clipping process 137,730 HiPS level 8 were clipped (of 786,432 over the entire sky). There were
12,236 tiles for which there was some exposure but no counts found. During the clipping process
2 photons were found on pixels where there was no corresponding exposure in the exposure tiles.
This can happen when the pixel assignment process noted above shifts a photon just outside the
exposed region but should be -- as it was -- rare. These photons were deleted.
-
After creating the clipped level 8 counts maps, level 7 to 3 tiles and an all sky map
where generated by averaging pixels 2x2 to decrease each level.
When adding the four pixels in the level N map together
only pixels whose value was not NaN were considered.
-
Finally an intensity map was created by dividing the counts tiles by the exposure tiles.
To eliminate gross fluctuations due to rare counts in regions with very low exposure, only
regions with exposure > 1 second were retained. A total of 30 photons were deleted due to
this criterion.
Note that while any sampler may in principle be used with these data, the Spline sampler may
give unexpected results. The spline computation propogates NaNs thought the image and
means that even occasional NaNs can corrupt the
output image completely. NaNs are very common in this dataset.
Also, if the region straddles a boundary in the HEALPix projection,
the size of the requested input region is likely to exceed memory limits since the HiPS
data are considered a single very large image.
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 360 PHz (1.5 keV) |
| Bandpass | 48 PHz - 2,400 PHz (0.2-10 keV) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~6% of the sky |
| PixelScale | 1.6" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | s |
| Resolution | 18" (HPD) |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to May 2017 |
| Reference |
The XRT Web Site or
Burrows et al 2005, instrument reference
|
Swift XRT Combined Intensity Images
Short name[s] used to specify survey:XRTInt, Swift XRT Intensity, SwiftXRTInt
Description
The Swift XRT (Burrows et al 2005, SSRv, 120, 165)
is a sensitive, broad-band (0.2 - 10 keV) X-ray imager
with an effective area of about 125 cm**2 at 1.5 keV.
The 600 x 600 pixel CCD at the focus provides
a 23.6' x 23.6' field of view with a pixel scale
of 2.36". The point spread function
is 18" (HPD) at 1.5 keV.
These XRT surveys represent the data from the first 12.5 years of Swift X-ray observations.
They include all data taken in photon counting mode. A total of just over 8% of the sky
has some non-zero exposure. The fraction of sky exposed as a function of the exposure is given
in the following table:
| Exposure | >0 | 10 | 30 | 100 | 300 | 1000 | 3000 |
1000 | 30000 | 100000 | 300000 |
|---|
| Coverage |
8.42 | 8.37 | 8.29 | 7.67 | 7.29 | 5.68 |
3.40 | 1.26 | 0.35 | 0.044 | 0.00118 |
|---|
The individual exposure and counts maps have been combined
into a Hierarchical Progressive Survey (HiPS) where the data are stored in tiles
in the HEALPix projection at a number of different resulutions. The highest resolution
pixels (HEALPix order 17) have a size of roughly 1.6". Data are also stored at lower
resolutions at factors of 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, and 1/32, and in an all sky image with a resolution
1/256 of the higest resolution. An intensity map has been created as the ratio
of the counts and exposure maps.
These surveys combine the basic count and exposure maps provided as standard products
in the Swift XRT archive in obsid/xrt/products/*xpc_(sk|ex).img.gz. The surveys were created as follows:
- All of the exposure maps available in the archive in mid-May 2017 were combined
using the CDS-developed Hipsgen tool. This includes 129,063 observations for which
both count and exposure files were found in PC mode. Three exposures where there was
a counts map but no exposure map were ignored. A few exposure files had more than
one exposure extension. 1,082 files had two extensions and 1 file had 3 extensions.
The 1084 HDUs in extensions were extracted as separate files and included in the total exposure.
The value of 0 was given to the Hipsgen software as the null value for the FITS files.
This caused the CDS software to treat such pixels as missing rather than 0 exposure.
-
The counts data was extracted from the counts maps for each observation using SkyView
developed software. For any pixel in which a count was recorded, the corresponding
exposure file was checked and if there was any exposure (in any of the associated
extensions), then the count was retained. If there was no exposure in any of the extensions
of the corresponding exposure file, the counts in the pixel were omitted. Once a count
was accepted, the overlap between the counts map pixel and the pixels of the corresponding
HiPS tile (or tiles) was computed. Each count was then assigned entirely to a single
pixel in the HiPS tile randomly but with the destination pixel probabilities weighted by area of
the overlap. Thus if several pixels were found in a given counts map pixel they
might be assigned to different pixels in the output image. The HiPS pixels (~1.6") used were
of substantially higher resolution than the XRT resolution of 18" and somewhat higher than
the counts map resolution of 2.36".
A total of 183,750,428 photons were extracted from the counts maps while 15,226 were rejected
as being from pixels with 0 exposure. There were 501 pixels which required special
treatment as straddling the boundaries of the HEALPix projection.
-
The resulting counts tiles were then clipped using the exposure tiles that had been
previously generated. Basically this transferred the coverage of the exposure tiles
to the counts tiles. Any counts pixel where the corresponding exposure pixel was a NaN
was changed to a NaN to indicate that there was no coverage in this region.
During the clipping process 137,730 HiPS level 8 were clipped (of 786,432 over the entire sky). There were
12,236 tiles for which there was some exposure but no counts found. During the clipping process
2 photons were found on pixels where there was no corresponding exposure in the exposure tiles.
This can happen when the pixel assignment process noted above shifts a photon just outside the
exposed region but should be -- as it was -- rare. These photons were deleted.
-
After creating the clipped level 8 counts maps, level 7 to 3 tiles and an all sky map
where generated by averaging pixels 2x2 to decrease each level.
When adding the four pixels in the level N map together
only pixels whose value was not NaN were considered.
-
Finally an intensity map was created by dividing the counts tiles by the exposure tiles.
To eliminate gross fluctuations due to rare counts in regions with very low exposure, only
regions with exposure > 1 second were retained. A total of 30 photons were deleted due to
this criterion.
Note that while any sampler may in principle be used with these data, the Spline sampler may
give unexpected results. The spline computation propogates NaNs thought the image and
means that even occasional NaNs can corrupt the
output image completely. NaNs are very common in this dataset.
Also, if the region straddles a boundary in the HEALPix projection,
the size of the requested input region is likely to exceed memory limits since the HiPS
data are considered a single very large image.
| Provenance | Data generated from public images at HEASARC archive |
| Copyright | Public Domain |
| Regime | X-ray |
| NSurvey | 3 |
| Frequency | 360 PHz (1.5 keV) |
| Bandpass | 48 PHz - 2,400 PHz (0.2-10 keV) |
| Coverage | Patches over ~6% of the sky |
| PixelScale | 1.6" (Highest resolution/Hierarchical) |
| PixelUnits | Counts/s |
| Resolution | 18" (HPD) |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Projection | HEALPix/HIPS |
| Epoch | January 2005 to May 2017 |
| Reference |
The XRT Web Site or
Burrows et al 2005, instrument reference
|
Gamma ray surveys
CGRO Compton Telescope: 3 channel data
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Comptel,CGRO Comptel
Description
This survey is a maximum entropy solution to the data taken by the
CompTel instrument on the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory.
The data in this survey are intended only to give the general appearance
of the MeV gamma-ray sky. Fluxes, flux limits and spectra should be
derived using the Compass system for the analysis of CompTel
data. Compass is available at the
Compton Observatory
Science Support Center .
The maps were originally generated
by the CompTel Instrument Team
as three separate maps in the bands:
- 1-3 MeV
- 3-10 MeV
- 10-30 MeV
All CompTel observations from phases 1, 2 and 3 were included in the
maps (May 1991 through October 1994).
These maps were combined into a single 3-D map at SkyView
| Provenance | CompTel Instrument Team. Maps generated
by Andrew Strong, Max-Planck
Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (Garching).
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Gamma Ray |
| NSurvey | 1 survey with 3 bands |
| Frequency | 2.4 ZHz |
| Bandpass | 0.24-7.2 ZHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| PixelScale | 1d |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/cm2/steradian |
| Resolution | ~3d |
| Epoch | May 1991 to October 1994 |
| CoordinateSystem | Galactic |
| Projection | Rectangular (CAR) |
| Reference |
Comptel Instrument Team Home Page
|
Energetic Gamma-Ray Event Telescope: Hard
Short name[s] used to specify survey:EGRETHard, EGRET1000, EGRET >100 MeV
Description
These data are from the Compton GRO EGRET team. Data are from all pointings
of the EGRET instrument in the verification phase and phase 1-4 of the Compton
mission. The maps exist in energies 30-100 MeV, 100-100000 MeV, and
as a multi-dimensional, 10 channel survey. For the multi-dimensional
survey, channels 1-3 comprise energies less than 100 MeV, and channels
4-10 comprise energies greater than 100 MeV. Note that the energies
are not uniformly split among the channels.
The EGRET 3D map is comprised of ten channels with the following
energy ranges:
- Channel 1 30-50 MeV
- Channel 2 50-70 MeV
- Channel 3 70-100 MeV
- Channel 4 100-150 MeV
- Channel 5 150-300 MeV
- Channel 6 300-500 MeV
- Channel 7 500-1000 MeV
- Channel 8 1000-2000 MeV
- Channel 9 2000-4000 MeV
- Channel 10 4000-10000 MeV
The default two dimensional image for the EGRET 3D survey is an average
of Channels 4 - 10 (energies greater than 100 MeV).
| Provenance | EGRET Instrument team, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Gamma Ray |
| NSurveys | 3 |
| Frequency | 72 ZHz |
| Bandpass | 24-2400 ZHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| Resolution | ca. 5d below 100 MeV, ca. 2d above 100 MeV |
| PixelScale | 0.5 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/cm2/steradian |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Rectangular |
| Epoch | 1992-1995 |
| Reference |
Hartman, et al., 1999, The Third EGRET
Source Catalog, ApJ Supplement, 123, 79-202
|
Energetic Gamma-Ray Event Telescope: Soft
Short name[s] used to specify survey:EGRETSoft, EGRET30, EGRET <100 MeV
Description
These data are from the Compton GRO EGRET team. Data are from all pointings
of the EGRET instrument in the verification phase and phase 1-4 of the Compton
mission. The maps exist in energies 30-100 MeV, 100-100000 MeV, and
as a multi-dimensional, 10 channel survey. For the multi-dimensional
survey, channels 1-3 comprise energies less than 100 MeV, and channels
4-10 comprise energies greater than 100 MeV. Note that the energies
are not uniformly split among the channels.
The EGRET 3D map is comprised of ten channels with the following
energy ranges:
- Channel 1 30-50 MeV
- Channel 2 50-70 MeV
- Channel 3 70-100 MeV
- Channel 4 100-150 MeV
- Channel 5 150-300 MeV
- Channel 6 300-500 MeV
- Channel 7 500-1000 MeV
- Channel 8 1000-2000 MeV
- Channel 9 2000-4000 MeV
- Channel 10 4000-10000 MeV
The default two dimensional image for the EGRET 3D survey is an average
of Channels 4 - 10 (energies greater than 100 MeV).
| Provenance | EGRET Instrument team, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Gamma Ray |
| NSurveys | 3 |
| Frequency | 15 ZHz |
| Bandpass | 7.2-24 ZHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| Resolution | ca. 5d below 100 MeV, ca. 2d above 100 MeV |
| PixelScale | 0.5 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/cm2/steradian |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Rectangular |
| Epoch | 1992-1995 |
| Reference |
Hartman, et al., 1999, The Third EGRET
Source Catalog, ApJ Supplement, 123, 79-202
|
Energetic Gamma-Ray Event Telescope: 10 channel data
Short name[s] used to specify survey:EGRET3D,EGRET(3D), EGRET (3D)
Description
These data are from the Compton GRO EGRET team. Data are from all pointings
of the EGRET instrument in the verification phase and phase 1-4 of the Compton
mission. The maps exist in energies 30-100 MeV, 100-10000 MeV, and
as a multi-dimensional, 10 channel survey. For the multi-dimensional
survey, channels 1-3 comprise energies less than 100 MeV, and channels
4-10 comprise energies greater than 100 MeV. Note that the energies
are not uniformly split among the channels.
The EGRET 3D map is comprised of ten channels with the following
energy ranges:
- Channel 1 30-50 MeV
- Channel 2 50-70 MeV
- Channel 3 70-100 MeV
- Channel 4 100-150 MeV
- Channel 5 150-300 MeV
- Channel 6 300-500 MeV
- Channel 7 500-1000 MeV
- Channel 8 1000-2000 MeV
- Channel 9 2000-4000 MeV
- Channel 10 4000-10000 MeV
The default two dimensional image for the EGRET 3D survey is an average
of Channels 4 - 10 (energies greater than 100 MeV).
| Provenance | EGRET Instrument team, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Gamma Ray |
| NSurveys | 3 |
| Frequency | 24 ZHz |
| Bandpass | .24-2400 ZHz |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| Resolution | ca. 5d below 100 MeV, ca. 2d above 100 MeV |
| PixelScale | 0.5 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | cts/s/cm2/steradian |
| Coordinates | Galactic |
| Projection | Rectangular |
| Epoch | 1992-1995 |
| Reference |
Hartman, et al., 1999, The Third EGRET
Source Catalog, ApJ Supplement, 123, 79-202
|
Fermi Map: Band 1
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Fermi 1, Fermi1, Fermi band 1
Description
This survey sums all data observed by the Fermi mission up to week 396.
This version of the Fermi survey are intensity maps where the summed counts data
are divided by the exposure for each pixel (in cm^2 s) and the area of the pixel.
Data is broken into 5 energy bands
- 30-100 MeV Band 1
- 100-300 MeV Band 2
- 300-1000 MeV Band 3
- 1-3 GeV Band 4
- 3-300 GeV Band 5
The SkyView data are based upon a Cartesian projection of the counts divided by
the exposure maps. In the Cartesian projection pixels near the pole have
a much smaller area than pixels on the equator, so these pixels have smaller
integrated flux.
When creating large
scale images in other projections users may
wish to make sure to compensate for this effect
the flux conserving clip-resampling option.
| Provenance | Fermi LAT instrument team, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Gamma Ray |
| NSurveys | 5 |
| Frequency | 12 ZHz |
| Bandwidth | 7-24 ZHz (30-100 MeV) |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| Resolution | 3 degrees. |
| PixelScale | 0.1 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | cnts/s/cm^2/sr |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Rectangular |
| Epoch | 2008-2012 |
| Reference |
Data
and survey paper (ADS)
|
Fermi Map: Band 2
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Fermi 2, Fermi2, Fermi band 2
Description
This survey sums all data observed by the Fermi mission up to week 396.
This version of the Fermi survey are intensity maps where the summed counts data
are divided by the exposure for each pixel (in cm^2 s) and the area of the pixel.
Data is broken into 5 energy bands
- 30-100 MeV Band 1
- 100-300 MeV Band 2
- 300-1000 MeV Band 3
- 1-3 GeV Band 4
- 3-300 GeV Band 5
The SkyView data are based upon a Cartesian projection of the counts divided by
the exposure maps. In the Cartesian projection pixels near the pole have
a much smaller area than pixels on the equator, so these pixels have smaller
integrated flux.
When creating large
scale images in other projections users may
wish to make sure to compensate for this effect
the flux conserving clip-resampling option.
| Provenance | Fermi LAT instrument team, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Gamma Ray |
| NSurveys | 5 |
| Frequency | 40 ZHz |
| Bandwidth | 24-70 ZHz (100-300 MeV) |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| Resolution | 2 degrees. |
| PixelScale | 0.1 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | cnts/s/cm^2/sr |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Rectangular |
| Epoch | 2008-2012 |
| Reference |
Data
and survey paper (ADS)
|
Fermi Map: Band 3
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Fermi 3, Fermi3, Fermi band 3
Description
This survey sums all data observed by the Fermi mission up to week 396.
This version of the Fermi survey are intensity maps where the summed counts data
are divided by the exposure for each pixel (in cm^2 s) and the area of the pixel.
Data is broken into 5 energy bands
- 30-100 MeV Band 1
- 100-300 MeV Band 2
- 300-1000 MeV Band 3
- 1-3 GeV Band 4
- 3-300 GeV Band 5
The SkyView data are based upon a Cartesian projection of the counts divided by
the exposure maps. In the Cartesian projection pixels near the pole have
a much smaller area than pixels on the equator, so these pixels have smaller
integrated flux.
When creating large
scale images in other projections users may
wish to make sure to compensate for this effect
the flux conserving clip-resampling option.
| Provenance | Fermi LAT instrument team, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Gamma Ray |
| NSurveys | 5 |
| Frequency | 150 ZHz |
| Bandwidth | 70-240 ZHz (300-1000 MeV) |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| Resolution | 1 degrees. |
| PixelScale | 0.1 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | cnts/s/cm^2/sr |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Rectangular |
| Epoch | 2008-2012 |
| Reference |
Data
and survey paper (ADS)
|
Fermi Map: Band 4
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Fermi 4, Fermi4, Fermi band 4
Description
This survey sums all data observed by the Fermi mission up to week 396.
This version of the Fermi survey are intensity maps where the summed counts data
are divided by the exposure for each pixel (in cm^2 s) and the area of the pixel.
Data is broken into 5 energy bands
- 30-100 MeV Band 1
- 100-300 MeV Band 2
- 300-1000 MeV Band 3
- 1-3 GeV Band 4
- 3-300 GeV Band 5
The SkyView data are based upon a Cartesian projection of the counts divided by
the exposure maps. In the Cartesian projection pixels near the pole have
a much smaller area than pixels on the equator, so these pixels have smaller
integrated flux.
When creating large
scale images in other projections users may
wish to make sure to compensate for this effect
the flux conserving clip-resampling option.
| Provenance | Fermi LAT instrument team, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Gamma Ray |
| NSurveys | 5 |
| Frequency | 400 ZHz |
| Bandwidth | 240-700 ZHz (1-3 GeV) |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| Resolution | 0.4 degrees. |
| PixelScale | 0.1 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | cnts/s/cm^2/sr |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Rectangular |
| Epoch | 2008-2012 |
| Reference |
Data
and survey paper (ADS)
|
Fermi Map: Band 5
Short name[s] used to specify survey:Fermi 5, Fermi5, Fermi band 5
Description
This survey sums all data observed by the Fermi mission up to week 396.
This version of the Fermi survey are intensity maps where the summed counts data
are divided by the exposure for each pixel (in cm^2 s) and the area of the pixel.
Data is broken into 5 energy bands
- 30-100 MeV Band 1
- 100-300 MeV Band 2
- 300-1000 MeV Band 3
- 1-3 GeV Band 4
- 3-300 GeV Band 5
The SkyView data are based upon a Cartesian projection of the counts divided by
the exposure maps. In the Cartesian projection pixels near the pole have
a much smaller area than pixels on the equator, so these pixels have smaller
integrated flux.
When creating large
scale images in other projections users may
wish to make sure to compensate for this effect
the flux conserving clip-resampling option.
| Provenance | Fermi LAT instrument team, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
|
| Copyright | Public domain |
| Regime | Gamma Ray |
| NSurveys | 5 |
| Frequency | 1400 ZHz |
| Bandwidth | 700-70000 ZHz (3-300 GeV) |
| Coverage | All-sky |
| Resolution | 0.2 degrees. |
| PixelScale | 0.1 degrees/pixel |
| PixelUnits | cnts/s/cm^2/sr |
| Coordinates | Equatorial |
| Equinox | 2000 |
| Projection | Rectangular |
| Epoch | 2008-2012 |
| Reference |
Data
and survey paper (ADS)
|

